|
Infantile Systemic Hyalinosis
Infantile systemic hyalinosis is an allelic autosomal-recessive condition characterized by multiple skin nodules, hyaline deposition, gingival hypertrophy, osteolytic bone lesions and joint contractures.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Genetics This disease is caused by mutations in the CMG2 gene (''ANTXR2'').Vahidnezhad H, Ziaee V, Youssefian L, Li Q, Sotoudeh S, Uitto J (2015) Infantile systemic hyalinosis in an Iranian family with a mutation in the CMG2/ANTXR2 gene. Clin Exp Dermatol doi: 10.1111/ced.12616 Diagnosis Management See also * Skin lesion * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier agai ... References External links GeneReview/N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from el, ὑάλινος, translit=hyálinos, lit=transparent, and el, ὕαλος, translit=hýalos, lit=crystal, glass, label=none. Histopathology Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellular matrix of hyaline cartilage looks homogeneously pink, and the term "hyaline" is used to describe similarly homogeneously pink material besides the cartilage. Hyaline material is usually acellular and proteinaceous. For example, arterial hyaline is seen in aging, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ... and in association with some drugs (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
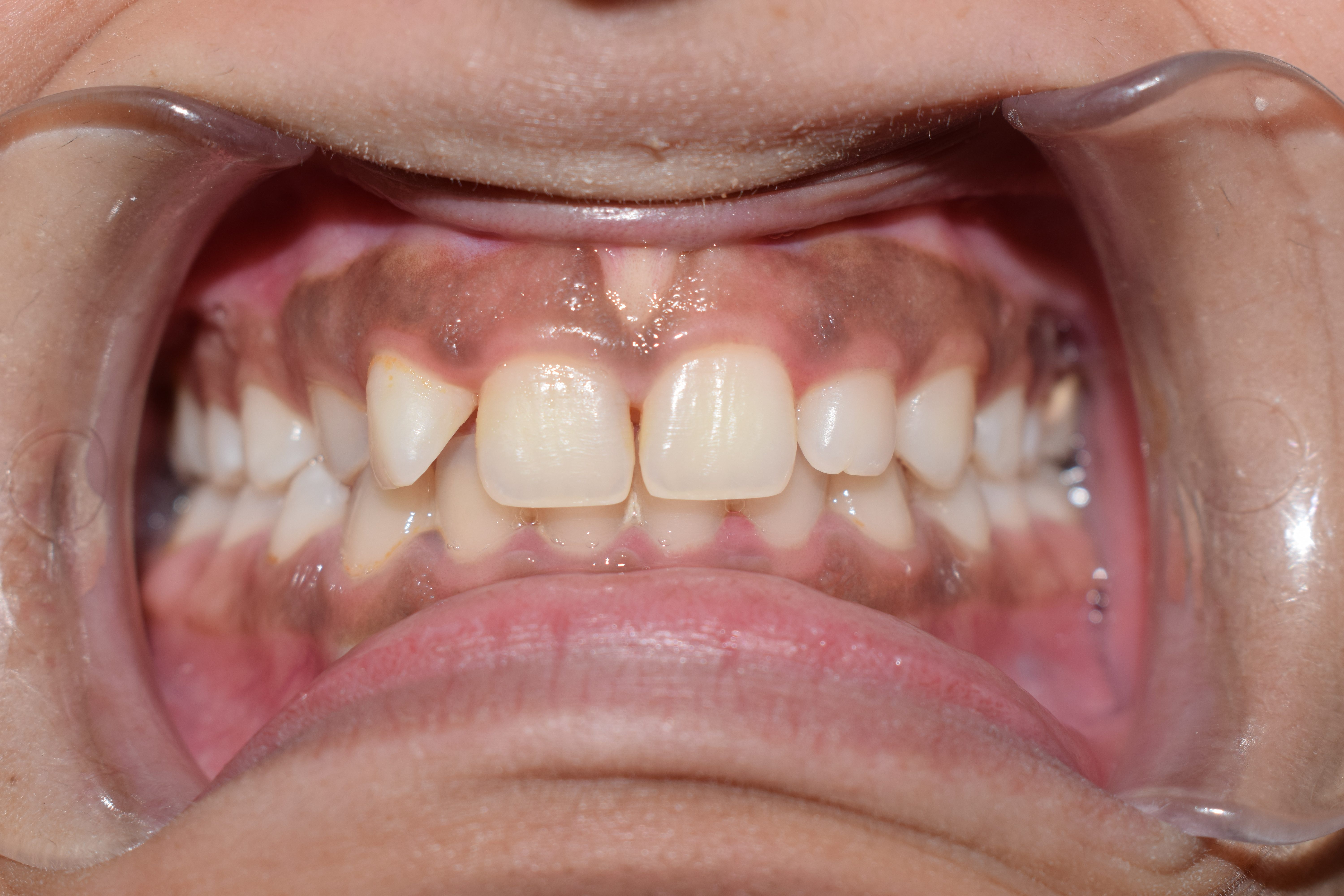
Gingival
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteolytic Lesion
An osteolytic lesion (from the Greek words for "bone" (ὀστέον), and "to unbind" (λύειν)) is a softened section of a patient's bone formed as a symptom of specific diseases, including breast cancer and multiple myeloma. This softened area appears as a hole on X-ray scans due to decreased bone density, although many other diseases are associated with this symptom. Osteolytic lesions can cause pain, increased risk of bone fracture, and spinal cord compression. These lesions can be treated using biophosphonates or radiation, though new solutions are being tested in clinical trials. Cellular causes Bone lesions are caused by an imbalance of regulatory factors, characterized by an increased depletion and resorption of old bone tissue and a decrease in bone rebuilding, known as bone remodeling. This imbalance is due to a flooding of regulatory factors released by specific tumors, thus overwhelming the tissue repair system and resulting in these lesions. The over-activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMG2 Gene
CMG may refer to: Companies * Capitol Music Group, a music label * China Media Group, the predominant state radio and television broadcaster in the PRC * China Media Group Co., Ltd., publicly listed Chinese holding company in the media sector * Chipotle Mexican Grill, which trades on the NYSE as CMG * Cinema Management Group, film sales company * CMG (company), a telecommunications and IT consultancy company * Computer Measurement Group, a worldwide non-profit organization of data processing professionals * Computer Modelling Group, a producer of reservoir simulation software * Concord Music Group, American independent music publisher * Cool Math Games, an online browser game portal * Cox Media Group, a broadcasting, publishing, direct marketing, digital media company * EMI CMG (EMI Christian Music Group), a music label Space * Castor Moving Group, a moving group of stars sharing similar velocities * Control moment gyroscope, orbital facility component Other * California me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Lesion
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermal And Subcutaneous Growths
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders Of Musculoskeletal System
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |