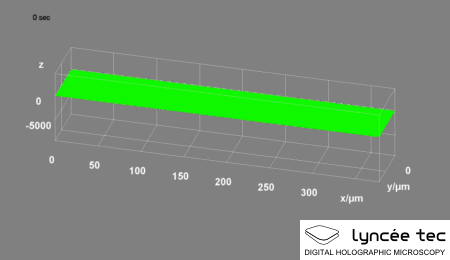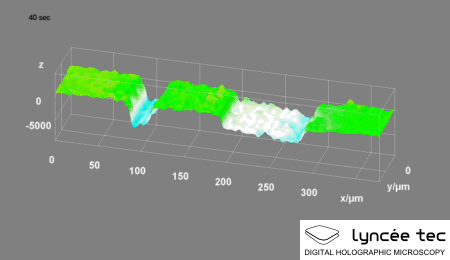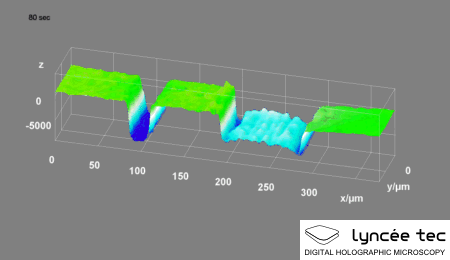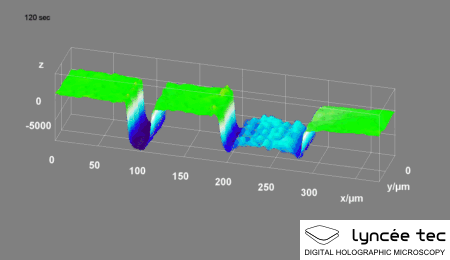
|
Interferometric Microscopy
Interferometric microscopy or imaging interferometric microscopy is the concept of microscopy which is related to holography, synthetic-aperture imaging, and off-axis-dark-field illumination techniques. Interferometric microscopy allows enhancement of resolution of optical microscopy due to interferometric (holographic) registration of several partial images (amplitude and phase) and the numerical combining. Combining of partial images In interferometric microscopy, the image of a micro-object is synthesized numerically as a coherent combination of partial images with registered amplitude and phase. For registration of partial images, a conventional holographic set-up is used with a reference wave, as is usual in optical holography. Capturing multiple exposures allows the numerical emulation of a large numerical aperture objective from images obtained with an objective lens with smaller-value numerical aperture. Similar techniques allows scanning and precise detection of small part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of Holography#Non-optical holography, wave. A hologram is a recording of an Wave interference, interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Physics B
The ''Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by IOP Publishing. It was established in 1968 from the division of the earlier title, '' Proceedings of the Physical Society''. In 2006, the '' Journal of Optics B: Quantum and Semiclassical Optics'' was merged with the ''Journal of Physics B''. The editor-in-chief is Marc Vrakking (Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy). Scope The journal covers research on atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Topics include atomic and molecular structure, spectra and collisions, ultracold matter, quantum optics and non linear optics, quantum information, laser physics, intense laser fields, ultrafast and x-ray An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical microscope, optical, electron microscope, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection (physics), reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the Laboratory specimen, specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscope, transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Limited
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of resolution performance. Other factors may affect an optical system's performance, such as lens imperfections or aberrations, but these are caused by errors in the manufacture or calculation of a lens, whereas the diffraction limit is the maximum resolution possible for a theoretically perfect, or ideal, optical system. The diffraction-limited angular resolution, in radians, of an instrument is proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and inversely proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Microscope
The Raman microscope is a laser-based microscopic device used to perform Raman spectroscopy.''Microscopical techniques in the use of the molecular optics laser examiner Raman microprobe'', by M. E. Andersen, R. Z. Muggli, Analytical Chemistry, 1981, 53 (12), pp 1772–177/ref> The term MOLE (molecular optics laser examiner) is used to refer to the Raman-based microprobe. The technique used is named after C. V. Raman, who discovered the scattering properties in liquids. Configuration The Raman microscope begins with a standard optical microscope, and adds an excitation laser, laser rejection filters, a spectrometer or monochromator, and an optical sensitive detector such as a charge-coupled device (CCD), or photomultiplier tube, (PMT). Traditionally Raman microscopy was used to measure the Raman spectrum of a point on a sample, more recently the technique has been extended to implement Raman spectroscopy for direct chemical imaging over the whole field of view on a 3D sample. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface (e.g., a flat interface). The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an Objective (optics), objective (and hence its light-gathering ability and Optical resolution, resolution), and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it. General optics In most areas of optics, and especially in microscopy, the numerical aperture of an optical system such as an objective lens is defined by \mathrm = n \sin \t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of Holography#Non-optical holography, wave. A hologram is a recording of an Wave interference, interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Holographic Microscopy
Digital holographic microscopy (DHM) is digital holography applied to microscopy. Digital holographic microscopy distinguishes itself from other microscopy methods by not recording the projected image of the object. Instead, the light wave front information originating from the object is digitally recorded as a hologram, from which a computer calculates the object image by using a numerical reconstruction algorithm. The image forming lens (optics), lens in traditional microscopy is thus replaced by a computer algorithm. Other closely related microscopy methods to digital holographic microscopy are interferometric microscopy, optical coherence tomography and diffraction phase microscopy. Common to all methods is the use of a reference wave front to obtain amplitude (intensity) ''and'' phase (waves), phase information. The information is recorded on a digital image sensor or by a photodetector from which an image of the object is created (reconstructed) by a computer. In traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic De Broglie Microscope
The scanning helium microscope (SHeM) is a form of microscopy that uses low-energy (5–100 meV) neutral helium atoms to image the surface of a sample without any damage to the sample caused by the imaging process. Since helium is inert and neutral, it can be used to study delicate and insulating surfaces. Images are formed by rastering a sample underneath an atom beam and monitoring the flux of atoms that are scattered into a detector at each point. The technique is different from a scanning helium ion microscope, which uses charged helium ions that can cause damage to a surface. Motivation Microscopes can be divided into two general classes: those that illuminate the sample with a beam, and those that use a physical scanning probe. Scanning probe microscopies raster a small probe across the surface of a sample and monitor the interaction of the probe with the sample. The resolution of scanning probe microscopies is set by the size of the interaction region between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Aperture
Aperture synthesis or synthesis imaging is a type of interferometry that mixes signals from a collection of telescopes to produce images having the same angular resolution as an instrument the size of the entire collection. At each separation and orientation, the lobe-pattern of the interferometer produces an output which is one component of the Fourier transform of the spatial distribution of the brightness of the observed object. The image (or "map") of the source is produced from these measurements. Astronomical interferometers are commonly used for high-resolution optical, infrared, submillimetre and radio astronomy observations. For example, the Event Horizon Telescope project derived the first image of a black hole using aperture synthesis. Technical issues Aperture synthesis is possible only if both the amplitude and the phase of the incoming signal are measured by each telescope. For radio frequencies, this is possible by electronics, while for optical frequencies, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energetic Neutral Atom
Energetic Neutral Atom (ENA) imaging is a technology used to create global images of otherwise invisible phenomena in the magnetospheres of planets and throughout the heliosphere. Charged particles— protons, electrons, and various nuclei— emitted from solar wind are the basis of the interstellar medium. These charged particles have the ability to be redirected by magnetic fields such as the magnetic field surrounding the Earth. Occasionally charged particles within the plasma of the solar wind will collide with neutral atoms. This collision results in the previously charged particle becoming a neutrally charged atom. Due to the loss of charge, the atom no longer experiences magnetic attraction while maintaining its gravitational attraction and velocity. These atoms are Energetic Neutral Atoms and the detection of these atoms can be reconstructed to build ENA images. Earth's magnetosphere preserves its atmosphere and protects life on Earth from cell-damaging radiation. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |