|
Integrated Marine And Coastal Regionalisation Of Australia
The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0. IMCRA actually defines two bioregionalisations: a benthic bioregionalisation, based on biogeography of fish together with geophysical data; and a pelagic bioregionalisation, base on oceanographic characteristics. The benthic bioregionalisation incorporates three separate regionalisations: #A regionalisation of the EEZ into provincial bioregions, based on the biogeography of bottom dwelling fishes. In IMCRA 4.0, 41 provincial bioregions, consisting of 24 ''provinces'' and 17 ''transitions''. #A regionalisation of the continental shelf into ''meso-scale regions'' based on biological and physical characters, and the distance from the coast. In IMCRA 4.0 there are 60 meso-scale re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMCRA Provincial Bioregions
The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeography, biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0. IMCRA actually defines two bioregionalisations: a benthic bioregionalisation, based on biogeography of fish together with geophysics, geophysical data; and a pelagic bioregionalisation, base on oceanography, oceanographic characteristics. The benthic bioregionalisation incorporates three separate regionalisations: #A regionalisation of the EEZ into provincial bioregions, based on the biogeography of bottom dwelling fishes. In IMCRA 4.0, 41 provincial bioregions, consisting of 24 ''provinces'' and 17 ''transitions''. #A regionalisation of the continental shelf into ''meso-scale regions'' based on biological and physical characters, and the distance from the coast. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark Bay
Shark Bay () is a World Heritage Site in the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. The area is located approximately north of Perth, on the westernmost point of the Australian continent. UNESCO's listing of Shark Bay as a World Heritage Site reads: The bay features Australia's most abundant marine ecosystems. It is a popular fishing spot. History The record of Indigenous Australians, Australian Aboriginal occupation of Shark Bay extends to years Before Present, BP. At that time most of the area was dry land, and rising sea levels flooded Shark Bay between BP and BP. A considerable number of Aboriginal midden sites have been found, especially on Peron Peninsula and Dirk Hartog Island, which provide evidence of some of the foods gathered from the waters and nearby land areas. An expedition led by Dirk Hartog happened upon the area in 1616, becoming the second group of Europeans known to have visited Australia, after the crew of ''Duyfken'' under Willem Janszoon had visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
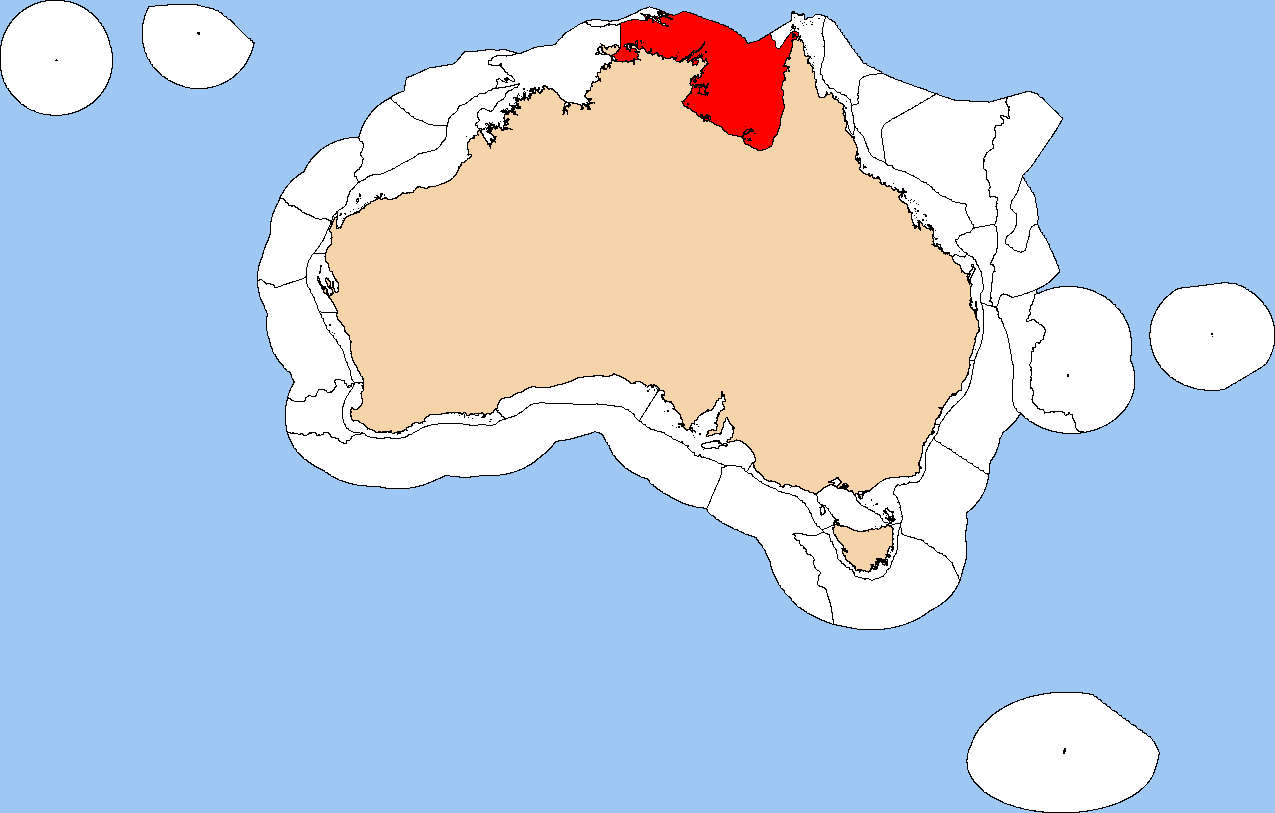
Van Diemens Gulf
Van Diemen Gulf is a gulf in the Northern Territory of Australia. It connects to the Timor Sea in the north via Dundas Strait. Most of its area is also gazetted as a locality with the name Van Diemen Gulf. History The gulf was named after the Dutch colonial governor, Anthony van Diemen (1593–1645). Phillip Parker King and his crew in the 76-tonne cutter surveyed the coastline in early 1818, encountering local Aboriginal people and proas sailed by Makassans, and passed by the Gulf on other voyages. Geography The gulf connects to the Timor Sea in the north via Dundas Strait, and is also connected to the Beagle Gulf in the west by the Clarence Strait. It is partially enclosed by Melville Island and the Cobourg Peninsula, and measures about by . Rivers draining into the Gulf include the South Alligator River, the East Alligator River, the Mary River, Wildman River and the Adelaide River. The Kakadu National Park adjoins its south-east coast. Administrative status On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Shelf Province
The Northern Shelf Province, also known as Arnhem Coast to Gulf of Carpentaria, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf. It includes the coastal waters of Arnhem Land and the Gulf of Carpentaria in Northern Australia. Geography The Northwest Shelf Transition includes the coastal waters and continental shelf of Northern Australia, extending from the Northern Territory's Tiwi Islands eastwards along the coast of Arnhem Land and the Gulf of Carpentaria to Cape York. The Northwest Shelf Transition lies to the west, and the Northeast Shelf Transition to the northeast. To the north the shallow continental shelf extends outside Australian waters to New Guinea."A Guide to the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia Version 4.0". Department of Environment and Heritage, Government of Australia. June 2006. ISBN 0 642 552274. Meso-scale bioregions The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) identifies ten distinct meso-scale b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torres Strait And Northern Great Barrier Reef
The Northeast Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an islan ... waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the northern Great Barrier Reef and the Torres Strait in northeastern-most Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system."A Guide to the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia Version 4.0". Department of Environment and Heritage, Government of Australia. June 2006. ISBN 0 642 552274. It corresponds to the Torres Strait and Northern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the World Wildlife Fund, WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system. Geography The Northeast Shelf Province extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes ( Kalaw Lagaw Ya#Phonology 2, [ˈzen̪ad̪ kes]), is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mainland. To the north is the Western Province (Papua New Guinea), Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is named after the Spanish navigator Luís Vaz de Torres, who sailed through the strait in 1606. History Pre-colonisation The islands of the Torres Strait have been inhabited by humans for at least 2,500 years and possibly much longer. The various Torres Strait Islanders, Torres Strait Islander communities have a unique culture and long-standing history with the islands and nearby coastlines. Their maritime-based trade and interactions with the Papuans to the north and the Australian Aborigines, Australian Aboriginal communities have maintained a steady cultural diffusion among the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Shelf Transition
The Northeast Shelf Transition is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the northern Great Barrier Reef and the Torres Strait in northeastern-most Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system."A Guide to the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia Version 4.0". Department of Environment and Heritage, Government of Australia. June 2006. ISBN 0 642 552274. It corresponds to the Torres Strait and Northern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system. Geography The Northeast Shelf Province extends along the eastern coast of Australia, from west of Cape York, the northern tip of Australia, southwards to Cooktown/Cairns. It extends from the shore to the edge of the continental shelf, and includes the Northern portion of the Great Barrier Reef and the waters around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central And Southern Great Barrier Reef
The Northeast Shelf Province is a biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the central and southern Great Barrier Reef in northeastern Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system."A Guide to the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia Version 4.0". Department of Environment and Heritage, Government of Australia. June 2006. ISBN 0 642 552274. It corresponds to the Central and Southern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system. Geography The Northeast Shelf Province extends along the eastern coast of Australia, from Cooktown/Cairns at its northern end to just north of Baffle Creek at its southern end. It extends from the shore to the edge of the continental shelf, and includes the central and southern portion of the Great Barrier Reef. On the north it adjoins the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Shelf Province
The Northeast Shelf Province is a biogeography, biogeographic region of Australia's coastal and continental shelf waters. It includes the tropical coastal waters of the central and southern Great Barrier Reef in northeastern Australia. It is a provincial level bioregion in the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA) system."A Guide to the Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia Version 4.0". Department of Environment and Heritage, Government of Australia. June 2006. ISBN 0 642 552274. It corresponds to the Central and Southern Great Barrier Reef marine ecoregion in the World Wildlife Fund, WWF's Marine Ecoregions of the World system. Geography The Northeast Shelf Province extends along the eastern coast of Australia, from Cooktown, Queensland, Cooktown/Cairns, Queensland, Cairns at its northern end to just north of Baffle Creek, Queensland, Baffle Creek at its southern end. It extends from the shore to the edge of the continental shelf, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island is a subantarctic island in the south-western Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. It has been governed as a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1880. It became a Protected areas of Tasmania, Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978 and was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997. Macquarie Island is an exposed portion of the Macquarie Fault Zone, Macquarie Ridge and is located where the Australian Plate meets the Pacific Plate. The island is home to the entire royal penguin population during their annual nesting season. Ecologically, the island is part of the Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion. History 19th century Frederick Hasselborough, an Australian, discovered the uninhabited island on 11 July 1810, while looking for new seal hunting, sealing grounds. He claimed Macquarie Island for United Kingdom, Britain and annexation, annexed it to the colony of New South Wales in 1810. The island was named for Colonel Lachla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Australian Bight
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight (geography), bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern Coast, coastline of mainland Australia. There are two definitions for its extent—one by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and another by the Australian Hydrographic Service (AHS). The bight is generally considered part of the Indian Ocean, although the AHS classifies it as part of the Southern Ocean. Its coastline is characterized by cliff faces and rocky capes, making it an ideal location for whale-watching. This oceanic feature was first encountered by European explorers in 1627, and was accurately charted by English navigator Matthew Flinders in 1802. The Great Australian Bight came into existence about 50 million years ago when the supercontinent Gondwana broke apart, separating Antarctica from Australia. The Bight's waters are highly Biodiversity, biodiverse, especially in zooplankton, due to specific ocean currents. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Australian Bight Shelf Transition
The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern coastline of mainland Australia. There are two definitions for its extent—one by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) and another by the Australian Hydrographic Service (AHS). The bight is generally considered part of the Indian Ocean, although the AHS classifies it as part of the Southern Ocean. Its coastline is characterized by cliff faces and rocky capes, making it an ideal location for whale-watching. This oceanic feature was first encountered by European explorers in 1627, and was accurately charted by English navigator Matthew Flinders in 1802. The Great Australian Bight came into existence about 50 million years ago when the supercontinent Gondwana broke apart, separating Antarctica from Australia. The Bight's waters are highly biodiverse, especially in zooplankton, due to specific ocean currents. However, more research is needed to fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |