|
International Education
International education refers to a dynamic concept that involves a journey or movement of people, minds, or ideas across political and cultural frontiers. It is facilitated by the globalization phenomenon, which increasingly erases the constraints of geography on economic, social, and cultural arrangements. The concept involves a broad range of learning, for example, Formal learning, formal education and informal learning (e.g. training, Student exchange program, exchange programs, and cross-cultural communication). It could also involve a reorientation of academic outlook such as the pursuit of "worldmindedness" as a goal so that a school or its academic focus is considered International school, international. For example, the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities, National Association of State Universities prescribes the adoption of "proper education" that reflects the full range of international, social, political, cultural, and economic dialogue. International edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, the liberalization of capital movements, the development of transportation, and the advancement of information and communication technologies. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20th century (supplanting an earlier French term ''mondialisation''). It developed its current meaning sometime in the second half of the 20th century, and came into popular use in the 1990s to describe the unprecedented international connectivity of the Post–Cold War era, post–Cold War world. The origins of globalization can be traced back to the 18th and 19th centuries, driven by advances in transportation and communication technologies. These developments increased global interactions, fostering the growth of international trade and the exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all Europeans claim to speak at least one language other than their mother tongue; but many read and write in one language. Being multilingual is advantageous for people wanting to participate in trade, globalization and cultural openness. Owing to the ease of access to information facilitated by the Internet, individuals' exposure to multiple languages has become increasingly possible. People who speak several languages are also called '' polyglots''. Multilingual speakers have acquired and maintained at least one language during childhood, the so-called first language (L1). The first language (sometimes also referred to as the mother tongue) is usually acquired without formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. Liberals espouse various and often mutually conflicting views depending on their understanding of these principles but generally support private property, market economies, individual rights (including civil rights and human rights), liberal democracy, secularism, rule of law, Economic freedom, economic and political freedom, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and freedom of religion.Generally support: * * * * * * *constitutional government and privacy rights * Liberalism is frequently cited as the dominant ideology of modern history.Wolfe, p. 23. Liberalism became a distinct Political movement, movement in the Age of Enlightenment, gaining popularity among Western world, Western philosophers and economists. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Education
Comparative education is a discipline in the social sciences which entails the scrutiny and evaluation of different educational systems, such as those in various countries. Professionals in this area of endeavor are absorbed in advancing evocative terminologies and guidelines for education worldwide, enhancing educational structures and producing a context to which the success and effectivity of education programs and initiatives can be assessed. Objectives According to scholars in the field, comparative education has five purposes: * To describe educational systems, processes, or outcomes. * To assist in the development of educational institutions and practices. *To highlight the relationships between education and society. *To establish generalized statements about education that are valid in more than one country. *To help the current generation understand the nowadays education systems with reference to the past. Comparative education is often incorrectly assumed to exclusiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Decade Of Education For Sustainable Development
The Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (DESD) 2005–2014 was an Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) initiative of the United Nations. The Decade was delivered by UNESCO as lead agency, and gave rise to Regional Centres of Expertise (RCE) networks, and the GUPES universities' partnership. The launch of the United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development started a global movement to reorient education to address the challenges of sustainable development. It was the first UN Decade to establish a global monitoring and evaluation process and expert group. Building on the achievement of the Decade, stated in the Aichi-Nagoya Declaration on ESD, UNESCO endorsed the Global Action Programme on ESD (GAP) in the 37th session of its General Conference. Acknowledged by UN general assembly Resolution A/RES/69/211 and launched at the UNESCO World Conference on ESD in 2014, the GAP aims to scale-up actions and good practices. UNESCO has a major role, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
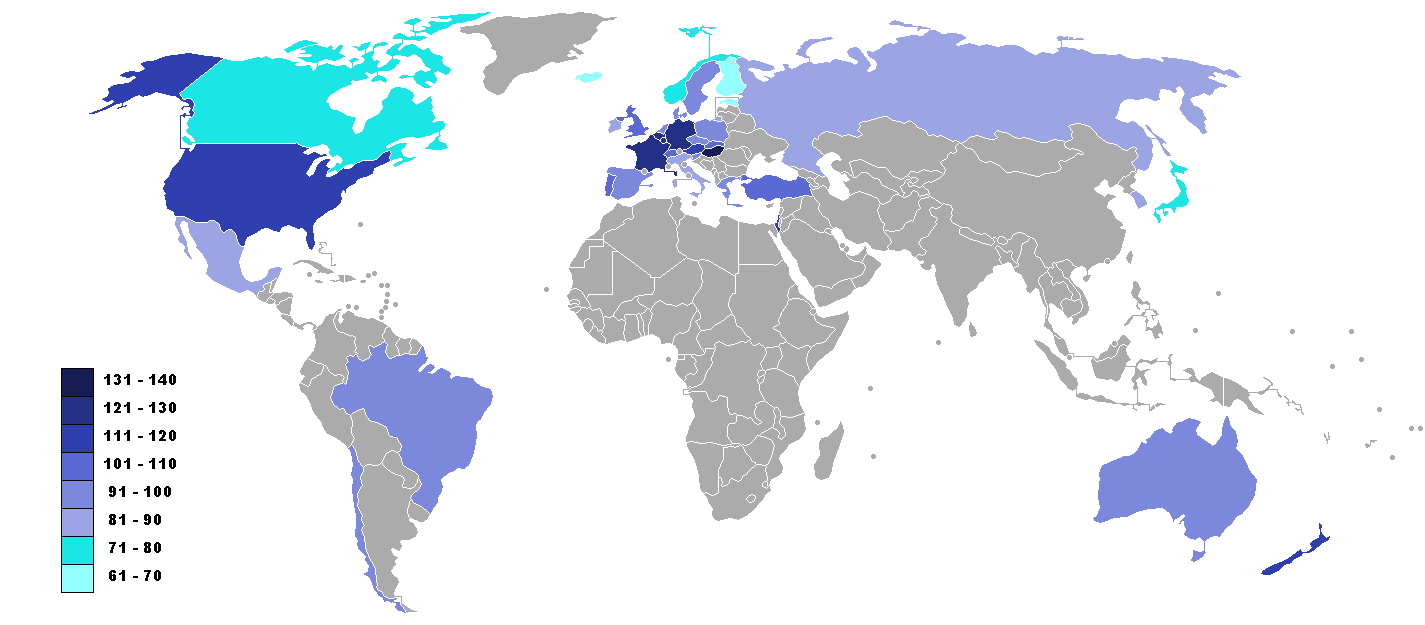
Official Development Assistance
Official development assistance (ODA) is a category used by the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to measure foreign aid. The DAC first adopted the concept in 1969. It is widely used as an indicator of international aid flow. It refers to material resources given by the governments of richer countries to promote the economic development of poorer countries and the welfare of their people. The donor government agency may disburse such resources to the government of the recipient country or through other organizations. Most ODA is in the form of grants, but some is measured as the concessional value in soft (low-interest) loans. In 2019, the annual amount of state donor aid counted as ODA was US$168 billion, of which US$152 billion came from DAC donors. Concept and definition In order to co-ordinate and measure international aid effectively, the DAC needs its members to have agreed clear criteria for what i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Developed Countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) on 18 November 1971. A country is classified among the Least Developed Countries if it meets three criteria:UN-OHRLLS . * Poverty – adjustable criterion based on Gross national income (GNI) per capita averaged over three years. , a country must have GNI per capita less than US$1,025 to be included on the list, and over $1,230 to graduate from it. * Human resource weakness (based on indicators of nutrition, health, education and adult literacy). * Economic vulnerability (based on instability of agricultural production, instability of exports of goods and services, economic importance of non-traditional activities, merchandise export concentration, handicap of economic smallness, and the percenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning is the "ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated" pursuit of learning for either personal or professional reasons. Lifelong learning is important for an individual's competitiveness and employability, but also enhances social inclusion, active citizenship, and personal development. Professions typically recognize the importance of developing practitioners becoming lifelong learners. Many licensed professions mandate that their members continue learning to maintain a license.Merriam, S. B. & Caffarella, R.S. (2007) Learning in adulthood: A comprehensive guide. San Francisco: Josseey-Bass (3rd. Edition) Lifelong learning institutes are educational organisations specifically for lifelong learning purposes. Informal lifelong learning communities also exist around the world. History In some contexts, the term "lifelong learning" evolved from the term "life-long learners", created by Leslie Watkins and used by Clint Taylor, professor at CSULA and Superinten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
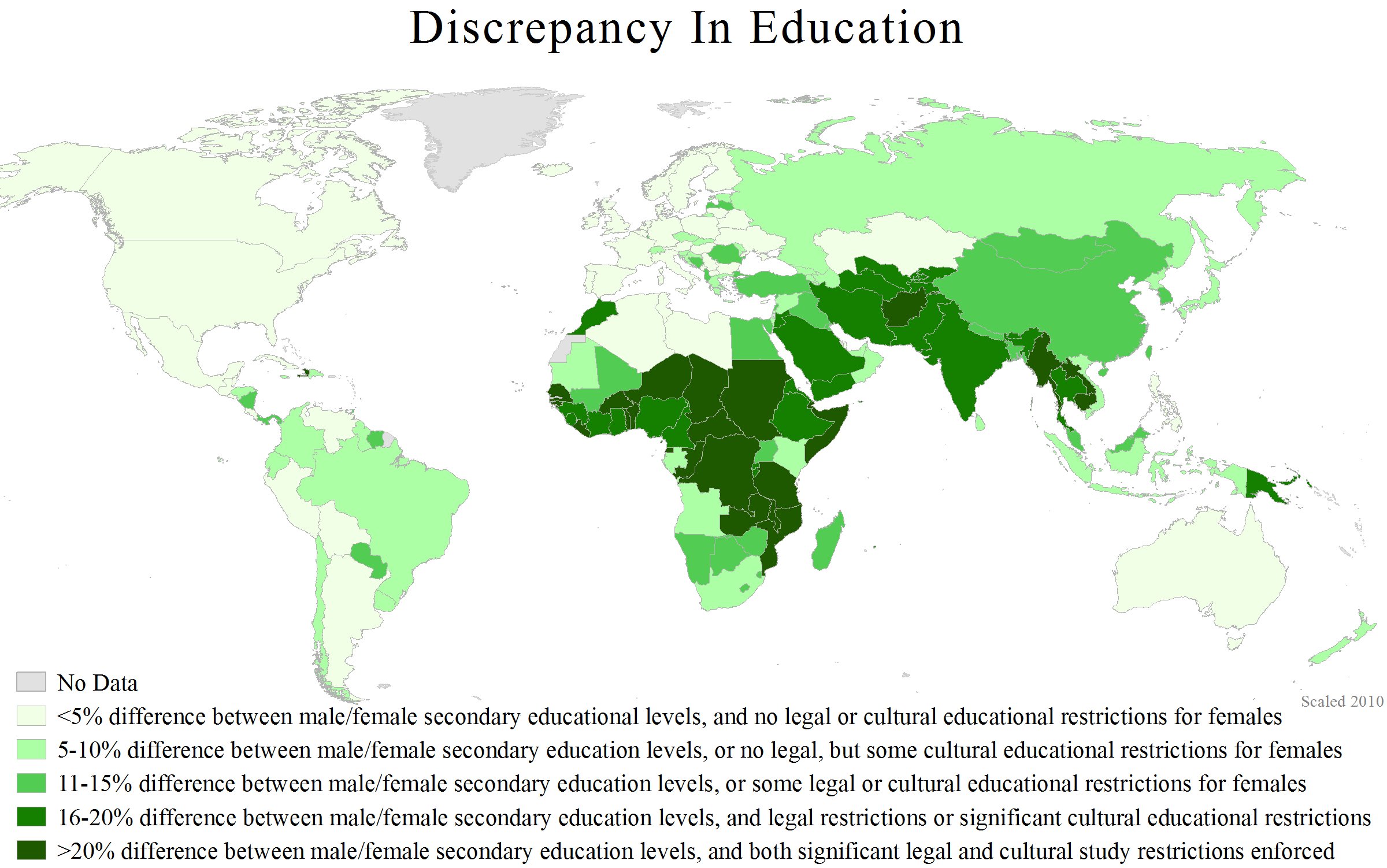
Educational Equity
Educational equity, also known as equity in education, is a measure of equity in education. Educational equity depends on two main factors. The first is distributive justice, which implies that factors specific to one's personal conditions should not interfere with the potential of academic success. The second factor is inclusion, which refers to a comprehensive standard that applies to everyone in a certain education system. These two factors are closely related and depend on each other for an educational system's success. Education equity can include the study of excellence and equity. Educational equity's growing importance is based on the premise that a person's level of education directly correlates with their quality of life and that an academic system that practices educational equity is thus a strong foundation for a fair and thriving society. But inequity in education is hard to avoid because of inequities in socioeconomic standing, race, gender, and disability. Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclusion (education)
Inclusion in education refers to including all students to equal access to equal opportunities of education and learning, and is distinct from educational equality or educational equity. It arose in the context of special education with an individualized education program or 504 plan, and is built on the notion that it is more effective for students with special needs to have the said mixed experience for them to be more successful in social interactions leading to further success in life. The philosophy behind the implementation of the inclusion model does not prioritize, but still provides for the utilization of special classrooms and special schools for the education of students with disabilities. Inclusive education models are brought into force by educational administrators with the intention of moving away from seclusion models of special education to the fullest extent practical, the idea being that it is to the social benefit of general education students and specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – while tackling climate change and working to preserve oceans and forests. The SDGs highlight the connections between the environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Sustainability is at the center of the SDGs, as the term ''sustainable development'' implies. These goals are ambitious, and the reports and outcomes to date indicate a challenging path. Most, if not all, of the goals are unlikely to be met by 2030. Rising inequalities, climate change, and biodiversity loss are topics of concerns threatening progress. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 to 2023 made these challenges worse, and some regions, such as Asia, have experienced significant setbacks during that time. There are cross-cutting issues and synergy, syner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender Disparity
Sex differences in humans have been studied in a variety of fields. Sex chromosome#Sex determination, Sex determination generally occurs by the presence or absence of a Y chromosome in the 23rd pair of chromosomes in the human genome. ''phenotype, Phenotypic sex'' refers to an individual's sex as determined by their internal and external sex organ, genitalia and expression of secondary sex characteristics. Sex differences generally refer to phenotypic trait, traits that are sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic. A subset of such differences is hypothesized to be the product of the evolutionary process of sexual selection.Mealey, L. (2000). ''Sex differences''. NY: Academic Press. Medicine Sex differences in medicine include sex-specific diseases, which are diseases that occur ''only'' in people of one sex; and sex-related diseases, which are diseases that are more usual to one sex, or which manifest differently in each sex. For example, certain autoimmune diseases may occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |