|
Iberian Language
The Iberian language was the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre- Migration Era (before about 375 AD). The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC. The Iberian language, like all the other Paleohispanic languages except Basque, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by Latin due to the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula. Iberian is unclassified: while the scripts used to write it have been deciphered to various extents, the language itself remains largely unknown. Links with other languages have been suggested, especially the Basque language, based largely on the observed similarities between the numerical systems of the two. In contrast, the Punic language of Carthaginian settlers was Semitic, while Indo-European languages of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unclassified Language
An unclassified language is a language whose genetic affiliation to other languages has not been established. Languages can be unclassified for a variety of reasons, mostly due to a lack of reliable data but sometimes due to the confounding influence of language contact, if different layers of its vocabulary or morphology point in different directions and it is not clear which represents the ancestral form of the language. Some poorly known extinct languages, such as Gutian and Cacán, are simply unclassifiable, and it is unlikely the situation will ever change. A supposedly unclassified language may turn out not to be a language at all, or even a distinct dialect, but merely a family, tribal or village name, or an alternative name for a people or language that is classified. If a language's genetic relationship has not been established after significant documentation of the language and comparison with other languages and families, as in the case of Basque in Europe, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
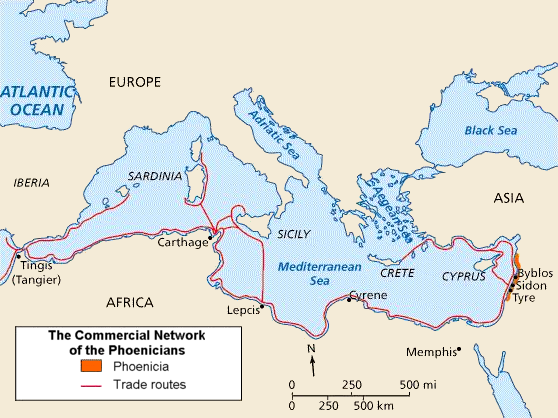
Carthaginian Iberia
The Carthaginian presence in Iberia is long and has been influential on the region. Background The Phoenicians were a people from the eastern Mediterranean who were mainly traders from the cities of Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. They established many trading colonies around the Mediterranean Sea, including colonies in Spain. In the year 814 BC, they founded the city of Carthage on the north African coast in what is now Tunisia. After the fall of Phoenicia to the Babylonians and then the Persians, Carthage became the most powerful Phoenician city in the Mediterranean and the Carthaginians annexed many of the other Phoenician colonies around the coasts of the western Mediterranean, such as Hadrumetum and Thapsus. They also annexed territory in Sicily, Africa, Sardinia. The Spanish city of Cartagena was founded around 227 BC by the Carthaginian Hasdrubal the Fair as ''Qart Hadasht'' ( phn, 𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤇𐤃𐤔𐤕 QRT𐤟ḤDŠT; meaning 'New Town'), the same name as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béziers
Béziers (; oc, Besièrs) is a subprefecture of the Hérault department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. Every August Béziers hosts the famous ''Feria de Béziers'', which is centred on bullfighting. A million visitors are attracted to the five-day event. The town is located on a small bluff above the river Orb, about from the Mediterranean coast and southwest of Montpellier. At Béziers, the Canal du Midi passes over the river Orb by means of the '' Pont-canal de l'Orb'', an aqueduct claimed to be the first of its kind. History Béziers is one of the oldest cities in France. Research published in March 2013 shows that Béziers dates from 575 BC, making it older than Agde (Greek Agathe Tyche, founded in 525 BC) and a bit younger than Marseille (Greek Massalia, founded in 600 BC). The site has been occupied since Neolithic times, before the influx of Celts. Roman ''Betarra'' was on the road that linked Provence with Iberia. The Romans refoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and was historically a prosperous port. From the 14th century it declined following a change in the course of the river Aude. It is marginally the largest commune in Aude. But the capital of the Aude department is the smaller commune of Carcassonne. Geography Narbonne is linked to the nearby Canal du Midi and the river Aude by the Canal de la Robine, which runs through the centre of town. It is very close to the A9 motorway, which connects Montpellier and Nîmes to Perpignan and, across the border, to Barcelona in Spain. There is also a recently renovated train station which serves the TGV to Spain, Paris and Calais, which in turn connects to the Eurostar. Narbonne is only 10 km from Narbonne Plage (beach), but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppidum D'Ensérune
The Oppidum d'Ensérune is an ancient hill-town (or ''oppidum'') near the village of Nissan-lez-Ensérune, France, located between Béziers and Narbonne close to the D609 (formerly RN9) and Canal du Midi. It has been listed since 1935 as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture. Oppidum d'Ensérune The settlement was occupied without interruption between the 6th century BC and 1st century AD on a hill with good views over the coastal plain, being close to the |
Hérault (river)
The Hérault (; oc, Erau) is a river in southern France. Its length is . Its source is on the slopes of Mont Aigoual in the Cévennes mountains. It reaches the Mediterranean Sea near Agde. Name The river was known in Latin as ''Arauris'' (or ''Araura'' by Strabo). The name is sometimes considered Pre-Celtic although the element ''Ara-'' suggests a Celtic root.http://docshare02.docshare.tips/files/28516/285161581.pdf Towns The Hérault flows through the following departments and towns: *Gard: Valleraugue. *Hérault (named after the river): Ganges, Pézenas (nearby), Agde. Tributaries Navigation The lower reaches of the Hérault, from Bessan to the sea at Agde, are navigable. The lowest are tidal, whilst the next forms part of the Canal du Midi The Canal du Midi (; ) is a long canal in Southern France (french: le Midi). Originally named the ''Canal royal en Languedoc'' (Royal Canal in Languedoc) and renamed by French revolutionaries to ''Canal du Midi'' in 1789, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Coast
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapa Llengües Paleohispàniques-ang
Mapa or MAPA may refer to: People * Alec Mapa (born 1965), American actor, comedian and writer * Dennis Mapa (born 1969), Filipino economist and statistician * Jao Mapa (born 1976), Filipino actor * Placido Mapa Jr. (born 1932), Filipino businessman, economist, and government official * Suraj Mapa (born 1980), Sri Lankan actor * Victorino Mapa (1855–1927), Filipino chief justice and government official Other uses * "Mapa" (song), a 2021 song by SB19 * Mexican American Political Association * Mapa (publisher), an Israeli subsidiary of Ituran * Mapa Group, a Turkish conglomerate * Mapa, a company producing latex gloves that merged with Hutchinson SA in 1973 * Most Affected People and Areas, a climate justice concept See also * * Mappa (other) * Mapah (other) Mapah may refer to: * ''Ha-Mapah'' (Hebrew: "the tablecloth"), a commentary on the Shulchan Aruch by Moses Isserles * The Mapah, title of the French mystic Simon Ganneau Simon Ganneau (born circa 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Romance Languages
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languagesIberian languages is also used as a more inclusive term for all languages spoken on the Iberian Peninsula, which in antiquity included the non-Indo-European Iberian language. are a group of Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar, Andorra and southern France. They are today more commonly separated into West Iberian and Occitano-Romance language groups. Evolved from the Vulgar Latin of Iberia, the most widely spoken Iberian Romance languages are Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan-Valencian-Balear, and Galician. These languages also have their own regional and local varieties. Based on mutual intelligibility, Dalby counts seven "outer" languages, or language groups: Galician-Portuguese, Spanish, Asturleonese, "Wider"- Aragonese, "Wider"-Catalan, Provençal+Lengadocian, and "Wider"- Gascon. In addition to those languages, there are a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Latin
Latin is a member of the broad family of Italic languages. Its alphabet, the Latin alphabet, emerged from the Old Italic alphabets, which in turn were derived from the Etruscan, Greek and Phoenician scripts. Historical Latin came from the prehistoric language of the Latium region, specifically around the River Tiber, where Roman civilization first developed. How and when Latin came to be spoken by the Romans are questions that have long been debated. Various influences on Latin of Celtic dialects in northern Italy, the non-Indo-European Etruscan language in Central Italy, and the Greek in some Greek colonies of southern Italy have been detected, but when these influences entered the native Latin is not known for certain. Surviving Latin literature consists almost entirely of Classical Latin in its broadest definition. It includes a polished and sometimes highly stylized literary language sometimes termed Golden Latin, which spans the 1st century BC and the early years of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Greek
Ionic Greek ( grc, Ἑλληνικὴ Ἰωνική, Hellēnikē Iōnikē) was a subdialect of the Attic–Ionic or Eastern dialect group of Ancient Greek. History The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland across the Aegean at the time of the Dorian invasions, around the 11th century BC during the early Greek Dark Ages. By the end of Archaic Greece and early Classical Greece in the 5th century BC, the central west coast of Asia Minor, along with the islands of Chios and Samos, formed the heartland of Ionia proper. The Ionic dialect was also spoken on islands across the central Aegean and on the large island of Euboea north of Athens. The dialect was soon spread by Ionian colonization to areas in the northern Aegean, the Black Sea, and the western Mediterranean, including Magna Graecia in Sicily and Italy. The Ionic dialect is generally divided into two major time periods, Old Ionic (or Old Ionian) and New Ionic (or New Ionian). The transitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtiberian Language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river. This language is directly attested in nearly 200 inscriptions dated to the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, mainly in Celtiberian script, a direct adaptation of the northeastern Iberian script, but also in the Latin alphabet. The longest extant Celtiberian inscriptions are those on three Botorrita plaques, bronze plaques from Botorrita near Zaragoza, dating to the early 1st century BC, labeled Botorrita I, III and IV (Botorrita II is in Latin). In the northwest was another Celtic language, Gallaecian (also known as Northwestern Hispano-Celtic), that was closely related to Celtiberian. Overview Enough is preserved to show that the Celtiberian language could be Q-Celtic (like Goidelic), and not P-Celtic like Gaulish or Brittonic. Cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |