|
Iris Fosteriana
''Iris fosteriana'' is a species in the genus ''Iris'', subgenus '' Scorpiris''. It was named after Michael Foster (a known British Iris expert) by Dr Aitchison, and found in Pendjeh, Turkmenistan. First described in transactions of the Linnean Society of London in April 1888 and then published by John Gilbert Baker in Botanical Magazine in 1892. Iris fosteriana is an accepted name by the RHS. It has many similarities with other iris species in the Xiphium. Habit It has a slim bulb (coloured cream) with a long thin neck. Below the bulb are tuberous roots that are white, thin and 6in long. The fragile roots mean that the bulb does not take transplanting very well. In Spring, (March in the UK) it has 1 or 2 long tubed flowers that are 4–5 cm (1.5 or 2in) wide with downward-turned rich purple (or deep purple) standards and creamy yellow (or pale yellow) falls. The flowers do not produce any scent. After flowering, it produces seeds, but there is no aril (coating) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothenburg Botanical Garden
The Gothenburg Botanical Garden () is located in Gothenburg, Sweden, and is one of the larger botanical gardens in Europe. History The Gothenburg Botanical Garden is situated in a formerly completely rural area, where earlier a great country estate named Stora Änggården was located. The garden was initially funded by a donation from the Charles Felix Lindberg Foundation, in special memory of himself. Lindberg was a Swedish businessman and donor, who died in 1909. The Gothenburg City Council took the initiative to the botanical garden in 1912. The decision was finally taken in 1915 and work started in 1916. The park was opened to the public in 1919 (the Woodlands) and in 1923 (the cultivated areas). It was first planned as "a field for experimentation and biological demonstrations, and a nature park". Stora Änggården was built in 1812 and renovated under the supervision of the architect Sigfrid Ericson in 1919 and is now used as staff residence. The Gothenburg Botanical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aril
An aril (), also called arillus, is a specialized outgrowth from a seed that partly or completely covers the seed. An arillode, or false aril, is sometimes distinguished: whereas an aril grows from the attachment point of the seed to the ovary (botany), ovary (from the Ovule, funiculus or ''Hilum (biology), hilum''), an arillode forms from a different point on the seed coat. The term "aril" is sometimes applied to any fleshy appendage of the seed in flowering plants, such as the mace (spice), mace of the nutmeg seed. Arils and arillodes are often edible enticements that encourage animals to transport the seed, thereby assisting in seed dispersal. Pseudarils are aril-like structures commonly found on the Pyrena, pyrenes of Burseraceae species that develop from the mesocarp of the ovary. The fleshy, edible pericarp splits neatly in two halves, then falling away or being eaten to reveal a brightly coloured pseudaril around the black seed. The aril may create a fruit-like structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
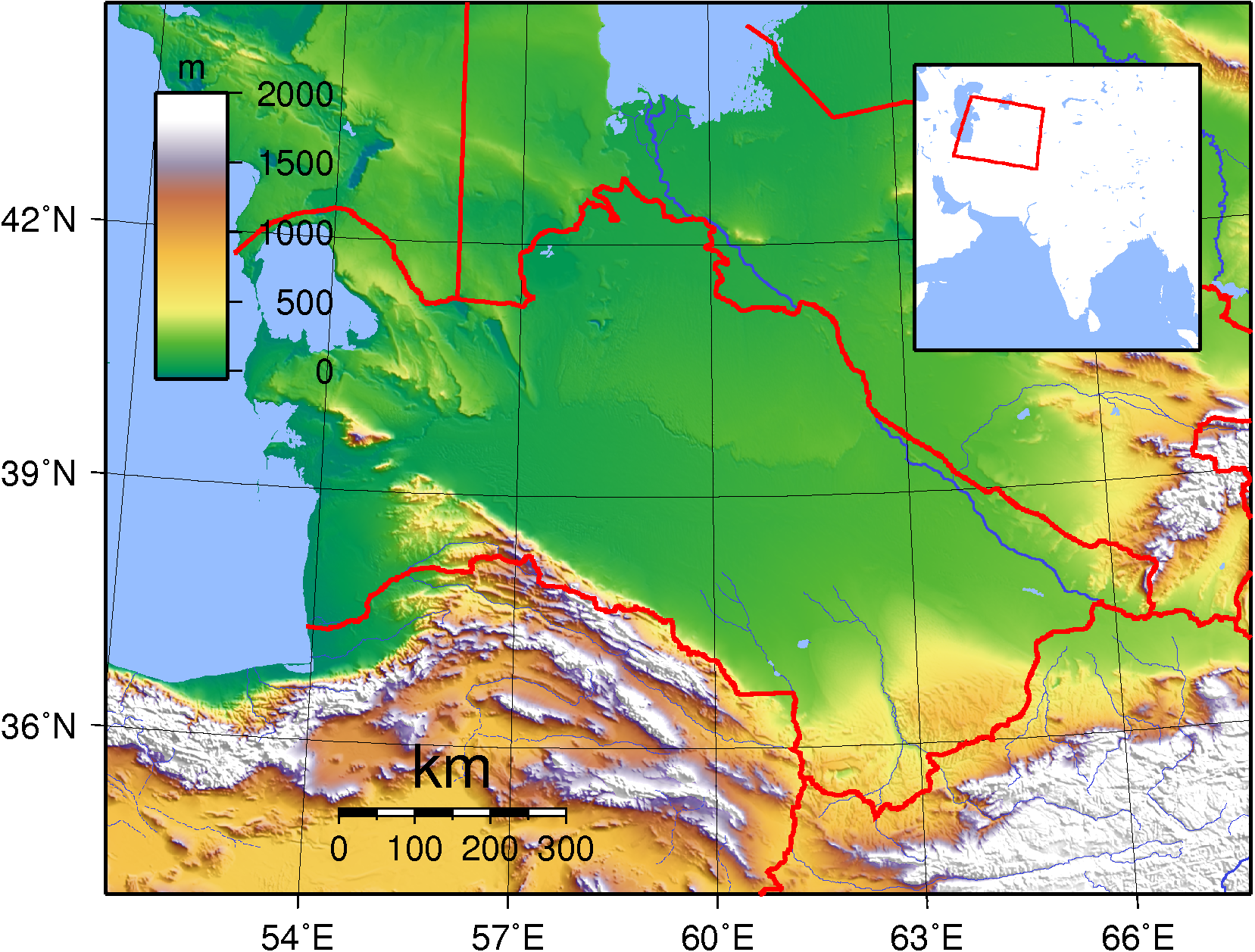
Flora Of Turkmenistan
The wildlife of Turkmenistan is the flora and fauna of Turkmenistan, and the natural habitats in which they live. Turkmenistan is a country in Central Asia to the east of the Caspian Sea. Two thirds of the country is hot dry plains and desert, and the rest is more mountainous. Very little rain falls in summer and the chief precipitation occurs in the southern part of the country in the winter and spring. The Caspian coast has milder winters. The desert sees limited plant growth in the winter, with grasses and xeric plants and shrubs sprouting, and with the arrival of spring, the rains encourage the growth and flowering of ephemeral plants. The mountains in the south of the country are covered in shrublike and juniper woodlands, and larger trees grow in the gullies and river valleys. A wide range of animals are found in Turkmenistan, including 91 species of mammal, 82 species of reptile and nearly 400 species of bird. A number of nature reserves and sanctuaries have been created f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Iran
The wildlife of Iran include the fauna and flora of Iran. One of the most famous animals of Iran is the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus venaticus''), which today survives only in Iran. Another notable species is the Iranian ground jay (''Podoces pleskei''), the only bird endemic to Iran. History The animals of Iran were described by Hamdallah Mustawfi in the 14th century. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin and Édouard Ménétries explored the Caspian Sea area and the Talysh Mountains to document Caspian fauna. Several naturalists followed in the 19th century, including Filippo de Filippi, William Thomas Blanford, and Nikolai Zarudny who documented mammal, bird, reptile, amphibian and fish species. The Complete Fauna of Iran by Eskandar Firouz, documents a wide range of species across the country’s ecosystems Flora More than one-tenth of the country is forested. The most extensive forest is found on the mountain slopes rising from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Afghanistan
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 1888
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants (hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, conifers and other gymnosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kopet Dag
The Köpet Dag, Kopet Dagh, or Koppeh Dagh (; ), also known as the Turkmen-Khorasan Mountain Range, is a mountain range on the border between Turkmenistan and Iran that extends about along the border southeast of the Caspian Sea, stretching northwest-southeast from near the Caspian Sea in the northwest to the Harirud River in the southeast. In the southwest it borders on the parallel eastern endings of the Alborz mountains being together part of the much larger Alpide belt. The highest peak of the range in Turkmenistan is the Mount Rizeh (Kuh-e Rizeh), located at the southwest of the capital Ashgabat and stands at . The highest Iranian summit is Mount Quchan (Kuh-e Quchan) at . Etymology Vambery conjectured that ''köpet'' originates from the Turkmen language where "köp" means "a lot" or "many" and the word "dag" means "mountain" or "peak". He thus translated Köpetdag as "Many mountains (peaks)". He and others noted that in Persian ''koppeh'' means "pile" or "heap", and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes. Steppe biomes may include: * the montane grasslands and shrublands biome * the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome * the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome A steppe is usually covered with grass and shrubs, depending on the season and latitude. The term ''steppe climate'' denotes a semi-arid climate, which is encountered in regions too dry to support a forest, but not dry enough to be a desert. Steppes are usually characterized by a semi-arid or continental climate. Temperature extremes can be recorded in the summer of up to and in winter of down to . Besides this major seasonal difference, fluctuations between day and night are also significant: in both the highlands of Mongolia and northern Nevada, can be reached during the day with sub-freezing readings at night. Steppes ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's capital and largest city. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36 and 50 million. Ancient history of Afghanistan, Human habitation in Afghanistan dates to the Middle Paleolithic era. Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulran
Gulran is a village in Herat Province, Afghanistan. It is the center of the Gulran District. the population is overwhelmingly Pashtun with small pockets of Tajik population. Climate Gulran has a cold steppe climate (Köppen: ''BSk'') with very hot summers and cool winters. References See also *Herat Province Herat ( Dari: هرات) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the western part of the country. Together with Badghis, Farah, and Ghor provinces, it makes up the north-western region of Afghanistan. Its primary city a ... Populated places in Herat Province {{Herat-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulb Frame
In botany, a bulb is a short underground stem with fleshy leaves or leaf basesBell, A.D. 1997. ''Plant form: an illustrated guide to flowering plant morphology''. Oxford University Press, Oxford, U.K. that function as food storage organs during dormancy. In gardening, plants with other kinds of storage organ are also called ornamental bulbous plants or just ''bulbs''. Description The bulb's leaf bases, also known as scales, generally do not support leaves, but contain food reserves to enable the plant to survive adverse conditions. At the center of the bulb is a vegetative growing point or an unexpanded flowering shoot. The base is formed by a reduced stem, and plant growth occurs from this basal plate. Roots emerge from the underside of the base, and new stems and leaves from the upper side. Tunicate bulbs have dry, membranous outer scales that protect the continuous lamina of fleshy scales. Species in the genera ''Allium'', ''Hippeastrum'', '' Narcissus'', and ''Tulipa'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |