|
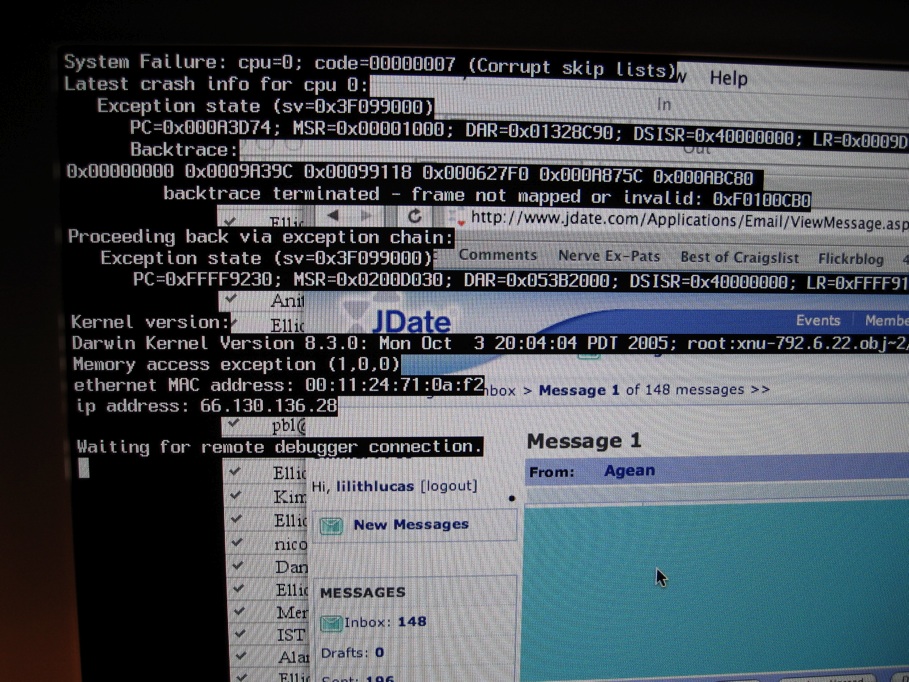
Input Kludge
In computer programming, an input kludge is a type of failure in software (an anti-pattern) where simple user input is not handled. For example, if a computer program accepts free text input from the user, an ''ad hoc'' algorithm will mishandle many combinations of legal and illegal input strings. Input kludges are usually difficult for a programmer to detect in a unit test, but very easy for the end user to find. The evidence exists that the end user can easily crash software that fails to correctly handle user input. Indeed, the buffer overflow security hole is an example of the problems caused. To remedy input kludges, one may use input validation algorithms to handle user input. A monkey test can be used to detect an input kludge problem. A common first test to discover this problem is to roll one's hand across the computer keyboard or to 'mash' the keyboard to produce a large junk input, but such an action often lacks reproducibility. Greater systematicity and reproducibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th century. Early programs were written in the machine language specific to the hardware. The introduction of high-level programming languages in 1958 allowed for more human-readable instructions, making software development easier and more portable across different computer architectures. Software in a programming language is run through a compiler or Interpreter (computing), interpreter to execution (computing), execute on the architecture's hardware. Over time, software has become complex, owing to developments in Computer network, networking, operating systems, and databases. Software can generally be categorized into two main types: # operating systems, which manage hardware resources and provide services for applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-pattern
An anti-pattern in software engineering, project management, and business processes is a common response to a recurring problem that is usually ineffective and risks being highly counterproductive. The term, coined in 1995 by computer programmer Andrew Koenig (programmer), Andrew Koenig, was inspired by the book ''Design Patterns'' (which highlights a number of design patterns in software development that its authors considered to be highly reliable and effective) and first published in his article in the ''Journal of Object-Oriented Programming''. A further paper in 1996 presented by Michael Ackroyd at the Object World West Conference also documented anti-patterns. It was, however, the 1998 book ''AntiPatterns'' that both popularized the idea and extended its scope beyond the field of software design to include software architecture and project management. Other authors have extended it further since to encompass environmental, organizational, and cultural anti-patterns. Definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangible components. A ''computer program'' in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to Execution (computing), execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be Translator (computing), translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an Assembler (computing), assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter (computing), interpreter written for the language. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system Loader (computing), loads it into Random-access memory, memory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Test
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the integration or system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Mercury project, where individual units developed by different programmes underwent "unit tests" before being integrated together. In 1969, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crash (computing)
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal or unauthorized opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Validation
In computing, data validation or input validation is the process of ensuring data has undergone data cleansing to confirm it has data quality, that is, that it is both correct and useful. It uses routines, often called "validation rules", "validation constraints", or "check routines", that check for correctness, meaningfulness, and security of data that are input to the system. The rules may be implemented through the automated facilities of a data dictionary, or by the inclusion of explicit application program validation logic of the computer and its application. This is distinct from formal verification, which attempts to prove or disprove the correctness of algorithms for implementing a specification or property. Overview Data validation is intended to provide certain well-defined guarantees for fitness and data consistency, consistency of data in an application or automated system. Data validation rules can be defined and designed using various methodologies, and be deployed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkey Test
In software testing, monkey testing is a technique where the user tests the application or system by providing random inputs and checking the behavior, or seeing whether the application or system will crash. Monkey testing is usually implemented as random, automated unit tests. While the source of the name "monkey" is uncertain, it is believed by some that the name has to do with the infinite monkey theorem, which states that a monkey hitting keys at random on a typewriter keyboard for an infinite amount of time will almost surely type a given text, such as the complete works of William Shakespeare. Some others believe that the name comes from the classic Mac OS application "The Monkey" developed by Steve Capps prior to 1983. It used journaling hooks to feed random events into Mac programs, and was used to test for bugs in MacPaint. Monkey Testing is also included in Android Studio as part of the standard testing tools for stress testing. Types of monkey testing Monkey testing ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Keyboard
A computer keyboard is a built-in or peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or Push-button, keys to act as Mechanical keyboard, mechanical levers or Electronic switching system, electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards have been the main input device, input method for computers since the 1970s, supplemented by the computer mouse since the 1980s, and the touchscreen since the 2000s. Keyboard keys (buttons) typically have a set of characters Engraving, engraved or Printing, printed on them, and each press of a key typically corresponds to a single written symbol. However, producing some symbols may require pressing and holding several keys simultaneously or in sequence. While most keys produce character (computing), characters (Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers or symbols), other keys (such as the escape key) can prompt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproducibility
Reproducibility, closely related to replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a statistical analysis of a data set should be achieved again with a high degree of reliability when the study is replicated. There are different kinds of replication but typically replication studies involve different researchers using the same methodology. Only after one or several such successful replications should a result be recognized as scientific knowledge. History The first to stress the importance of reproducibility in science was the Anglo-Irish chemist Robert Boyle, in England in the 17th century. Boyle's air pump was designed to generate and study vacuum, which at the time was a very controversial concept. Indeed, distinguished philosophers such as René Descartes and Thomas Hobbes denied the very possibility of vacuum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzz Testing
In programming and software development, fuzzing or fuzz testing is an automated software testing technique that involves providing invalid, unexpected, or random data as inputs to a computer program. The program is then monitored for exceptions such as crashes, failing built-in code assertions, or potential memory leaks. Typically, fuzzers are used to test programs that take structured inputs. This structure is specified, such as in a file format or protocol and distinguishes valid from invalid input. An effective fuzzer generates semi-valid inputs that are "valid enough" in that they are not directly rejected by the parser, but do create unexpected behaviors deeper in the program and are "invalid enough" to expose corner cases that have not been properly dealt with. For the purpose of security, input that crosses a trust boundary is often the most useful. For example, it is more important to fuzz code that handles a file uploaded by any user than it is to fuzz the code th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |