|
Inositol Pentakisphosphate
Inositol pentakisphosphate (abbreviated IP5) is a molecule derived from inositol tetrakisphosphate by adding a phosphate group with the help of Inositol-polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK). It is believed to be one of the many second messengers in the inositol phosphate Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexaphosphorylated inositols. Each form of inositol phosphate is distinguished by the number and position of the phosphate group on the inositol ring. * inositol monophosphate (IP) * inositol bisphospha ... family. It "is implicated in a wide array of biological and pathophysiological responses, including tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis, therefore specific inhibitors of the kinase may prove useful in cancer therapy." IP5 also plays a role in defense signaling in plants. It potentiates the interaction of the plant hormone JA-Ile by its receptor. References Organophosphates Inositol Phosphate esters {{Biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Tetrakisphosphate
In biochemistry, medicine, and related sciences, inositol generally refers to ''myo''-inositol (formerly ''meso''-inositol), the most important stereoisomer of the chemical compound cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol. Its formula is ; the molecule has a ring of six carbon atoms, each with a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group (–OH). In ''myo''-inositol, two of the hydroxyls, neither adjacent nor opposite, lie above the respective hydrogens relative to the mean plane of the ring. The compound is a carbohydrate, specifically a sugar alcohol (as distinct from aldoses like glucose) with half the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar). It is one of the most ancient components of living beings with multiple functions in eukaryotes, including structural lipids and secondary messengers. A human kidney makes about two grams per day from glucose, but other tissues synthesize it too. The highest concentration is in the brain, where it plays an important role in making other neurotransmitters and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Group
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus. In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid, phosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one proton gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion while removal of two protons gives the hydrogen phosphate ion . These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate or orthophosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol-polyphosphate Multikinase
Inositol-polyphosphate multikinase (, ''IpK2'', ''IP3/IP4 6-/3-kinase'', ''IP3/IP4 dual-specificity 6-/3-kinase'', ''IpmK'', ''ArgRIII'', ''AtIpk2alpha'', ''AtIpk2beta'', ''inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-/5-kinase'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''ATP:1D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 6-phosphotransferase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ... : 2 ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate \rightleftharpoons 2 ADP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate (overall reaction) :(1a) ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate \rightleftharpoons ADP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate :(1b) ATP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate \rightleftharpoons ADP + 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
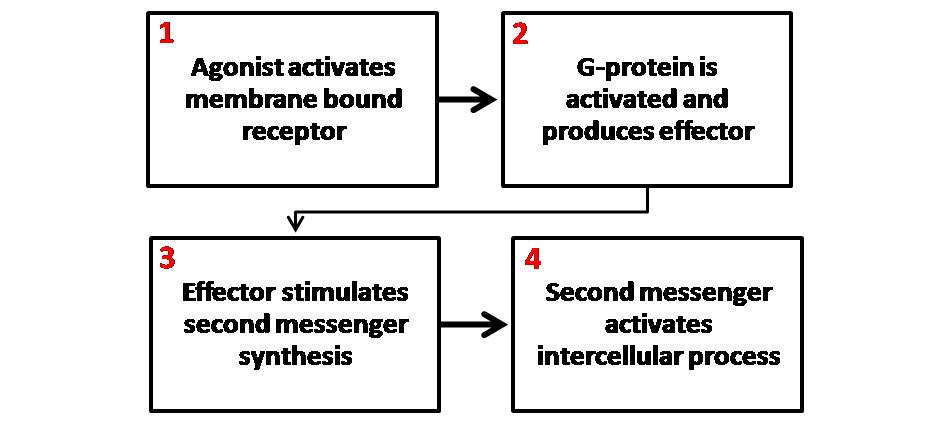
Second Messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first mess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Phosphate
Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexaphosphorylated inositols. Each form of inositol phosphate is distinguished by the number and position of the phosphate group on the inositol ring. * inositol monophosphate (IP) * inositol bisphosphate (IP2) * inositol trisphosphate (IP3) * inositol tetrakisphosphate (IP4) * inositol pentakisphosphate (IP5) * inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) also known as phytic acid, or phytate (as a salt). A series of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation reactions are carried out by at least 19 phosphoinositide kinases and 28 phosphoinositide phosphatase enzymes allowing for the inter-conversion between the inositol phosphate compounds based on cellular demand. Inositol phosphates play a crucial role in various signal transduction pathways responsible for cell growth and differentiation, apoptosis, DNA repair, RNA export, regeneration of ATP and more. Functions Inositol trisphosphate The inositol-phospholipid signaling pathway is responsible for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogene (journal)
''Oncogene'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal published under the Springer Nature addressing cancer cell genetics and the structure and function of oncogenes. The journal has editorial office in London, London, England. The journal was established in 1987. An open access online-only sister journal, Oncogenesis (journal), ''Oncogenesis'', was established in 2012 by Douglas R. Green, who was then ''Oncogene''s editor-in-chief. ''Oncogene'' received a 2023 impact factor of 6.9 and received ''Journal Citation Reports'' rankings of 18th out of 191 in the category ''Genetics & Heredity'', 29th out of 205 in the category ''Cell Biology'', 32nd out of 313 in the category ''Biochemistry & Molecular Biology'', and 43rd out of 322 journals in the category ''Oncology''. The current editors-in-chief are George Miller and Justin Stebbing. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: EBSCO Discovery Service, Summon by ProQuest, BIOSIS, Current Contents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasmonate
Jasmonate (JA) and its derivatives are lipid-based plant hormones that regulate a wide range of processes in plants, ranging from growth and photosynthesis to reproductive development. In particular, JAs are critical for plant defense against herbivory and plant responses to poor environmental conditions and other kinds of abiotic and biotic challenges. Some JAs can also be released as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to permit communication between plants in anticipation of mutual dangers. History The isolation of methyl jasmonate (MeJA) from jasmine oil derived from '' Jasminum grandiflorum'' led to the discovery of the molecular structure of jasmonates and their name in 1962 while jasmonic acid itself was isolated from '' Lasiodiplodia theobromae'' by Alderidge et al in 1971. Biosynthesis Biosynthesis is reviewed by Acosta and Farmer 2010, Wasternack and Hause 2013, and Wasternack and Song 2017. Jasmonates (JA) are oxylipins, i.e. derivatives of oxygenated fatty acid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Plant Journal
''The Plant Journal'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of plant science published by Wiley-Blackwell for the Society for Experimental Biology. It was established in 1991 and is currently edited by Katherine J. Denby. The journal is published twice per month. Indexing and abstracting ''The Plant Journal'' is abstracted and indexed in several bibliographic databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 7.091, ranking it 17th out of 238 journals in the category "Plant Sciences". References Further reading * External links *''The Plant Journal''at the Society of Experimental Biology {{DEFAULTSORT:Plant Journal, The Academic journals established in 1991 English-language jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphates
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Organophosphates are best known for their use as pesticides. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physically rather than by chemical bond. Due to this, OPEs leak int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol
In biochemistry, medicine, and related sciences, inositol generally refers to ''myo''-inositol (formerly ''meso''-inositol), the most important stereoisomer of the chemical compound cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol. Its elemental formula, formula is ; the molecule has a ring of six carbon atoms, each with a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group (–OH). In ''myo''-inositol, two of the hydroxyls, neither adjacent nor opposite, lie above the respective hydrogens relative to the mean plane of the ring. The compound is a carbohydrate, specifically a sugar alcohol (as distinct from aldoses like glucose) with half the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar). It is one of the most ancient components of living beings with multiple functions in eukaryotes, including structural lipids and secondary messengers. A human kidney makes about two grams per day from glucose, but other tissues synthesize it too. The highest concentration is in the brain, where it plays an important role in making other neurot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |