|
Isotopes Of Lead
Lead (82Pb) has four observationally stable isotopes: 204Pb, 206Pb, 207Pb, 208Pb. Lead-204 is entirely a primordial nuclide and is not a radiogenic nuclide. The three isotopes lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208 represent the ends of three decay chains: the uranium series (or radium series), the actinium series, and the thorium series, respectively; a fourth decay chain, the neptunium series, terminates with the thallium isotope 205Tl. The three series terminating in lead represent the decay chain products of long-lived primordial 238U, 235U, and 232Th. Each isotope also occurs, to some extent, as primordial isotopes that were made in supernovae, rather than radiogenically as daughter products. The fixed ratio of lead-204 to the primordial amounts of the other lead isotopes may be used as the baseline to estimate the extra amounts of radiogenic lead present in rocks as a result of decay from uranium and thorium. (See lead–lead dating and uranium–lead dating.) The longest-liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * ''Half Life: A Parable for the Nuclear Age'', a 1985 Australian documentary film Literature * Half Life (Jackson novel), ''Half Life'' (Jackson novel), a 2006 novel by Shelley Jackson * Half-Life (Krach novel), ''Half-Life'' (Krach novel), a 2004 novel by Aaron Krach * Halflife (Michalowski novel), ''Halflife'' (Michalowski novel), a 2004 novel by Mark Michalowski * ''Rozpad połowiczny'' (), a 1988 award-winning dystopia novel by Edmund Wnuk-Lipiński Music *Half Life (3 album), ''Half Life'' (3 album) (2001) *Halflife (EP), ''Halflife'' (EP), an EP by Lacuna Coil and the title track *''Half-Life E.P.'', an EP by Local H * "Half Life", a song by 10 Years from ''The Autumn Effect'' * "Half Life", a song by Come from ''Near-Life Experience'' * "Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observationally Stable
Stable nuclides are isotopes of a chemical element whose nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The nuclei of such isotopes are not radioactive and unlike radionuclides do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When these nuclides are referred to in relation to specific elements they are usually called that element's stable isotopes. The 80 elements with one or more stable isotopes comprise a total of 251 nuclides that have not been shown to decay using current equipment. Of these 80 elements, 26 have only one stable isotope and are called monoisotopic. The other 56 have more than one stable isotope. Tin has ten stable isotopes, the largest number of any element. Definition of stability, and naturally occurring nuclides Most naturally occurring nuclides are stable (about 251; see list at the end of this article), and about 35 more (total of 286) are known to be radioactive with long enou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino. : : or when written as a nuclear reaction equation, ^_e + ^_p -> ^_n + ^_ ν_e Since this single emitted neutrino carries the entire decay energy, it has this single characteristic energy. Similarly, the momentum of the neutrino emission causes the daughter atom to recoil with a single characteristic momentum. The resulting daughter nuclide, if it is in an excited state, then transitions to its ground state. Usually, a gamma ray is emitted during this transition, but nuclear de-excitation may also take place by internal conversion. Following capture of an inner electron from the atom, an outer elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
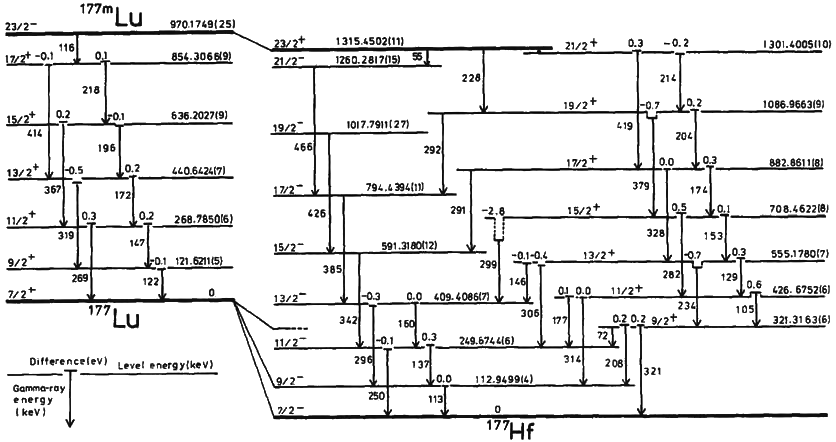
Isomeric Transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer, 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). Some references recommend seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , , , , and multiple holmium isomers. Sometimes, the gamma decay from a metastable state is referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decay Energy
The decay energy is the energy change of a nucleus having undergone a radioactive decay. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting ionizing particles and radiation. This decay, or loss of energy, results in an atom of one type (called the parent nuclide) transforming to an atom of a different type (called the daughter nuclide). Decay calculation The energy difference of the reactants is often written as ''Q'': :Q = \left( \text \right)_\text - \left( \text \right)_\text, :Q = \left(\text \right)_ c^2 - \left( \text \right )_\text c^2 . Decay energy is usually quoted in terms of the energy units MeV (million electronvolts) or keV (thousand electronvolts): : Q \text = -931.5 \Delta M \text,~~(\text\Delta M = \Sigma M_\text - \Sigma M_\text). Types of radioactive decay include * gamma ray * beta decay (decay energy is divided between the emitted electron and the neutrino which is emitted at the same time) * alpha decay Alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in what is called ''positron emission''. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron emission to be energeticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Mercury
There are seven stable isotopes of mercury (80Hg) with 202Hg being the most abundant (29.86%). The longest-lived radioisotopes are 194Hg with a half-life of 444 years, and 203Hg with a half-life of 46.612 days. Most of the remaining 40 radioisotopes have half-lives that are less than a day. 199Hg and 201Hg are the most often studied NMR-active nuclei, having spin quantum numbers of 1/2 and 3/2 respectively. All isotopes of mercury are either radioactive or observationally stable, meaning that they are predicted to be radioactive but no actual decay has been observed. These isotopes are predicted to undergo either alpha decay or double beta decay. List of isotopes , -id=Mercury-170 , 170Hg , style="text-align:right" , 80 , style="text-align:right" , 90 , 170.00581(32)# , 310(250) μs , α , 166Pt , 0+ , , , -id=Mercury-171 , 171Hg , style="text-align:right" , 80 , style="text-align:right" , 91 , 171.00359(33)# , 70(30) μs , α , 167Pt , 3/2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of and a mass of , and is represented as ^_\alpha. For example, uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay to form thorium-234. While alpha particles have a charge , this is not usually shown because a nuclear equation describes a nuclear reaction without considering the electrons – a convention that does not imply that the nuclei necessarily occur in neutral atoms. Alpha decay typically occurs in the heaviest nuclides. Theoretically, it can occur only in nuclei somewhat heavier than nickel (element 28), where the overall binding energy per nucleon is no longer a maximum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
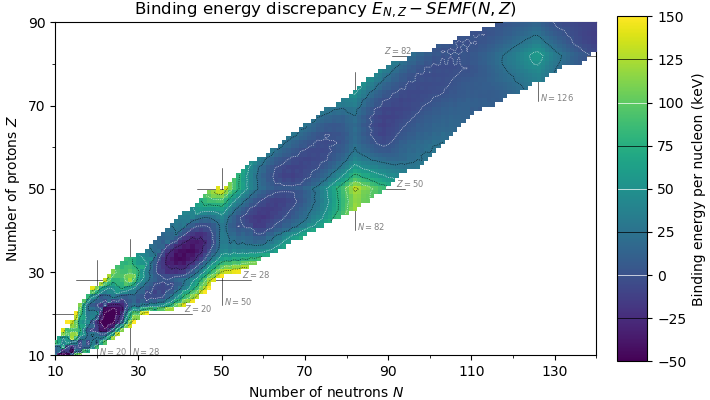
Magic Number (physics)
In nuclear physics, a magic number is a number of nucleons (either protons or neutrons, separately) such that they are arranged into complete shells within the atomic nucleus. As a result, atomic nuclei with a "magic" number of protons or neutrons are much more stable than other nuclei. The seven most widely recognized magic numbers as of 2019 are 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126. For protons, this corresponds to the elements helium, oxygen, calcium, nickel, tin, lead, and the hypothetical unbihexium, although 126 is so far only known to be a magic number for neutrons. Atomic nuclei consisting of such a magic number of nucleons have a higher average binding energy per nucleon than one would expect based upon predictions such as the semi-empirical mass formula and are hence more stable against nuclear decay. The unusual stability of isotopes having magic numbers means that transuranium elements could theoretically be created with extremely large nuclei and yet not be subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |