|
Initial Operating Capability
Initial operating capability or initial operational capability (IOC) is the state achieved when a capability is available in its minimum usefully deployable form. The term is often used in government or military procurement. The United States Department of Defense chooses to use the term ''initial operational capability'' when referring to IOC. For a U.S. Department of Defense military acquisition, IOC includes operating the training and maintaining parts of the overall system per DOTMLPF, and is defined as:"In general, attained when some units and/or organizations in the force structure scheduled to receive a system have received it and have the ability to employ and maintain it. The specifics for any particular system IOC are defined in that system’s Capability Development Document (CDD) and Capability Production Document (CPD)."The date at which IOC is achieved often defines the in-service date (ISD) for an associated system A system is a group of interacting or interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capability Management
Capability management is a high-level management function, with particular application in the context of defense. Capability management aims to balance economy in meeting current operational requirements, with the sustainable use of current capabilities, and the development of future capabilities, to meet the sometimes competing strategic and current operational objectives of an enterprise. Accordingly, effective capability management: * Assists organizations to better understand, and effectively integrate the total enterprise ability or capacity to achieve strategic and current operational objectives; and * Develops and provides solutions that focus on the management of the interlinking functions and activities in the enterprise's strategic and current operational contexts. In military contexts, capabilities may also be analysed in terms of Force Structure and the Preparedness of elements or groupings within that Force Structure. Preparedness in turn may be analysed in terms of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Procurement
Government procurement or public procurement is the purchase of goods, works (construction) or services by the state, such as by a government agency or a state-owned enterprise. In 2019, public procurement accounted for approximately 12% of GDP in OECD countries. In 2021 the World Bank Group estimated that public procurement made up about 15% of global GDP. Therefore, government procurement accounts for a substantial part of the global economy. Public procurement is based on the idea that governments should direct their society while giving the private sector the freedom to decide the best practices to produce the desired goods and services. One benefit of public procurement is its ability to cultivate innovation and economic growth. The public sector picks the most capable nonprofit or for-profit organizations available to issue the desired good or service to the taxpayers. This produces competition within the private sector to gain these contracts that then reward the organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procurement
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as '' government procurement'' or public procurement. Procurement as an organizational process is intended to ensure that the buyer receives goods, services, or works at the best possible price when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Corporations and public bodies often define processes intended to promote fair and open competition for their business while minimizing risks such as exposure to fraud and collusion. Almost all purchasing decisions include factors such as delivery and handling, marginal benefit, and fluctuations in the prices of goods. Org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
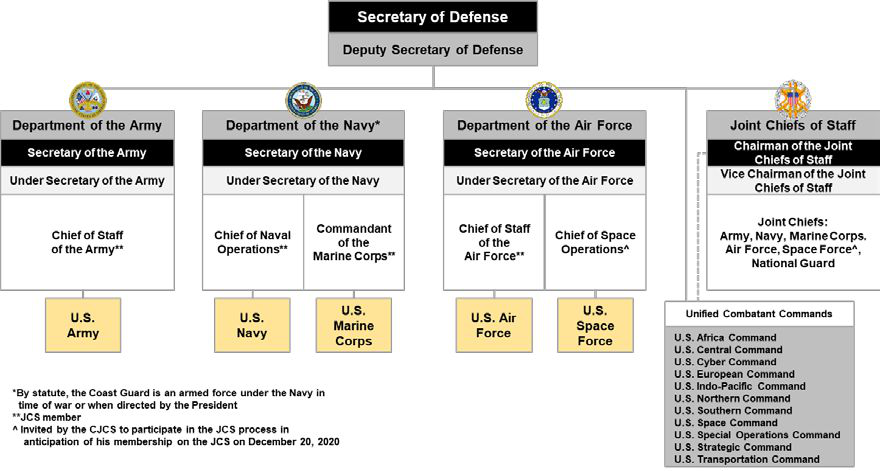
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Acquisition
Military acquisition or defense acquisition is the "bureaucracy, bureaucratic management and procurement process", dealing with a nation's investments in the technologies, programs, and product support necessary to achieve its national National Security Strategy (United States), security strategy and support its Military, armed forces. Its objective is to acquire products that satisfy specified needs and provide measurable improvement to mission capability at a fair and reasonable price. Concept Military acquisition has a long history spanning from ancient times (e.g., blacksmithing, shipbuilding) to modern times. Modern military acquisition is a complex blend of science, management, and engineering disciplines within the context of a nation's law and regulation framework to produce military material and technology. This complexity evolved from the increasing complexity of weapon systems starting in the 20th century. For example, the Manhattan Project involved more than 130,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOTMLPF
DOTMLPF (pronounced "Dot-MiL-P-F") stands for doctrine, organization, training, materiel, leadership and education, personnel, and facilities. It is used by the US Department of Defense and was defined in the Joint Capabilities Integration Development System, or JCIDS Process as the framework to design what administrative changes and/or acquisition efforts would fill a capability need required to accomplish a mission. Because combatant commanders define requirements in consultation with the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD), they are able to consider gaps in the context of strategic direction for the total US military force and influence the direction of requirements earlier in the acquisition process, in particular, materiel. DOTMLPF It also serves as a mnemonic for staff planners to consider certain issues prior to undertaking a new effort. *Doctrine *Organization *Training *Materiel *Leadership *Personnel * Facilities Here is an example of how DOTMLPF would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Operational Capability
In military acquisition, full operating capability or full operational capability (FOC) is the completion of a development effort. This is usually preceded by an initial operating capability or initial operational capability (IOC) phase. For the United States Department of Defense military acquisition Military acquisition or defense acquisition is the "bureaucracy, bureaucratic management and procurement process", dealing with a nation's investments in the technologies, programs, and product support necessary to achieve its national National ... FOC is defined as "''in general attained when all units and/or organizations in the force structure scheduled to receive a system have received it and have the ability to employ and maintain it. The specifics for any particular system FOC are defined in that system’s Capability Development Document (CDD) and Capability Production Document (CPD)''." FOC is a certification event marking completion of training, providing maintenance fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of European Union Directives
This list of European Union Directives is ordered by theme to follow EU law. For a date based list, see the :European Union directives by number. From 1 January 1992 to 31 December 2014, numbers assigned by the General Secretariat of the Council followed adoption, for instance: Directive 2010/75/EU. Since 2015, acts have been numbered following the pattern (domain) YYYY/N, for instance "Regulation (EU) 2016/1627" with * domain being "EU" for the European Union, "Euratom" for the European Atomic Energy Community, "EU, Euratom" for the European Union and the European Atomic Energy Community, "CFSP" for the Common Foreign and Security Policy * year being the 4 digit year * the sequential number. Some older directives had an ordinal number in their name, for instance: "First Council Directive 73/239/EEC". Free movement and trade Goods *Commission Directive 66/683/EEC of 7 November 1966 eliminating all differences between the treatment of national products and that of products w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procurement
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as '' government procurement'' or public procurement. Procurement as an organizational process is intended to ensure that the buyer receives goods, services, or works at the best possible price when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Corporations and public bodies often define processes intended to promote fair and open competition for their business while minimizing risks such as exposure to fraud and collusion. Almost all purchasing decisions include factors such as delivery and handling, marginal benefit, and fluctuations in the prices of goods. Org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |