|
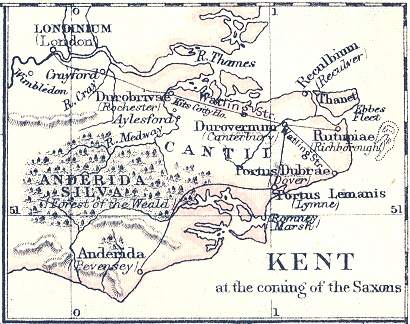
Isle Of Thanet
The Isle of Thanet () is a peninsula forming the easternmost part of Kent, England. While in the past it was separated from the mainland by the Wantsum Channel, it is no longer an island. Archaeological remains testify to its settlement in ancient times. Today, it is a tourist destination, and has an active agricultural base. Etymology The island of Thanet is mentioned as ''Tonetic'' (c. AD 150; the TON- of this form was misread as TOΛI-, hence it appears as ''Toliatis'' in the surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy); ''Tanat's'', ''Athanatos'' and ''Thanatos'' (in various copies of 3rd C AD, Solinus); ''Tanatos'' (AD 731); ''Tenid'' in 679 and ''Tenet'' (e.g. charters of AD 679, 689 and thereafter); and the Old Welsh forms ''Tanet'' and ''Danet'', found in the ''Historia Brittonum'' (c. AD 829/30) and Armes Prydein (c. AD 930). Standard reference works for English place-names (such as Eilert Ekwall's ''Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-Names'') state the name ''Tane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanet - Thanet Scenery (geograph 5434042)
Thanet may refer to: * Isle of Thanet, a former island, now a peninsula, at the most easterly point of Kent, England * Thanet District, a local government district containing the island *Thanet College, former name of East Kent College * Thanet Canal, a short branch of the Leeds and Liverpool Canal * Earl of Thanet, a title in the Peerage of England created in 1628 * Thanet Formation, a geological formation found in the London Basin of southeastern England * HMS ''Thanet'' (H29), an S-class destroyer of the Royal Navy * Thanet Wind Farm, an offshore wind farm 7 miles (11 km) off the coast of Thanet district in Kent, England See also * Thanetian, in the ICS Geologic timescale, the latest age or uppermost stratigraphic stage of the Paleocene Epoch {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tite-Live
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on good terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and was a friend of Augustus. Livy encouraged Augustus’s young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged into Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection and pride for Patavium, and the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended between 4000 Anno Domini, BC and 2000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. It therefore represents nearly 99.3% of human history. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of Goldsmith, gold and Coppersmith, copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mappa Thaneti Insule
is a Japanese animation studio headquartered in Nakano, Tokyo (formerly in Suginami, Tokyo). Founded in 2011 by Madhouse co-founder and producer Masao Maruyama, it has produced anime works including ''Terror in Resonance'', ''Yuri!!! on Ice'', '' In This Corner of the World'', '' Kakegurui'', ''Banana Fish'', ''Zombie Land Saga'', ''Dororo'' (in co-production with Tezuka Productions), ''Dorohedoro'', ''The God of High School'', ''Jujutsu Kaisen'', ''Attack on Titan'' (season 4), '' Vinland Saga'' (season 2), ''Chainsaw Man'', '' Hell's Paradise: Jigokuraku'', and the 2024 adaptation of ''Ranma ½''. MAPPA is an acronym for Maruyama Animation Produce Project Association. Business History The studio was established on June 14, 2011, by Masao Maruyama, a co-founder and former producer of Madhouse, at the age of 70. Maruyama served as the company's first representative director, and the studio's initial goal was to produce Sunao Katabuchi's ''In This Corner of the World''. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Welsh
The history of the Welsh language () spans over 1400 years, encompassing the stages of the language known as Primitive Welsh, Old Welsh, Middle Welsh, and Modern Welsh. Origins Welsh evolved from British (Common Brittonic), the Celtic language spoken by the ancient Britons. Alternatively classified as Insular Celtic or P-Celtic, it probably arrived in Britain during the Bronze Age or Iron Age and was probably spoken throughout the island south of the Firth of Forth.Koch, pp. 291–292. During the Early Middle Ages, the British language began to fragment due to increased dialect differentiation, evolving into Welsh and the other Brythonic languages ( Breton, Cornish, and the extinct Cumbric). It is not clear when Welsh became distinct.Koch, p. 1757. Primitive Welsh (550–800) Kenneth H. Jackson suggested that the evolution in syllabic structure and sound pattern was complete by around 550, and labelled the period between then and about 800 "Primitive Welsh". This Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, has been called "Primitive"Koch, p. 1757. or "Archaic Welsh". Phonology The phonology of Old Welsh is as follows. * Older was diphthongized into in (stressed) final syllables, but it was retained elsewhere. Whilst this persisted as a diphthong in Middle Welsh, in Modern Welsh /aw/ has collapsed to following the stress shift to the penultimate, except in monosyllables. * and were allophones of and in unstressed non-final syllables. In Middle Welsh these merged to . * Old Welsh and became and in Modern Welsh final syllables, in dialects where /ɨ/ has not merged with /i/. Texts The oldest surviving text entirely in Old Welsh is understood to be that on a gravestone now in Tywyn – the Cadfan Stone – thought to date from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hengist And Horsa
Hengist (, ) and Horsa are legendary Germanic peoples, Germanic brothers who according to later English legends and ethnogenesis theories led the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes, the progenitor groups of modern English people, in their Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, supposed invasion of Great Britain in the 5th century. Tradition lists Hengist as the first of the Jutish kings, or alternatively as the founder itself, of the Kingdom of Kent. Modern scholarly consensus regards Hengist and Horsa as mythical figures, given their alliteration, alliterative animal names, the seemingly constructed nature of their genealogy, and the unknowable quality of Bede's sources.Halsall (2013:60-62). Their later detailed representation in texts such as the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle says more about ninth-century attitudes to the past than about the time in which they are said to have existed.Yorke (1993).Harland (2021:32). According to early sources, Hengist and Horsa arrived in Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutes
The Jutes ( ) were one of the Germanic people, Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the end of Roman rule in Britain, departure of the Roman Britain, Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations, along with the Angles (tribe), Angles and the Saxons: There is no consensus amongst historians on the origins of the Jutes. One hypothesis is that they originated from the Jutland Peninsula but after a Danish invasion of that area, migrated to the Frisian coast. From the Frisian coast they went on to settle southern Britain in the later fifth century during the Migration Period, as part of a larger wave of Germanic migration into Britain. They were possibly or probably related to the North Germanic tribe Geats. Settlement in southern Britain During the period after the Roman Britain, Roman occupation and before the Norman conquest, people of Germanic descent arrived in Britain, ultimately forming England. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanatos
In Greek mythology, Thanatos (; , ''Thánatos'', pronounced in "Death", from θνῄσκω ''thnēskō'' "(I) die, am dying") was the Personifications of death, personification of death. He was a minor figure in Greek mythology, often referred to but rarely appearing in person. His name is transliterated in Latin as ''Thanatus'', but his counterpart in Roman mythology is Mors (mythology), Mors or Letum. In myth and poetry The Greece, Greek poet Hesiod established in his ''Theogony'' that Thánatos has no father, but is the son of Nyx (mythology), Nyx (Night) and brother of Hypnos (Sleep).Hesiod, ''Theogony'' 758 ff, trans. Evelyn-White, Greek epic 8th or 7th century BC Homer earlier described Hypnos and Thanatos as twin brothers in his epic poem, the ''Iliad'', where they were charged by Zeus via Apollo with the swift delivery of the slain hero Sarpedon (Trojan War hero), Sarpedon to his homeland of Lycia. Counted among Thanatos' siblings were other negative personifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocrypha
Apocrypha () are biblical or related writings not forming part of the accepted canon of scripture, some of which might be of doubtful authorship or authenticity. In Christianity, the word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings that were to be read privately rather than in the public context of church services. Apocrypha were edifying Christian works that were not always initially included as Biblical canon, canonical scripture. The adjective "apocryphal", meaning of doubtful authenticity, mythical, fictional, is recorded from the late 16th century, then taking on the popular meaning of "false," "spurious," "bad," or "heretical." It may be used for any book which might have scriptural claims but which does not appear in the canon accepted by the author. A related term for non-canonical apocryphal texts whose authorship seems incorrect is pseudepigrapha, a term that means "false attribution". In Christianity, the name "biblical apocrypha, the Apocrypha" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |