|
Instruction-level Parallelism
Instruction-level parallelism (ILP) is the Parallel computing, parallel or simultaneous execution of a sequence of Instruction set, instructions in a computer program. More specifically, ILP refers to the average number of instructions run per step of this parallel execution. Discussion ILP must not be confused with Concurrency (computer science), concurrency. In ILP, there is a single specific Thread (computing), thread of execution of a Process (computing), process. On the other hand, concurrency involves the assignment of multiple threads to a Central processing unit, CPU's core in a strict alternation, or in true parallelism if there are enough CPU cores, ideally one core for each runnable thread. There are two approaches to instruction-level parallelism: Computer hardware, hardware and software. Hardware-level ILP works upon dynamic parallelism, whereas software-level ILP works on static parallelism. Dynamic parallelism means that the processor decides at run time whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing
Explicitly parallel instruction computing (EPIC) is a term coined in 1997 by the Itanium, HP–Intel alliance to describe a computing paradigm that researchers had been investigating since the early 1980s. This paradigm is also called ''Independence'' architectures. It was the basis for Intel and Hewlett-Packard, HP development of the Intel Itanium architecture, and Hewlett-Packard, HP later asserted that "EPIC" was merely an old term for the Itanium architecture. EPIC permits microprocessors to execute software instructions in parallel by using the compiler, rather than complex on-die (integrated circuit), die circuitry, to control parallel instruction execution. This was intended to allow simple performance scaling without resorting to higher clock rate, clock frequencies. Roots in VLIW By 1989, researchers at HP recognized that reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architectures were reaching a limit at one instruction per cycle. They began an investigation into a new archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superscalar
A superscalar processor (or multiple-issue processor) is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a superscalar processor can execute or start executing more than one instruction during a clock cycle by simultaneously dispatching multiple instructions to different execution units on the processor. It therefore allows more throughput (the number of instructions that can be executed in a unit of time which can even be less than 1) than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate. Each execution unit is not a separate processor (or a core if the processor is a multi-core processor), but an execution resource within a single CPU such as an arithmetic logic unit. While a superscalar CPU is typically also pipelined, superscalar and pipelining execution are considered different performance enhancement techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Prediction
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g., an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow in the instruction pipeline. Branch predictors play a critical role in achieving high performance in many modern pipelined microprocessor architectures. Two-way branching is usually implemented with a conditional jump instruction. A conditional jump can either be "taken" and jump to a different place in program memory, or it can be "not taken" and continue execution immediately after the conditional jump. It is not known for certain whether a conditional jump will be taken or not taken until the condition has been calculated and the conditional jump has passed the execution stage in the instruction pipeline (see fig. 1). Without branch prediction, the processor would have to wait until the conditional jump instruction has passed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Latency Prediction
Cache, caching, or caché may refer to: Science and technology * Cache (computing), a technique used in computer storage for easier data access * Cache (biology) or hoarding, a food storing behavior of animals * Cache (archaeology), artifacts purposely buried in the ground * InterSystems Caché, a database management system from InterSystems Places United States * Cache, Idaho, an unincorporated community * Cache, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Cache, Oklahoma, a city in Comanche County * Cache, Utah, Cache County, Utah * Cache County, Utah * Cache Peak (Idaho), a mountain in Castle Rocks State Park Other places * Cache, Aosta, a frazione in Italy * Cache Creek (other), several places Arts, entertainment and media * ''Caché'' (album), a 1993 album by Kirk Whalum * ''Caché'' (film), a 2005 film directed by Michael Haneke Commerce * Cache (retailer), a defunct retail clothing store * Caché, Inc., a Florida women's apparel company owned by Andr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Dependence Prediction
Memory dependence prediction is a technique, employed by high-performance out-of-order execution microprocessors that execute memory access operations (loads and stores) out of program order, to predict true dependencies between loads and stores at instruction execution Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in ... time. With the predicted dependence information, the processor can then decide to speculatively execute certain loads and stores out of order, while preventing other loads and stores from executing out-of-order (keeping them in-order). Later in the pipeline, memory disambiguation techniques are used to determine if the loads and stores were correctly executed and, if not, to recover. By using the memory dependence predictor to keep most dependent loads and stores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Prediction
Value or values may refer to: Ethics and social sciences * Value (ethics), concept which may be construed as treating actions themselves as abstract objects, associating value to them ** Axiology, interdisciplinary study of values, including ethical values * Social imaginary, set of morals, institutions, laws, and symbols common to a particular social group * Religious values, beliefs and practices which a religious adherent partakes in Economics * Value (economics), a measure of the benefit that may be gained from goods or service ** Theory of value (economics), the study of the concept of economic value ** Value (marketing), the difference between a customer's evaluation of benefits and costs ** Value investing, an investment paradigm * Values (heritage), the measure by which the cultural significance of heritage items is assessed * Present value, value of an expected income stream as of the date of valuation * Present value of benefits, discounted sum of a stream of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculative Execution
Speculative execution is an optimization (computer science), optimization technique where a computer system performs some task that may not be needed. Work is done before it is known whether it is actually needed, so as to prevent a delay that would have to be incurred by doing the work after it is known that it is needed. If it turns out the work was not needed after all, most changes made by the work are reverted and the results are ignored. The objective is to provide more Concurrency (computer science), concurrency if extra Resource (computer science), resources are available. This approach is employed in a variety of areas, including branch predictor, branch prediction in instruction pipeline, pipelined CPU, processors, value prediction for exploiting value locality, prefetching Instruction prefetch, memory and File system, files, and optimistic concurrency control in Relational database management system, database systems. Speculative multithreading is a special case of specu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register Renaming
In computer architecture, register renaming is a technique that abstracts logical processor register, registers from physical registers. Every logical register has a set of physical registers associated with it. When a machine language instruction refers to a particular logical register, the processor transposes this name to one specific physical register on the fly. The physical registers are opaque and cannot be referenced directly but only via the canonical names. This technique is used to eliminate false Data dependency, data dependencies arising from the reuse of registers by successive Instruction (computer science), instructions that do not have any real data dependencies between them. The elimination of these false data dependencies reveals more instruction-level parallelism in an instruction stream, which can be exploited by various and complementary techniques such as superscalar and out-of-order execution for better Computer performance, performance. Problem approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model that generally defines how software controls the CPU in a computer or a family of computers. A device or program that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation'' of that ISA. In general, an ISA defines the supported Machine code, instructions, data types, Register (computer), registers, the hardware support for managing Computer memory, main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as Computer performance, performa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compile Time
In computer science, compile time (or compile-time) describes the time window during which a language's statements are converted into binary instructions for the processor to execute. The term is used as an adjective to describe concepts related to the context of program compilation, as opposed to concepts related to the context of program execution ( run time). For example, ''compile-time requirements'' are programming language requirements that must be met by source code before compilation and ''compile-time properties'' are properties of the program that can be reasoned about during compilation. The actual length of time it takes to compile a program is usually referred to as ''compilation time''. Overview Most compilers have at least the following compiler phases (which therefore occur at compile-time): syntax analysis, semantic analysis, and code generation. During optimization phases, constant expressions in the source code can also be evaluated at compile-time usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
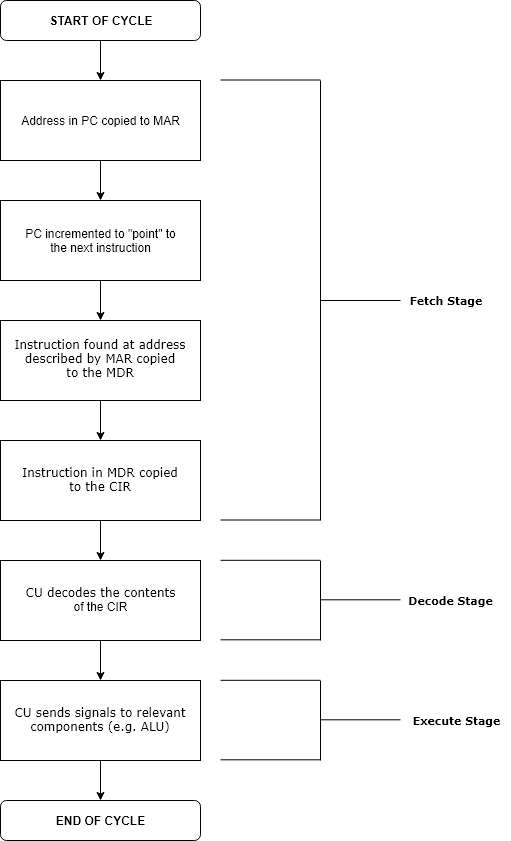
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |