|
Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia
Intestinal neuronal dysplasia (IND) is an inherited disease of the intestine that affects one in 3000 children and adults. The intestine uses peristalsis to push its contents toward the anus; people with IND have a problem with the motor neurons that lead to the intestine, inhibiting this process and thus preventing digestion. It can often be confused for Hirschsprung's disease, as both have similar symptoms. Presentation IND can be grouped into NID A and NID B, with the "A" form affecting the sympathetic innervation, and the "B" version affecting the parasympathetic innervation. In 2002 Martucciello and colleagues published the first analysis of associated anomalies in IND population is an important clinical approach to investigate possible pathogenetic correlations. Two recessive syndromes were identified (3 families). The first was characterized by NID B, intestinal malrotation, and congenital short bowel, the second by NID B, short stature, mental retardation, and facial dysmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
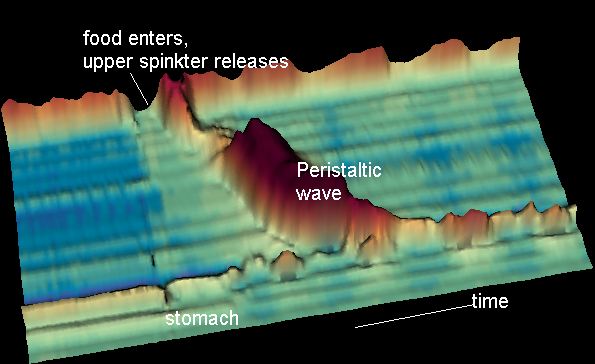
Peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which is preceded by a simultaneous contraction of the longitudinal muscle and relaxation of the circular muscle in the lining of the gut. In much of a digestive tract, such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus (digestion), bolus before being transformed into chyme in the stomach) along the tract. The peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. Earthworms use a similar mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facilitate the defecation, expulsion of wastes that remain after digestion. Bowel contents that pass through the anus include the gaseous flatus and the semi-solid feces, which (depending on the type of animal) include: indigestible matter such as bones, hair pellet (ornithology), pellets, endozoochory, endozoochorous seeds and gastrolith, digestive rocks; Summary at residual food material after the digestible nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; excretion, excreted metabolites like bilirubin-containing bile; and dead mucosal epithelia or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts. Passage of feces through the anus is typically controlled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons. A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibres and a muscle fibre can undergo many action potentials in the time taken for a single muscle twitch. Innervation takes place at a neuromuscular junction and twitches can become superimpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirschsprung's Disease
Hirschsprung's disease (HD or HSCR) is a birth defect in which nerves are missing from parts of the intestine. The most prominent symptom is constipation. Other symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and slow growth. Most children develop signs and symptoms shortly after birth. However, others may be diagnosed later in infancy or early childhood. About half of all children with Hirschsprung's disease are diagnosed in the first year of life. Complications may include enterocolitis, megacolon, bowel obstruction and intestinal perforation. The disorder may occur by itself or in association with other genetic disorders such as Down syndrome or Waardenburg syndrome. About half of isolated cases are linked to a specific genetic mutation, and about 20% occur within families. Some of these occur in an autosomal dominant manner. The cause of the remaining cases is unclear. If otherwise normal parents have one child with the condition, the next child has a 4% risk o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system functions to regulate the body's unconscious actions. The sympathetic nervous system's primary process is to stimulate the body's fight or flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basic level to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system is described as being antagonistic to the parasympathetic nervous system. The latter stimulates the body to "feed and breed" and to (then) "rest-and-digest". The SNS has a major role in various physiological processes such as blood glucose levels, body temperature, cardiac output, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed-and-breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cranial nerves, specifically the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve. Three spinal nerves in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laxative
Laxatives, purgatives, or aperients are substances that loosen stools and increase bowel movements. They are used to treat and prevent constipation. Laxatives vary as to how they work and the side effects they may have. Certain stimulant, lubricant, and saline laxatives are used to evacuate the colon for rectal and bowel examinations, and may be supplemented by enemas under certain circumstances. Sufficiently high doses of laxatives may cause diarrhea. Some laxatives combine more than one active ingredient, and may be administered orally or rectally. Types Bulk-forming agents Bulk-forming laxatives, also known as roughage, are substances, such as fiber in food and hydrophilic agents in over-the-counter drugs, that add bulk and water to stools so they can pass more easily through the intestines (lower part of the digestive tract). Properties * Site of action: small and large intestines * Onset of action: 12–72 hours * Examples: dietary fiber, Metamucil, Citrucel, Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enema
An enema, also known as a clyster, is the rectal administration of a fluid by injection into the Large intestine, lower bowel via the anus.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word ''enema'' can also refer to the liquid injected, as well as to a device for administering such an injection. In standard medicine, the most frequent uses of enemas are to relieve constipation and for bowel cleansing before a medical examination or procedure; also, they are employed as a lower gastrointestinal series (also called a barium enema), to treat Travelers' diarrhea, traveler's diarrhea, as a vehicle for the administration of food, water or medicine, as a stimulant to the general system, as a local application and, more rarely, as a means of reducing body temperature, as treatment for encopresis, and as a form of Management of dehydration, rehydration therapy (proctoclysis) in patients for whom intravenous therapy is not applicable. Medical usage The princip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon Resection
Colectomy (''wikt:colo-#Prefix, col-'' + ''wikt:-ectomy#Suffix, -ectomy'') is the surgical removal of any extent of the Large intestine#Structure, colon, the longest portion of the large bowel. Colectomy may be performed for prophylactic, curative, or palliative reasons. Indications include cancer, infection, infarction, perforation, and impaired function of the colon. Colectomy may be performed Laparotomy, open, Laparoscopy, laparoscopically, or Robot-assisted surgery, robotically. Following removal of the bowel segment, the surgeon may restore continuity of the bowel or create a colostomy. Partial or subtotal colectomy refers to removing a portion of the colon, while total colectomy involves the removal of the entire colon. Complications of colectomy include anastomotic leak, bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding structures. Indications Common indications for colectomy include: * Colon cancer, Colorectal cancer * Colorectal polyp, Colon polyps not amenable to removal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |