|
Institute Of Cytology And Genetics
Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences () is a research institute based in Novosibirsk, Russia. It was founded in 1957. Experiments * Fox domestication experiment Magazines * Vavilov's Journal of Genetics and Breeders * Ateroskleroz * The Siberian Scientific Medical Journal Monuments and memorials * Monument to the laboratory mouse The ''Monument to the laboratory mouse'' is a sculpture in Novosibirsk' Akademgorodok, Siberia, Russia. It is located in a park in front of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and was completed on July 1, 2 ... * Memorial to Dmitriy Belyaev and Domesticated Fox Gallery Georgian white Russian domesticated Red Fox.jpg, A Russian domesticated red fox with Georgian white fur color. References External links Adopt a Pet Fox, for Science's Sake. Live Science.* * C Biological research institutes Genetics or genomics research institutions Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Branch Of The Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (SBRAS) was established by the Decree of the Government of the USSR which was based on the proposal of Mikhail Lavrentyev, Sergei Sobolev and Sergey Khristianovich in 1957 as a regional division of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, replacing a previous small branch of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR. Novosibirsk State University was founded to serve as a staff base for the Siberian Branch. Lavrentyev was also the founding chairman of the branch. History During the war, hundreds of scientists were evacuated to Siberia, and in 1943 the West Siberian Branch (WSF) of the Soviet Union Academy of Sciences was created. Initially, the WSF allowed scientists to work in various cities. But since 1948, most scientists have been working in Novosibirsk. Formed in May 1957 on the initiative of academicians Mikhail Lavrentyev, Sergei Sobolev, and Sergey Khristianovich. When the department was organized, it included scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
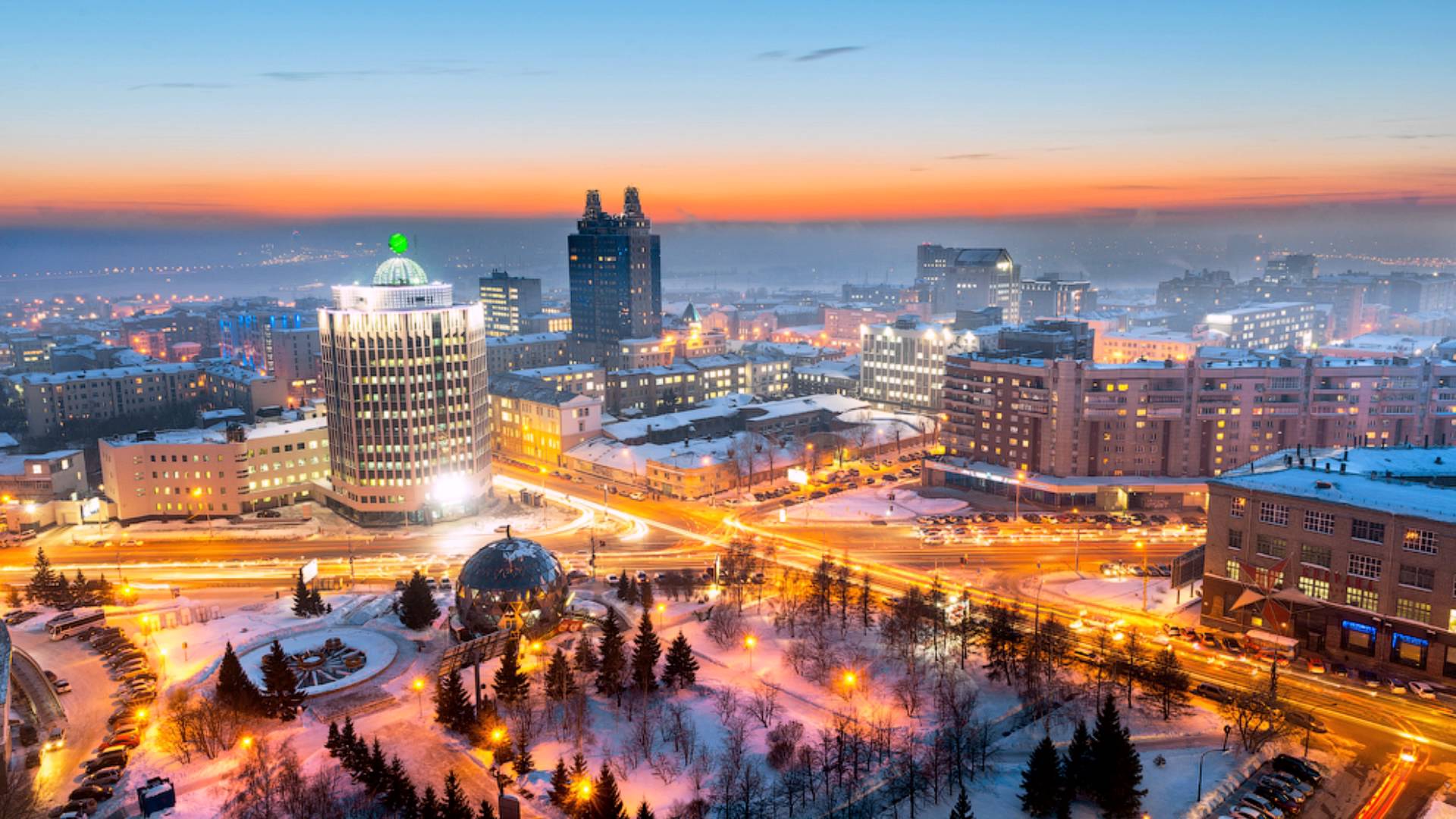
Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siberia and the list of cities and towns in Russia by population, third-most populous city in Russia after Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Additionally, it is the largest city in the Asian part of Russia and the most populous city in the country that does not have the status of a Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject. Novosibirsk is located in southwestern Siberia, on the banks of the Ob River. Novosibirsk was founded in 1893 on the Ob River crossing point of the future Trans-Siberian Railway, where the Novosibirsk Rail Bridge was constructed. Originally named Novonikolayevsk ("New Nicholas") in honor of Nicholas II of Russia, Emperor Nicholas II, the city rapidly grew into a major transport, commercial, and industrial hub. Novosibirsk was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academician Lavrentyev Avenue, Novosibirsk
Academician Lavrentyev Avenue () or Academician Lavrentyev Prospekt is a street in Akademgorodok of Novosibirsk, Russia. The avenue is named after Mikhail Lavrentyev, a Soviet mathematician and hydrodynamicist. Research institutes * Institute of Cytology and Genetics * Nikolaev Institute of Inorganic Chemistry * Rzhanov Institute of Semiconductor Physics * Institute of Soil Science and Agrochemistry * Lavrentyev Institute of Hydrodynamics * Institute of Chemical Biology and Fundamental Medicine * Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics * Institute of Laser Physics * Boreskov Institute of Catalysis * Institute of Computational Technologies * Ershov Institute of Informatics Systems * Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics * Kutateladze Institute of Thermophysics * Institute of Economics and Industrial Engineering * Vorozhtsov Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry * Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography Gallery Дерево А.А. Леоно� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
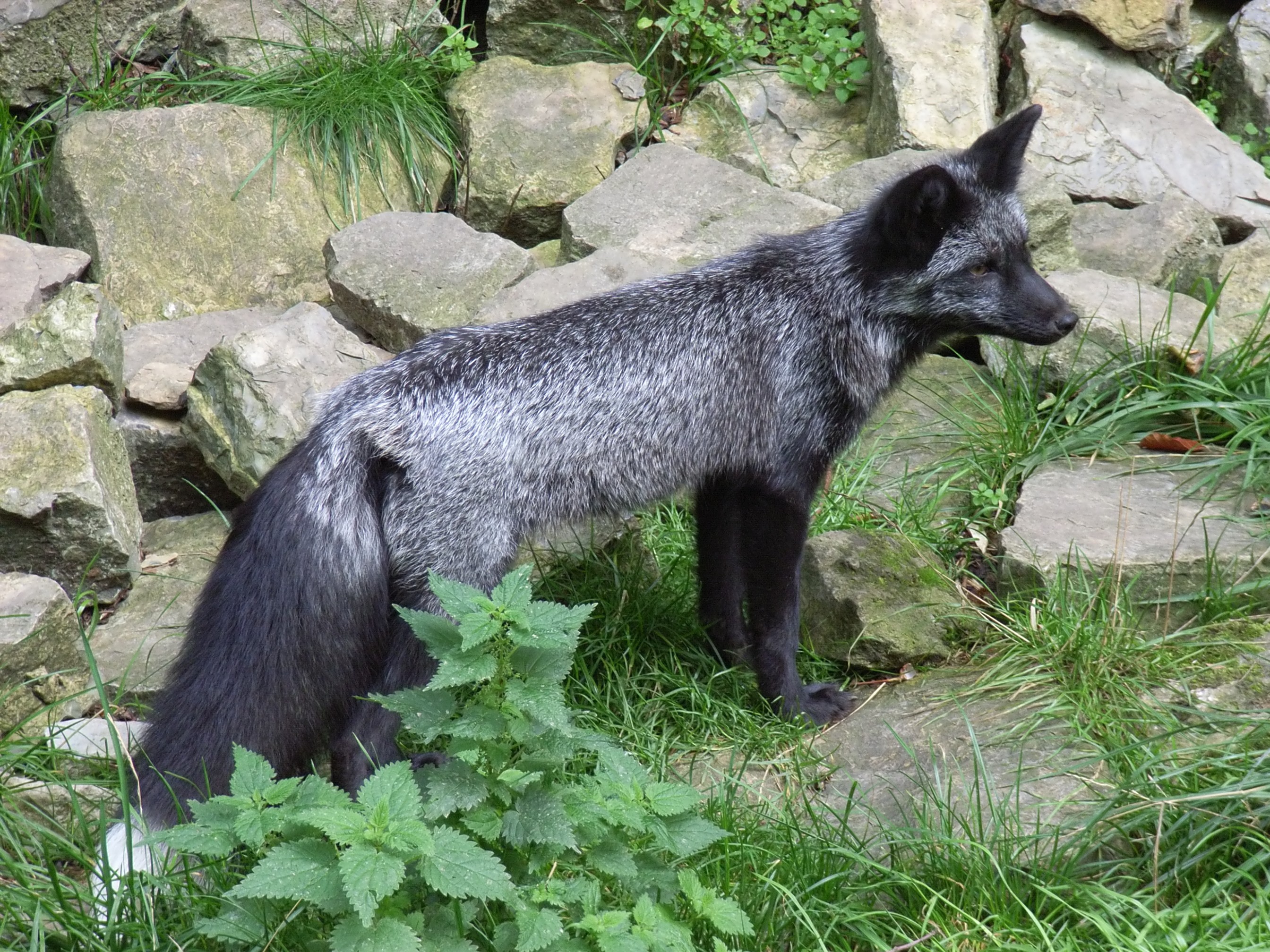
Domesticated Red Fox
The domesticated silver fox (''Vulpes vulpes'' forma ''amicus'') is a form of the silver fox that has been to some extent domesticated under laboratory conditions. The silver fox is a melanistic form of the wild red fox. Domesticated silver foxes are the result of an experiment designed to demonstrate the power of selective breeding to transform species, as described by Charles Darwin in ''On the Origin of Species''. The experiment at the Institute of Cytology and Genetics in Novosibirsk, Russia, explored whether selection for behaviour rather than morphology may have been the process that had produced dogs from wolves, by recording the changes in foxes when in each generation only the most tame foxes were allowed to breed. Many of the descendant foxes became both tamer and more dog-like in morphology, including displaying mottled- or spotted-coloured fur. In 2019, an international research team questioned the conclusion that this experiment had provided strong support for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Vavilov
Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov ( rus, Никола́й Ива́нович Вави́лов, p=nʲɪkɐˈlaj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ vɐˈvʲiləf, a=Ru-Nikolay_Ivanovich_Vavilov.ogg; – 26 January 1943) was a Russian and Soviet Union, Soviet agronomist, botanist and geneticist who identified the Vavilov Center, centers of origin of Horticulture, cultivated plants. His research focused on plant breeding, improvement of wheat, maize and other Cereal, cereal crops. Vavilov became the youngest member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. He was a member of the USSR Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, Central Executive Committee, a recipient of the Lenin Prize, and president of All-Union Geographical Society. He was a fellow of the Royal Society and of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Vavilov's work was criticized by Trofim Lysenko, whose anti-Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian concepts of plant biology had won favor with Joseph Stalin. As a result, Vavilov was arrested and subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument To The Laboratory Mouse
The ''Monument to the laboratory mouse'' is a sculpture in Novosibirsk' Akademgorodok, Siberia, Russia. It is located in a park in front of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and was completed on July 1, 2013, coinciding with the 120th anniversary of the founding of the city. The monument commemorates the sacrifice of the mice in genetic research used to understand biological and physiological mechanisms for developing new drugs and curing of diseases. Description The monument, which sits on a granite pedestal, is of a laboratory mouse wearing pince-nez on the tip of its nose. The mouse holds knitting needles in its paws and is shown knitting a double helix of DNA. The bronze figure is itself only high, but the total height of the monument including the pedestal is . The DNA spiral emerging from the knitting needles winds to the left, thus showing that it is the still poorly understood Z-DNA - this symbolic of scientific research that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Belyayev (zoologist)
Dmitry Konstantinovich Belyayev (Russian: Дми́трий Константи́нович Беля́ев; 17 July 1917 – 14 November 1985) was a Soviet geneticist and academician who served as director of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics (IC&G) of the USSR Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk, from 1959 to 1985. His decades-long effort to breed domesticated silver foxes was described by ''The New York Times'' as “arguably the most extraordinary breeding experiment ever conducted.” A 2010 article in Scientific American stated that Belyayev “may be the man most responsible for our understanding of the process by which wolves were domesticated into our canine companions.” Beginning in the 1950s, in order to uncover the genetic basis of the distinctive behavioral and physiological attributes of domesticated animals, Belyayev and his team spent decades breeding the silver fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') and selecting for reproduction only those individuals in each generation that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In Novosibirsk
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, economic, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Research Institutes
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Modern biology is groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics Or Genomics Research Institutions
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In The Soviet Union
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |