|
International Congress Of Physics
The International Congress of Physics () was a scientific conference held in Paris from 6 to 10 August 1900, in connection with the 1900 Exposition Universelle. It was the first large international conference about physics as a whole. Physicists from 15 countries took part, and there were over 70 scientific submissions. It included all major areas of physics at the time, including metrology, mechanical and thermal properties of matter, optics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, astronomy, gravitation and biophysics. One of the organizers, Charles Édouard Guillaume, reporting to ''Nature'', considered that the congress provided "the most complete representation of any science at a given epoch ever made." Novel discoveries at the time were discussed, including radioactivity, the electron and cathode rays, and challenges related to the black-body radiation and to the Michelson–Morley experiment. During the conference, the first experimental evidence of radiation pressure was prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Como Conference
The International Congress of Physicists (), better known as the Como Conference or the Volta Conference, was an international academic conference held from 11 to 27 September 1927, near Lake Como, Italy as part of a series of celebrations of the hundredth anniversary of the death of Alessandro Volta. This conference inspired the Volta Congresses held in Rome and organized since 1931. It concerned the topic of Volta's work and quantum mechanics. It gathered 61 physicists and mathematicians from all over the world. During the conference, Niels Bohr first introduced the principle of complementarity. The first quantum theory of metals was also discussed through the works of Arnold Sommerfeld and Enrico Fermi. Organization The conference was part of the Volta centennial anniversary celebrations () ordered by the government of Benito Mussolini. The physics conference was organized by the Italian Physical Society. The program was organized by Quirino Majorana, president of the soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
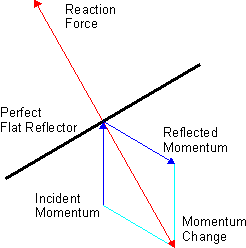
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, Reflection (physics), reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucien Poincaré
Lucien Poincaré (22 July 1862 – 9 March 1920) was a French physicist. Biography Poincaré was born at Bar-le-Duc July 22, 1862. After a distinguished academic career he became in succession inspector general of physical science in 1902, director of secondary education at the Ministry of Public Instruction in 1910, director of higher education in 1914 and rector of the Academie de Paris in 1917. In that capacity he received President Wilson at the Sorbonne on the occasion of his visit to Paris for the Peace Conference. He was the brother of French Prime Minister Raymond Poincaré and cousin of mathematician and theoretical physicist Henri Poincaré Jules Henri Poincaré (, ; ; 29 April 185417 July 1912) was a French mathematician, Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosophy of science, philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathemati .... Poincaré died in Paris March 9, 1920. Selected publications * La physique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Paul Cailletet
Louis-Paul Cailletet (21 September 1832 – 5 January 1913) was a French physicist and inventor. Life and work Cailletet was born in Châtillon-sur-Seine, Côte-d'Or. Educated in Paris, Cailletet returned to Châtillon to manage his father's ironworks. In an effort to determine the cause of accidents that occurred while tempering incompletely forged iron, Cailletet found that heating the iron put it in a highly unstable state, with gases dissolved in it. He then analyzed the gases from blast furnaces, which helped him understand the role of heat in the changes of states (phases) of metals. This brought him to the work of liquefying the various gases. Cailletet succeeded in producing droplets of liquid oxygen Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing. Physical ... in 1877 by a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Alfred Cornu
Marie Alfred Cornu (; 6 March 1841 – 12 April 1902) was a French physicist and professor of École polytechnique. The French generally refer to him as Alfred Cornu. The Cornu spiral, a graphical device for the computation of light intensities in Fresnel's model of near-field diffraction, is named after him. The spiral (or clothoid) is also used in geometric design of roads. The Cornu depolarizer is also named after him. Life Cornu was born at Orléans to François Cornu and Sophie Poinsellier. He was educated at the École polytechnique and the École des mines. Upon the death of Émile Verdet in 1866, Cornu became, in 1867, Verdet's successor as professor of experimental physics at the École polytechnique, where he remained throughout his life. Although he made various excursions into other branches of physical science, undertaking, for example, with Jean-Baptistin Baille about 1870 a repetition of Cavendish's experiment for determining the gravitational constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Française De Physique
The Société Française de Physique (SFP), or the French Physical Society, is the main professional society of French physicists. It was founded in 1873 by Joseph-Charles d'Almeida. History The French Physical Society is a state-approved non-profit scientific society aiming to promote the knowledge of physics. Its member include physicists living in France, regardless of background. As well as promoting physics, the SFP also acts as a lobbying organization with French policymakers alongside other scientific societies, the like the French Academy of Sciences, French Society of Mathematicians, and Union of Physicists. The SFP organizes a large number of events (conferences, workshops, exhibitions, etc.) for academic and general audiences. The SFP edits the ''Bulletin Newsletters'' and the review ''Reflets de la Physique''. Each year, the SFP awards several prizes to physicists in honor of specific works or actions towards the promotion of physics outside the community. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, was an anti-foreign, anti-imperialist, and anti-Christian uprising in North China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists, known as the "Boxers" in English due to many of its members having practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". It was defeated by the Eight-Nation Alliance of foreign powers. Following the First Sino-Japanese War, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign Spheres of influence#China, spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898, North China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, the movement spread across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and Orange Free State) over Britain's influence in Southern Africa. The Witwatersrand Gold Rush caused a large influx of "Uitlander, foreigners" (''Uitlanders'') to the South African Republic (SAR), mostly British from the Cape Colony. As they, for fear of a hostile takeover of the SAR, were permitted to vote only after 14 years of residence, they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed at the botched Bloemfontein Conference in June 1899. The conflict broke out in October after the British government decided to send 10,000 troops to South Africa. With a delay, this provoked a Boer and British ultimatum, and subsequent Boer Irregular military, irregulars and militia attacks on British colonial settlements in Natal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert's Problems
Hilbert's problems are 23 problems in mathematics published by German mathematician David Hilbert in 1900. They were all unsolved at the time, and several proved to be very influential for 20th-century mathematics. Hilbert presented ten of the problems (1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 13, 16, 19, 21, and 22) at the Paris conference of the International Congress of Mathematicians, speaking on August 8 at the Sorbonne. The complete list of 23 problems was published later, in English translation in 1902 by Mary Frances Winston Newson in the ''Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society''. Earlier publications (in the original German) appeared in ''Archiv der Mathematik und Physik''. and Of the cleanly formulated Hilbert problems, numbers 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, 18, 19, 21, and 20 have resolutions that are accepted by consensus of the mathematical community. Problems 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 15, and 22 have solutions that have partial acceptance, but there exists some controversy as to whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
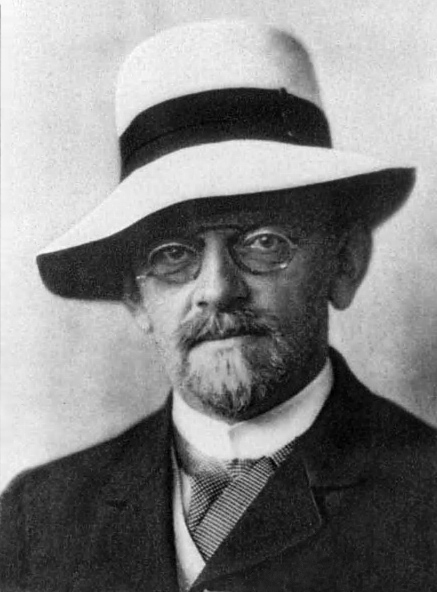
David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician and philosopher of mathematics and one of the most influential mathematicians of his time. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas including invariant theory, the calculus of variations, commutative algebra, algebraic number theory, the foundations of geometry, spectral theory of operators and its application to integral equations, mathematical physics, and the foundations of mathematics (particularly proof theory). He adopted and defended Georg Cantor's set theory and transfinite numbers. In 1900, he presented a collection of problems that set a course for mathematical research of the 20th century. Hilbert and his students contributed to establishing rigor and developed important tools used in modern mathematical physics. He was a cofounder of proof theory and mathematical logic. Life Early life and education Hilbert, the first of two children and only son of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Congress Of Mathematicians
The International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM) is the largest conference for the topic of mathematics. It meets once every four years, hosted by the International Mathematical Union (IMU). The Fields Medals, the IMU Abacus Medal (known before 2022 as the Nevanlinna Prize), the Carl Friedrich Gauss Prize, Gauss Prize, and the Chern Medal are awarded during the congress's opening ceremony. Each congress is memorialized by a printed set of Proceedings recording academic papers based on invited talks intended to be relevant to current topics of general interest. Being List of International Congresses of Mathematicians Plenary and Invited Speakers, invited to talk at the ICM has been called "the equivalent ... of an induction to a hall of fame". History German mathematicians Felix Klein and Georg Cantor are credited with putting forward the idea of an international congress of mathematicians in the 1890s.A. John Coleman"Mathematics without borders": a book review. ''CMS Notes'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |