|
Isabella Of England
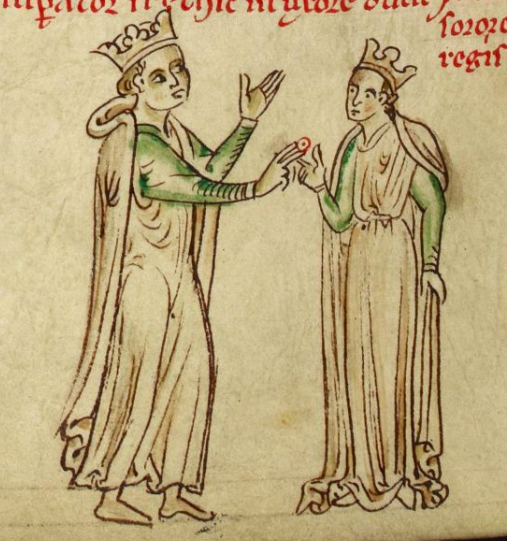
Isabella of England (1214 – 1 December 1241) was an English princess of the House of Plantagenet The House of Plantagenet (Help:IPA/English, /plænˈtædʒənət/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the Medieval France, French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by mo .... She became Holy Roman Empress, List of Sicilian consorts, Queen of Sicily, List of Italian royal consorts#House of Hohenstaufen, (1212–1250), Italy and List of German queens, Germany from 1235 until her death as the third wife of Emperor Frederick II. Life Birth and early years Isabella was born around 1214 as the fourth child and second daughter of John, King of England and his second wife Isabella of Angoulême. Her exact date of birth is unknown, and the year is calculated based on the fact that Matthew Paris reported that the princess got married at the age of 21. By the time Isabella was born, her parents' marriage had alrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empress
The Holy Roman Empress or Empress of the Holy Roman Empire (''Kaiserin des Heiligen Römischen Reiches'') was the wife or widow of the Holy Roman Emperor. The elective dignity of Holy Roman emperor was restricted to males only, but some empresses, such as Theophanu and Maria Theresa, were '' de facto'' rulers of the Empire. Holy Roman Empresses Before 924, the title of emperor was not always associated with the German kingdom; rather, it was initially associated with the Carolingian dynasty, and then possessed by several other figures of the 9th and 10th centuries. Their wives were thus empresses, but not necessarily German queens. Carolingian Holy Roman Empresses/Queens of Germany With the elevation of Otto I of Germany in 962 to the Imperial title, the title of Roman King or Emperor became inalienably associated with the Kingdom of Germany - although a King of Germany might not bear the title of Emperor, it would be impossible to become a Holy Roman Emperor without being K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabella Of Angoulême
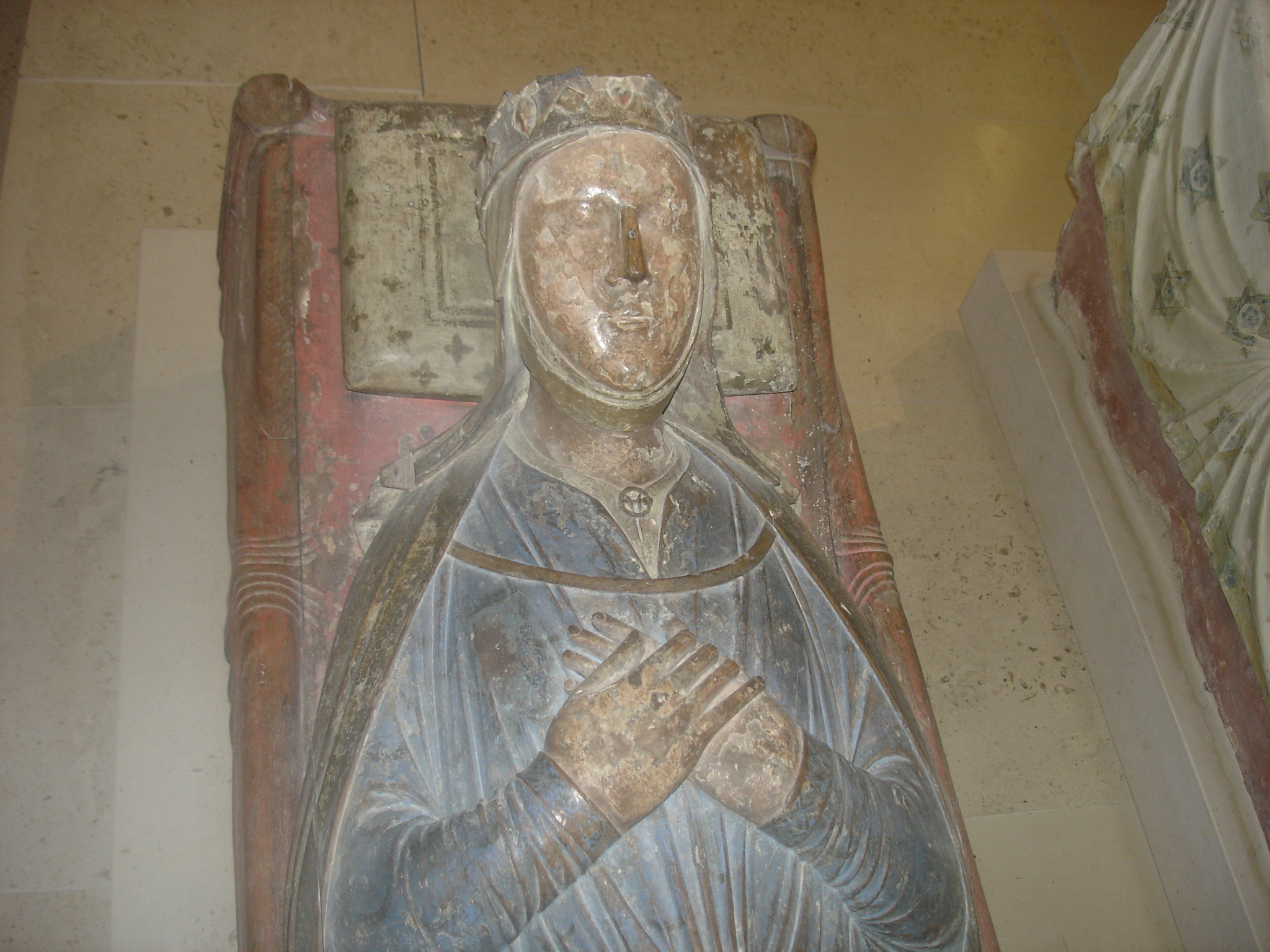
Isabella (, ; c. 1186/ 1188 – 4 June 1246) was Queen of England from 1200 to 1216 as the second wife of King John, Countess of Angoulême in her own right from 1202 until her death in 1246, and Countess of La Marche from 1220 to 1246 as the wife of Count Hugh. Isabella was the only child of Aymer, Count of Angoulême, and Alice of Courtenay. In 1200, she married King John, with whom she had five children, including the future Henry III of England. After John died in 1216, Isabella remarried in 1220 to Hugh X of Lusignan, Count of La Marche, by whom she had another nine children. Some of Isabella's contemporaries, as well as later writers, claim that she formed a conspiracy against King Louis IX of France in 1241, after being publicly snubbed by his mother, Blanche of Castile, for whom she harbored a deep-seated hatred. In 1244, after the plot had failed, Isabella was accused of attempting to poison the king. To avoid arrest, she sought refuge in Fontevraud Abbey, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh X Of Lusignan
Hugh X de Lusignan or Hugh V of La Marche (c. 1183 – c. 5 June 1249, Angoulême) was Seigneur de Lusignan and Count of La Marche in November 1219 and was Count of Angoulême by marriage. He was the son of Hugh IX. Background Hugh's father, Hugh IX of Lusignan, was betrothed to marry 12-year-old Isabel of Angoulême in 1200, but King John of England married her instead. As a result, the entire de Lusignan family rebelled against the English king. Hugh IX married Agathe de Preuilly instead. Hugh was born in 1183. He married Isabella, widow of King John of England, on 10 May 1220. By Hugh's marriage to Isabella, he became Count of Angoulême until her death in 1246. Together they founded the abbey of Valence. In 1224, Hugh joined with King Louis VIII of France against the Angevins, being promised the city of Bordeaux. By 1226, he had become embittered against Louis' lack of support in conquering Gascony. Marriage and issue Hugh and Isabella had: * Hugh XI de Lusign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in many Western Christian liturgical calendars on 29 September, and on 8 November in the Eastern Christian traditions. Michaelmas has been one of the four quarter days of the English and Irish financial, judicial, and academic year. In the Christian angelology of some traditions, the Archangel Michael is considered as the greatest of all the angels; being particularly honored for defeating the devil in the war in heaven. History The name Michaelmas comes from a shortening of "Michael's Mass", in the same style as Christmas (Christ's Mass) and Candlemas (Candle Mass, the Mass where traditionally the candles to be used throughout the year would be blessed). During the Middle Ages, Michaelmas was celebrated as a Holy Day of Obligation, but this tradition was abolished in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Scotland
Alexander II ( Medieval Gaelic: '; Modern Gaelic: '; nicknamed "the Peaceful" by modern historians; 24 August 1198 – 6 July 1249) was King of Alba (Scotland) from 1214 until his death. He concluded the Treaty of York (1237) which defined the boundary between England and Scotland, largely unchanged today. Early life Alexander was born at Haddington, East Lothian, the only son of the Scottish king William the Lion and Ermengarde de Beaumont. He was forced to spend time in England under the terms of the Treaty of Falaise, and (John of England knighted him at Clerkenwell Priory in 1213) before he returned home. He succeeded to the kingdom on the death of his father on 4 December 1214, being crowned at Scone on 6 December the same year. At the time of his accession, his sisters Isabella and Margaret had been sent to England as hostages to King John. He appealed to John through the Magna Carta, which promised to deal with the rights of Alexander and his family. King of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Of England, Queen Of Scotland
Joan of England (22 July 1210 – 4 March 1238), was Queen of Alba (Scotland) from 1221 until her death as the wife of Alexander II. She was the third child of John, King of England and Isabella of Angoulême. Life Joan was sought as a bride by Philip II of France for his son. In 1214, however, her father King John promised her in marriage to Hugh X of Lusignan, as compensation for his father Hugh IX of Lusignan being jilted by her mother Isabella. She was promised Saintes, Saintonge and the Isle of Oléron as dowry, and was sent to her future spouse in that year to be brought up at his court until marriage. Hugh X laid claim on her dowry already prior to their marriage, but when this did not succeed, he reportedly became less eager to marry her. On the death of John of England in 1216, queen dowager Isabella decided she should marry Hugh X herself. Hugh X kept Joan with him in an attempt to keep her dowry as well as having the dowry of her mother Isabella released fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York Castle
York Castle is a fortified complex in the city of York, England. It consists of a sequence of castles, prisons, court, law courts and other buildings, which were built over the last nine centuries on the north-west side of the River Foss.Cooper, p.149. The now ruined keep of the medieval Norman architecture, Norman castle is commonly referred to as Clifford's Tower. Built originally on the orders of William the Conqueror, William I to dominate the former Viking city of Jórvík, the castle suffered a tumultuous early history before developing into a major fortification with extensive water defences. After a major explosion in 1684 rendered the remaining military defences uninhabitable, York Castle continued to be used as a gaol and prison until 1929. The first motte and bailey castle on the site was built in 1068 following the Normans, Norman conquest of York. After the destruction of the castle by rebels and a Viking army in 1069, York Castle was rebuilt and reinforced with e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northampton Castle
Northampton Castle in Northampton, was one of the most prominent Norman castles in England. The castle site was outside the western city gate, and defended on three sides by deep trenches. A branch of the River Nene provided a natural barrier on the western side. The castle had extensive grounds and a large keep. The gates were surrounded by bulwarks made of earth, used to mount artillery. The castle was "obliterated" by the arrival of a railway branch of what is now the West Coast Main Line in the 19th century, the station of which was built on the castle site and the construction of the original Northampton Castle railway station. All that remains of the castle today is the Postern Gate, near Northampton Railway Station. History Early period The castle was built under the stewardship of Simon de Senlis, the first Earl of Northampton, in 1084. It took several years to complete, as there is no mention of it in the Domesday Book, the great survey of England completed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marlborough Castle
Marlborough Castle, locally known and recorded in historical documents as ''The Mound'', was an 11th-century royal castle located in the civil parish of Marlborough, a market town in the English county of Wiltshire, on the Old Bath Road, the old main road from London to Bath (). The barrow on which the fortification was built, perhaps the "barrow of Maerla", seems to be a prehistoric earthwork which formed the motte of the Norman Marlborough Castle. 'The borough of Marlborough', ''A History of the County of Wiltshire'' 12: Ramsbury and Selkley hundreds; the borough of Marlborough (1983:199–229) accessed 8 May 2010. It survives as a tree-covered mound known as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winchester Castle
Winchester Castle is a medieval building in Winchester, Hampshire, England. It was founded in 1067. Only the Great Hall still stands; it houses a museum of the history of Winchester. History Early history Around AD 70 the Romans constructed a massive earth rampart long and wide. On top of this they built a fort to protect the city of Venta Belgarum. This site was chosen by William the Conqueror as the site of one of the first Norman castles in England. The castle was built in 1067 and for over one hundred years it was the seat of Government of the Norman Kings. Henry II built a stone keep to house the royal treasury and the Domesday Book. A round tower from the original castle complete with sally ports is still visible. In 1141, during The Anarchy, forces of the Empress Matilda were besieged by the forces of King Stephen at the castle, in the Rout of Winchester. Building the Great Hall Between 1222 and 1235, Henry III, who was born at Winchester Castle, added the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative chambers which occupy the building. The palace is one of the centres of political life in the United Kingdom; "Westminster" has become a metonym for the UK Parliament and the British Government, and the Westminster system of government commemorates the name of the palace. The Elizabeth Tower of the palace, nicknamed Big Ben, is a landmark of London and the United Kingdom in general. The palace has been a Grade I listed building since 1970 and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1987. The building was originally constructed in the eleventh century as a royal palace and was the primary residence of the kings of England until 1512, when a fire destroyed the royal apartments. The monarch moved to the adjacent Palace of Whitehall, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodstock Palace
Woodstock Palace was a royal residence in the English town of Woodstock, Oxfordshire. Henry I of England built a hunting lodge here and in 1129 he built of walls to create the first enclosed park, where lions and leopards were kept. The lodge became a palace under Henry's grandson, Henry II, who spent time here with his mistress, Rosamund Clifford. Henry III frequently visited the palace for entertainment, including once in 1237 when he invited his long-confined cousin Eleanor, Fair Maid of Brittany. Timeline Important events that took place at the palace or manor include: * The marriage of William the Lion, king of Scots to Ermengarde de Beaumont in 1186; * The signing of the Treaty of Woodstock between Henry III of England and Llywelyn ap Gruffudd (1247); * The birth of Edmund of Woodstock, 1st Earl of Kent (1301-1330), the sixth son of King Edward I, and the second by his second wife Margaret of France, and a younger half-brother of King Edward II; * The birth of Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |