|
Inversion (evolutionary Biology)
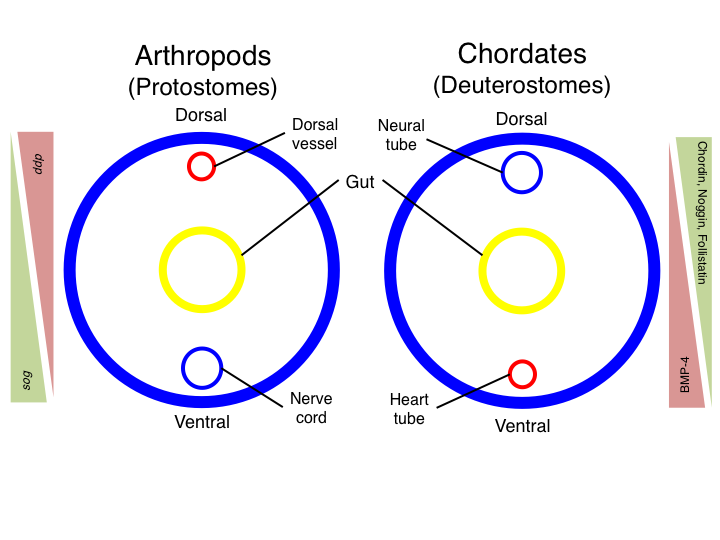
In evolutionary developmental biology, inversion refers to the hypothesis that during the course of animal evolution, the structures along the anatomical terms of location, dorsoventral (DV) axis have taken on an orientation opposite that of the ancestral form. Inversion was first noted in 1822 by the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, when he dissected a crayfish (an arthropod) and compared it with the vertebrate body plan. The idea was heavily criticised, but periodically resurfaced, and is now supported by some molecular embryologists. History As early as 1822, the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire noted that the organization of Anatomical_terms_of_location#Dorsal_and_ventral, dorsal and ventral structures in arthropods is opposite that of mammals. Five decades later, in light of Charles Darwin, Darwin's theory of "descent with modification", German zoologist Anton Dohrn proposed that these groups arose from a common descent, common ancestor which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
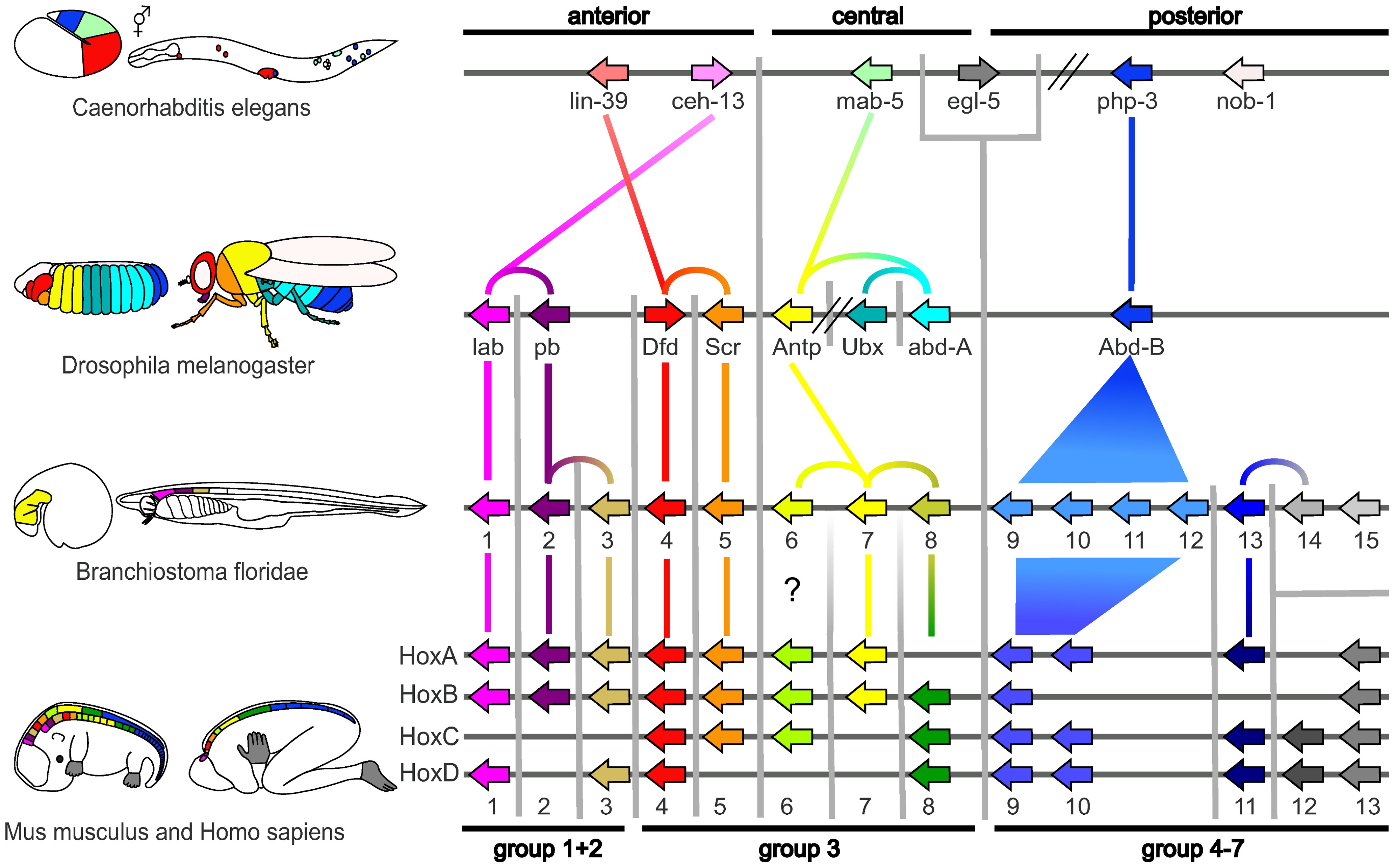
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoology, zoologists did not know how embryogenesis, embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was that of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Nerve Cord
The dorsal nerve cord is an anatomical feature found in chordate animals, mainly in the subphyla Vertebrata and Cephalochordata, as well as in some hemichordates. It is one of the five embryonic features unique to all chordates, the other four being a notochord, a post-anal tail, an endostyle, and pharyngeal slits. All chordates (vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates) have dorsal hollow nerve cords. The dorsal nerve cord is located ''dorsal'' to the notochord and thus also to the gut tube (hence the name). It is formed from clustered neuronal differentiation at the axial region of the ectoderm, known as the neural plate. During embryonic development, the neural plate first invaginates longitudinally to form the neural groove, whose edges ( neural folds) fuse over to form a hollow neural tube. This is an important feature as it distinguishes chordates from other invertebrate phyla such as annelids and arthropods, who have solid nerve cords that are located '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Formation
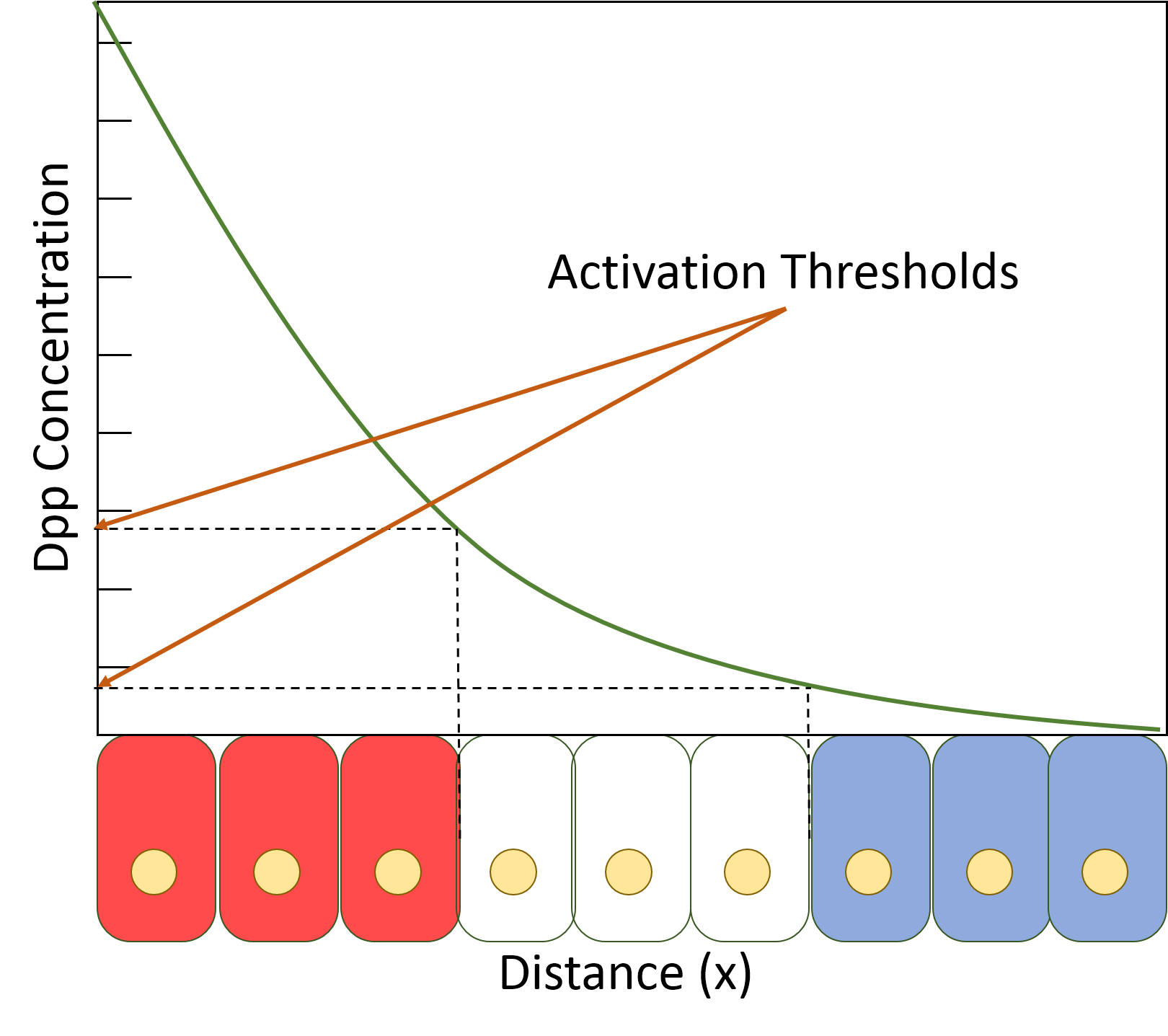
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature. In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fate determination, cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis, the creation of diverse anatomy, anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespot (mimicry), eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism. Patterns in nature Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follistatin
Follistatin, also known as activin-bindings protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FST'' gene. Follistatin is an autocrine glycoprotein that is expressed in nearly all tissues of higher animals. Its primary function is the binding and bioneutralization of members of the TGF-β superfamily, with a particular focus on activin, a paracrine hormone. An earlier name for the same protein was FSH-suppressing protein (FSP). At the time of its initial isolation from follicular fluid, it was found to inhibit the anterior pituitary's secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Biochemistry Follistatin is part of the inhibin-activin-follistatin axis. Three isoforms, FS-288, FS-300, and FS-315 have been reported. Two, FS-288 and FS-315, are created by alternative splicing of the primary mRNA transcript. FS-300 (porcine follistatin) is thought to be the product of posttranslational modification via truncation of the C-terminal domain from the primary amino-aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noggin (protein)
Noggin, also known as NOG, is a protein that is involved in the development of many Tissue (biology), body tissues, including Nervous tissue, nerve tissue, Skeletal muscle, muscles, and bones. In humans, noggin is encoded by the ''NOG'' gene. The Protein primary structure, amino acid sequence of human noggin is highly homologous to that of rat, mouse, and ''Xenopus'' (an aquatic frog genus). Noggin is an inhibitor of several Bone morphogenetic protein, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs): it inhibits at least Bone morphogenetic protein 2, BMP2, Bone morphogenetic protein 4, 4, Bone morphogenetic protein 5, 5, Bone morphogenetic protein 6, 6, Bone morphogenetic protein 7, 7, GDF6, 13, and GDF5, 14. The protein's name, which is a slang English-language word for "head", was coined in reference to its ability to produce embryos with large heads when exposed at high concentrations. Function Noggin is a Cell signaling, signaling molecule that plays an important role in promoting som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordin
Chordin (from Greek χορδή, string, catgut) is a protein with a prominent role in dorsal–ventral patterning during early embryonic development. In humans it is encoded for by the ''CHRD'' gene. History Chordin was originally identified in the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') in the laboratory of Edward M. De Robertis as a key developmental protein that dorsalizes early vertebrate embryonic tissues. It was first hypothesized that chordin plays a role in the dorsal homeobox genes in Spemann's organizer. The chordin gene was discovered through its activation following use of gsc ( goosecoid) and Xnot mRNA injections. The discoverers of chordin concluded that it is expressed in embryo regions where gsc and Xnot were also expressed, which included the prechordal plate, the notochord, and the chordoneural hinge. The expression of the gene in these regions led to the name chordin. Initial functions of chordin were thought to include recruitment of neighboring cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by ''BMP4'' gene. BMP4 is found on chromosome 14q22-q23. BMP4 is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein family which is part of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. The Protein family, superfamily includes large families of growth and differentiation factors. BMP4 is highly conserved evolutionarily. BMP4 is found in early embryonic development in the ventral marginal zone and in the eye, heart blood and otic vesicle. Discovery Bone morphogenetic proteins were originally identified by an ability of demineralized bone extract to induce endochondral osteogenesis in vivo in an extraskeletal site. Function BMP4 is a polypeptide belonging to the Transforming growth factor beta, TGF-β superfamily of proteins. It, like other bone morphogenetic proteins, is involved in bone and cartilage development, specifically tooth and limb development and fracture repair. This particular family member plays an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapentaplegic
''Decapentaplegic'' (''Dpp'') is a key morphogen involved in the development of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and is the first validated secreted morphogen. It is known to be necessary for the correct patterning and development of the early ''Drosophila'' embryo and the fifteen imaginal discs, which are tissues that will become limbs and other organs and structures in the adult fly. It has also been suggested that ''Dpp'' plays a role in regulating the growth and size of tissues. Flies with mutations in decapentaplegic fail to form these structures correctly, hence the name (''decapenta''-, fifteen; -''plegic'', paralysis). ''Dpp'' is the ''Drosophila'' homolog of the vertebrate bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are members of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily, TGF-β superfamily, a class of proteins that are often associated with their own specific signaling pathway. Studies of ''Dpp'' in ''Drosophila'' have led to greater understanding of the func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transforming Growth Factor Beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages. Activated TGF-β complexes with other factors to form a serine/threonine kinase complex that binds to TGF-β receptors. TGF-β receptors are composed of both type 1 and type 2 receptor subunits. After the binding of TGF-β, the type 2 receptor kinase phosphorylates and activates the type 1 receptor kinase that activates a signaling cascade. This leads to the activation of different downstream substrates and regulatory proteins, inducing transcription of different target genes that function in differentiation, chemotaxis, proliferation, and activation of many immune cells. TGF-β is secreted by many cell types, including macrophages, in a latent form in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (an insect of the Order (biology), order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly", "pomace fly", or "banana fly". In the wild, ''D. melanogaster'' are attracted to rotting fruit and fermenting beverages, and are often found in orchards, kitchens and pubs. Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and Life history theory, life history evolution. ''D. melanogaster'' was the first animal to be Fruit flies in space, launched into space in 1947. As of 2017, six Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''Drosophila melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |