|
Isoprenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant '' S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers are the main component of natural rubber. History and etymology Charles Greville Williams, C. G. Williams named the compound in 1860 after obtaining it from the pyrolysis of natural rubber. He correctly deduced the mass shares of carbon and hydrogen (but arrived at an incorrect formula C10H8 because the modern atomic weight of carbon was not adopted until the Karlsruhe Congress held later that year). He did not specify the reasons for the name, but it is hypothesized that it came from "propylene" with which isoprene shares some physical and chemical properties. The first one to observe recombination of isoprene into rubber-like substance was in 1879, and William A. Tilden identified its structure five years later. Natural occurrences Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly Pinophyta, conifers. In plants, terpenes and terpenoids are important mediators of ecological biological interaction, interactions, while some insects use some terpenes as a form of defense. Other functions of terpenoids include cell growth modulation and plant elongation, light harvesting and photoprotection, and membrane permeability and fluidity control. Terpenes are classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), as examples. The terpene alpha-pinene is a major component of the common solvent, turpentine. The one terpene that has major applications is natural rubber (i.e., polyisoprene). The possibility that other terpenes could be used as precursors to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attractant
An attractant is any chemical that attracts an organism, e.g. i) synthetic lures; ii) aggregation and sex pheromones (intraspecific interactions); and iii) synomone (interspecific interactions) Synomone An interspecific semiochemical that is beneficial to both interacting organisms, the emitter and receiver, e.g. floral synomone of certain '' Bulbophyllum'' species (Orchidaceae) attracts fruit fly males (Tephritidae: Diptera) as pollinator A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains. Insects are ...s. In this true mutualistic inter-relationship, both organisms gain benefits in their respective sexual reproduction - i.e. orchid flowers are pollinated and the '' Dacini'' fruit fly males are rewarded with a sex pheromone precursor or booster; and the floral synomones, also act as rewards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprenylation
Prenylation (also known as isoprenylation or lipidation) is the addition of hydrophobic molecules to a protein or a biomolecule. It is usually assumed that prenyl groups (3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) facilitate attachment to cell membranes, similar to lipid anchored protein, lipid anchors like the GPI anchor, though direct evidence of this has not been observed. Prenyl groups (also called isoprenyl groups, having one hydrogen atom more than isoprene) have been shown to be important for protein–protein binding through specialized prenyl-binding domains. Protein prenylation Protein prenylation involves the transfer of either a farnesyl or a geranylgeranylation, geranylgeranyl moiety to C-terminal cysteine(s) of the target protein. There are three enzymes that carry out prenylation in the cell, farnesyl transferase, Caax protease and geranylgeranyl transferase I. Farnesylation is a type of prenylation, a post-translational modification of proteins by which an isoprenyl group is added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on C3 position by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol (chemistry), alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most Eukaryote, eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to the structure of the cell membrane, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
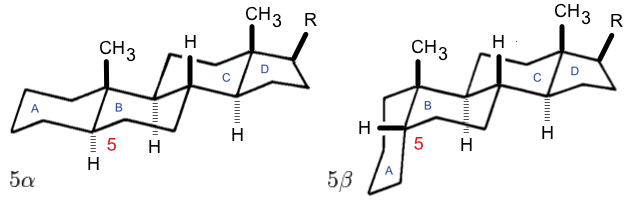
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes xanthophylls (which contain oxygen) and carotenes (which are purely hydrocarbons and contain no oxygen). All are derivatives of tetraterpenes, meaning that they are produced from 8 isoprene units and contain 40 carbon atoms. In general, carotenoids absorb wavelengths ranging from 400 to 550 nanometers (violet to green light). This causes the compounds to be deeply colored yellow, orange, or red. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf coloration of about 15-30% of tree species, but many plant colors, especially reds and purples, are due to polyphenols. Carotenoids serve two key roles in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Carotene
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced bilabial fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ('house', compare and ). In Greek, the name was , pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . The letter Β had the largest number of highly divergent local forms. Besides the standard form (either rounded or pointed, ), there were forms as varied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in Cannabis (drug), cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |