|
Inequity Aversion
Inequity aversion (IA) is the preference for fairness and resistance to incidental inequalities. The social sciences that study inequity aversion include sociology, economics, psychology, anthropology, and ethology. Researchers on inequity aversion aim to explain behaviors that are not purely driven by self-interests but fairness considerations. In some literature, the terminology inequality aversion was used in the places of inequity aversion. The discourses in social studies argue that "inequality" pertains to the gap between the distribution of resources, while "inequity" pertains to the fundamental and institutional unfairness. Therefore, the choice between using inequity or inequality aversion may depend on the specific context. Human studies Inequity aversion research on humans mostly occurs in the discipline of economics though it is also studied in sociology. Research on inequity aversion began in 1978 when studies suggested that humans are sensitive to inequities in fav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Preference
Social preferences describe the human tendency to not only care about one's own material payoff, but also the reference group's payoff or/and the intention that leads to the payoff. Social preferences are studied extensively in Behavioral economics, behavioral and experimental economics and social psychology. Types of social preferences include altruism, fairness, Reciprocity (social psychology), reciprocity, and inequity aversion. The field of economics originally assumed that humans were rational economic actors, and as it became apparent that this was not the case, the field began to change. The research of social preferences in economics started with lab experiments in 1980, where experimental economists found subjects' behavior deviated systematically from self-interest behavior in economic games such as ultimatum game and dictator game. These experimental findings then inspired various new economic models to characterize agent's altruism, fairness and reciprocity concern betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Iowa
The University of Iowa (U of I, UIowa, or Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 colleges offering more than 200 areas of study and 7 professional degrees. On an urban 1,880-acre campus on the banks of the Iowa River, the University of Iowa is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". In fiscal year 2021, research expenditures at Iowa totaled $818 million. The university was the original developer of the Master of Fine Arts degree, and it operates the Iowa Writers' Workshop, whose alumni include 17 of the university's 46 Pulitzer Prize winners. Iowa is a member of the Association of American Universities and the Universities Research Association. Among public universities in the United States, UI was the first to beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Binmore
Kenneth George "Ken" Binmore, (born 27 September 1940) is an English mathematician, economist, and game theorist, a Professor Emeritus of Economics at University College London (UCL) and a Visiting Emeritus Professor of Economics at the University of Bristol. As a founder of modern economic theory of bargaining (with Nash and Rubinstein), he made important contributions to the foundations of game theory, experimental economics, evolutionary game theory and analytical philosophy. He took up economics after holding the Chair of Mathematics at the London School of Economics. The switch has put him at the forefront of developments in game theory. His other interests include political and moral philosophy, decision theory, and statistics. He has written over 100 scholarly papers and 14 books. Education Binmore studied mathematics at Imperial College London, where he was awarded a 1st class-honours BSc with a Governor's Prize, and later a PhD in mathematical analysis. Research B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. It is one of the three ancient arts of discourse ( trivium) along with grammar and logic/ dialectic. As an academic discipline within the humanities, rhetoric aims to study the techniques that speakers or writers use to inform, persuade, and motivate their audiences. Rhetoric also provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations. Aristotle defined rhetoric as "the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion", and since mastery of the art was necessary for victory in a case at law, for passage of proposals in the assembly, or for fame as a speaker in civic ceremonies, he called it "a combination of the science of logic and of the ethical branch of politics". Aristotle also identified three persuasive audience appeals: logos, pathos, and ethos. The five canons of rhetoric, or phases of developing a persuasive speech, were first codified in classical Rome: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contract
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of those at a future date. The activities and intentions of the parties entering into a contract may be referred to as contracting. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or equitable remedies such as specific performance or rescission. A binding agreement between actors in international law is known as a treaty. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured. Like other areas of private law, contract law varies between jurisdictions. In general, contract law is exercised and governed either under common law jurisdictions, civil law jurisdictions, or mixed-law jurisdictions that combine elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance-related Pay
Performance-related pay or pay for performance, not to be confused with performance-related pay rise, is a salary or wages paid system based on positioning the individual, or team, on their pay band according to how well they perform. Car salesmen or production line workers, for example, may be paid in this way, or through commission (remuneration), commission. Many employers use this standards-based system for evaluating employees and for setting salaries. Standards-based methods have been in ''de facto'' use for centuries among commission-based sales staff: they receive a higher salary for selling more, and low performers do not earn enough to make keeping the job worthwhile even if they manage to keep the job. In effect, the salary would be re-evaluated up, or down, periodically (usually annually) based on the performance of the individual or team. The reward is the salary: with an expectation to be high on the pay band for high performance and low on the band for low performan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
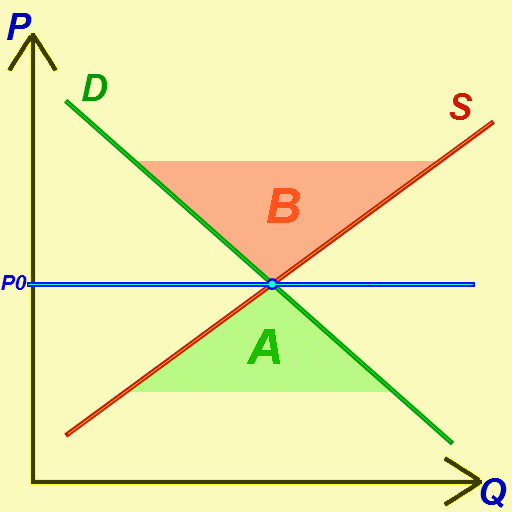
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Scandinavian Journal Of Economics
''The Scandinavian Journal of Economics'' was established as the ''Ekonomisk Tidskrift'' (in Swedish) in 1899 by David Davidson. It became ''The Swedish Journal of Economics'' in 1965 (in English) and then ''The Scandinavian Journal of Economics'' in 1976. Davidson was the editor until his retirement in 1939 at the age of 85, having run it virtually as a one-man operation. In its early history all articles were written in Swedish. The first article in English was printed in 1947. The journal published many important works by Gustaf Cassel, Knut Wicksell, Eli Heckscher, Gunnar Myrdal, and Erik Lindahl. It is owned by a non-profit association and published on its behalf by Wiley-Blackwell. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidarity
Solidarity or solidarism is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. True solidarity means moving beyond individual identities and single issue politics. Still, solidarity does not reject individuals and sees individuals as the basis of society. It refers to the ties in a society that bind people together as one. The term is generally employed in sociology and the other social sciences, as well as in philosophy and bioethics. It is a significant concept in Catholic social teaching and in Christian democratic political ideology. Although closely related to the concept of charity, solidarity aspires to change whole systems, not merely to help individuals. Solidarity is also one of six principles of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, and International Human Solidarity Day is recognized each year on December 20 as an international observance. Solidarity is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Job Performance
Job performance assesses whether a person performs a job well. Job performance, studied academically as part of industrial and organizational psychology, also forms a part of human resources management. Performance is an important criterion for organizational outcomes and success. John P. Campbell describes job performance as an individual-level variable, or something a single person does. This differentiates it from more encompassing constructs such as organizational performance or national performance, which are higher-level variables. Features There are several key features to Campbell's conceptualization of job performance which help clarify what job performance means. Outcomes First, Campbell defines performance as behavior, which is something done by an employee. This concept differentiates performance from outcomes. Outcomes result partially from an individual's performance, but they are also the result of other influences. In other words, there are more factors that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Management
Management (or managing) is the administration of organizations, whether businesses, nonprofit organizations, or a Government agency, government bodies through business administration, Nonprofit studies, nonprofit management, or the political science sub-field of public administration respectively. It is the process of managing the resources of businesses, governments, and other organizations. Larger organizations generally have three Hierarchy, hierarchical levels of managers, organized in a pyramid structure: * Senior management roles include the board of directors and a chief executive officer (CEO) or a President (corporate title), president of an organization. They set the strategic goals and policy of the organization and make decisions on how the overall organization will operate. Senior managers are generally executive-level professionals who provide direction to middle management. Compare governance. * Middle management roles include branch managers, regional managers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truman Bewley
Truman Fassett Bewley (born July 19, 1941) is an American economist. He is the Alfred Cowles Professor of Economics at Yale University. Originally specializing in mathematical economics and general equilibrium theory, since the late 1990s Bewley has gained renown for his work on sticky wages. In Bewley's 1999 book ''Why Wages Don't Fall During a Recession'', hundreds of interviews with executives, labor leaders, and other professionals establish morale as an important factor in why businesses are reluctant to decrease employee compensation at times of low demand. In general equilibrium theory, Bewley (1972) established key existence results for models with infinitely many goods. Due to Bewley (1977), Bewley is the namesake of Bewley models, the class of incomplete markets general equilibrium models in which agents face idiosyncratic income shocks and achieve ''partial'' insurance via, for example, a risk-free bond or capital. Aiyagari (1994), Huggett (1993), and Krusell and Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |