|
Indroda Dinosaur And Fossil Park
The Indroda Dinosaur and Fossil Park in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India, is a park that houses fossilized remains and petrified eggs of dinosaurs. It is a man-made fossil park and not the actual nesting grounds where the dinosaurs lived. The eggs and fossils on display here are from the world's 3rd-largest dinosaur fossil excavation site and 2nd-largest hatchery at Raiyoli, Balasinor, Gujarat. The Park was set up by the Geological Survey of India and is the only dinosaur museum in the country. History In 1970, the Forest Department of the Gujarat Government began its planting and restoration efforts. The park, also known as India's Jurassic Park, is 428 hectares in size and contains sections such as the dinosaur section, fossil section, etc. Now, the park is managed by the Gujarat Ecological and Research Foundation (GEER). The oldest record of dinosaur bone fossils is of middle Jurassic period, and they are found from Patcham formation of Kutch basin. The fossils which were fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar () is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the industrial corridor between the megacities of Delhi and Mumbai. Gandhinagar lies on the west bank of the Sabarmati River, about 545 km (338 miles) north of Mumbai and 901 km (560 miles) southwest of Delhi. The Akshardham temple is located in Gandhinagar. There was a determination to make Gandhinagar a purely Indian enterprise, partly because the state of Gujarat was the birthplace of Mahatma Gandhi. For this reason, the planning was done by two Indian town planners: Prakash M Apte and H. K. Mewada, who had apprenticed with Le Corbusier in Chandigarh. Etymology The name of the city means "Gandhi's city" and it is named after Mahatma Gandhi. History The city was planned by Chief Architect H.K. Mewada, a Cornell University graduate, and his assistant Prakash M Apte. It was developed in the 1960s. Demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiosaurus
''Brachiosaurus'' () is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic, about . It was first Species description, described by American paleontologist Elmer S. Riggs in 1903 in paleontology, 1903 from fossils found in the Colorado River valley in western Colorado, United States. Riggs named the dinosaur ''Brachiosaurus altithorax''; the Generic name (biology), generic name is Ancient Greek, Greek for "arm lizard", in reference to its proportionately long arms, and the specific name (zoology), specific name means "deep chest". ''Brachiosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long; body mass estimates of the subadult holotype specimen range from . It had a disproportionately long neck, small skull, and large overall size, all of which are typical for sauropods. Atypically, ''Brachiosaurus'' had longer forelimbs than hindlimbs, which resulted in a steeply inclined Torso, trunk, and a proportionally shorter tail. ''Brachiosaurus'' is the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Ahmedabad District
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be Domestic tourism, domestic (within the traveller's own country) or International tourism, international. International tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, tourism numbers declined due to a severe Economy, economic slowdown (see Great Recession) and the outbreak of the 2009 2009 flu pandemic, H1N1 influenza virus. These numbers, however, recovered until the COVID-19 pandemic put an abrupt end to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
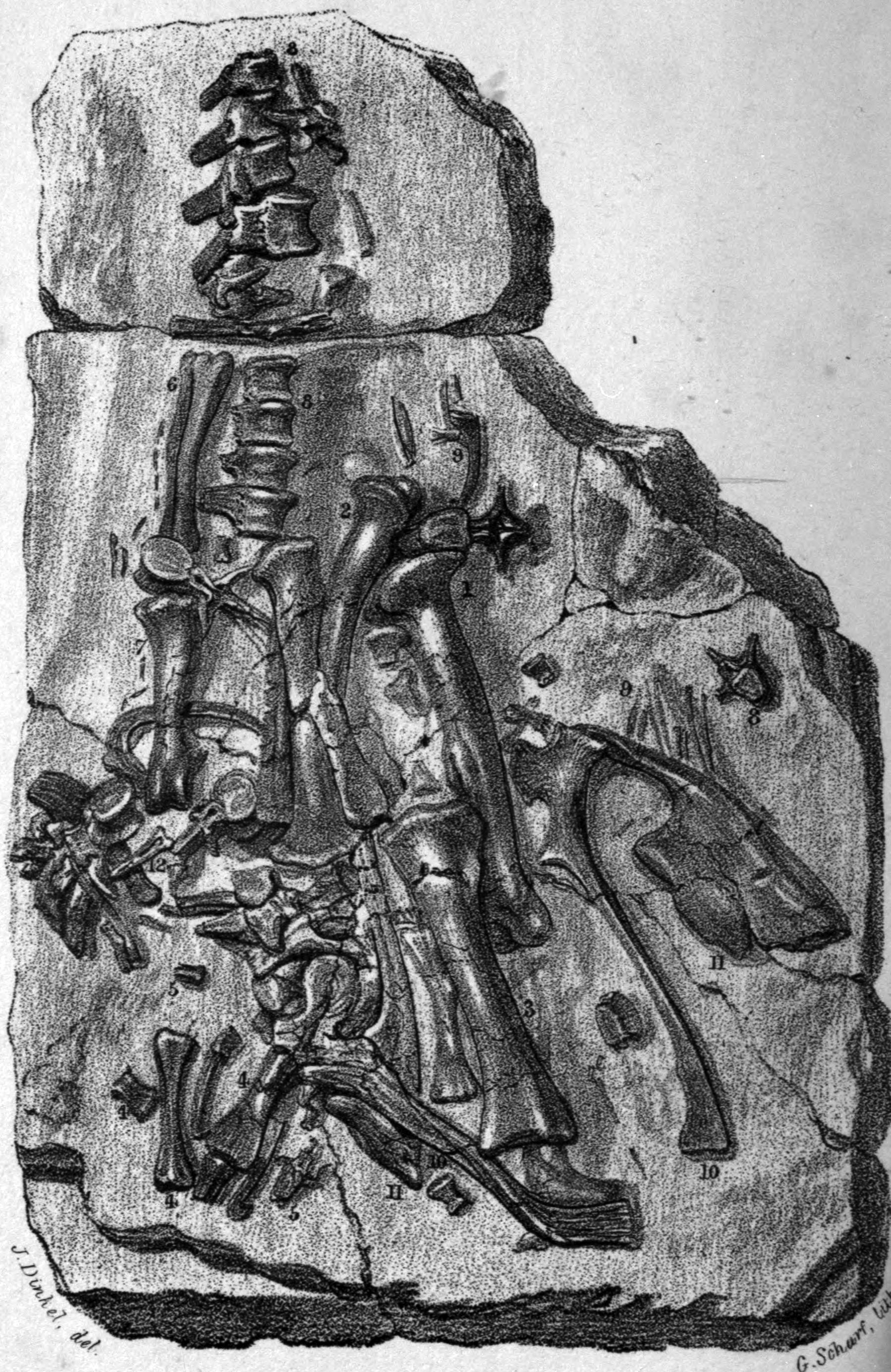
Fossil Trackways
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of Gujarat
The Gujarat state of western India has four National Parks and twenty-three wildlife sanctuaries which are managed by the Forest Department of the Government of Gujarat. National Parks Wildlife sanctuaries The wildlife sanctuaries are listed in descending order of area. Other protected areas See also * Arid Forest Research Institute cater the forestry research needs of the Arid and semi arid region of Rajasthan, Gujarat & Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman-Diu. References {{Gujarat * * National parks N Gujarat Gujarat Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ... Environment of Gujarat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology In India
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin who popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadodara
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is a city situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district. The city is named for its abundance of banyan (''vad'') trees. Vadodara is also locally referred to as the ''Sanskrutik Nagari'' () and ''Kala Nagari'' () of India. The city is prominent for landmarks such as the Laxmi Vilas Palace, which served as the residence of the Maratha royal Gaekwad dynasty that ruled over Baroda State. It is also the home of the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda. Etymology The city was once called Chandanavati after Raja Chandan of the Dod Parmar Rajputs. The capital was also known as Virakshetra (Land of Warriors). Later, it was known as Vadpatraka or Vadodará, and according to tradition, is a corrupt form of the Sanskrit word ''vatodara'', meaning "in the belly of the banyan tree". It is, as of 2009, almost impossible to ascertain when the vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
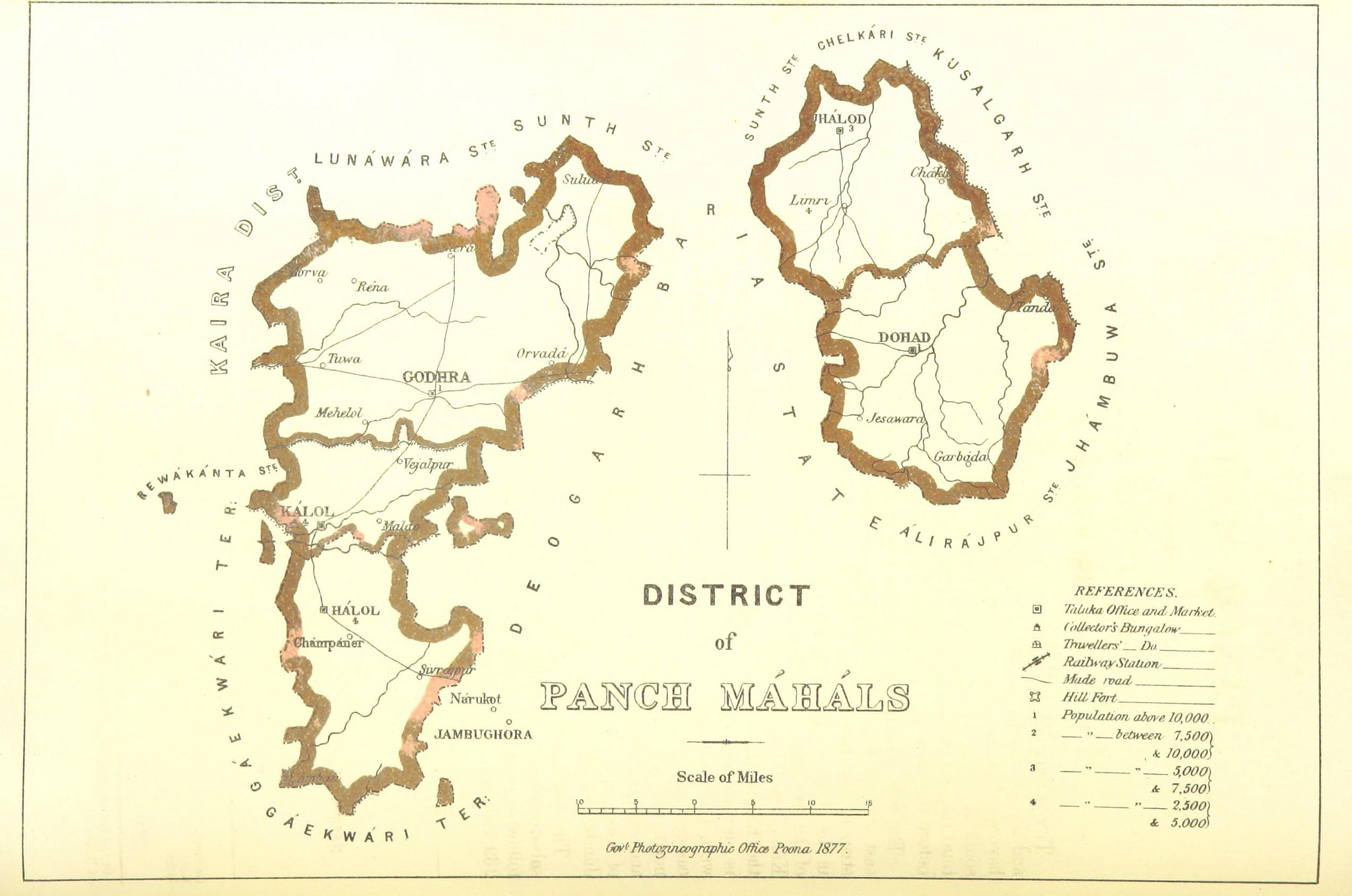
Panchmahal
Panchmahal, also rendered as Panch Mahal, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on the eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kheda
Kheda is a city and a municipality in the Indian state of Gujarat. Kheda was known as Kaira during the British Raj. It was the former administrative capital of Kheda district. The city is known for tobacco farming. The nearest railway station is and the nearest airport is Ahmedabad Airport. History The name Kheda originated from the Sanskrit term ''Kshetra'' (). Khetaka is used as a name of a region surrounding the place in ancient literature. It is also mentioned as a town from 12th to 17th century. ''Ganapatha'' (dated 2nd century BCE), one of the five volumes of Pāṇini' s grammar mentions Khetaka as a name of the region. It is also mentioned as Divyanagar in 133rd chapter of '' Padmapurana''. The 7th and 8th century copper-plates of Maitraka dynasty mentions Khetaka as an administrative division as well as there are mentions of it as a place of Brahmin residence and a Rashtrakuta-controlled town in other copper-plates. There were about 750 villages under that admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balasinor
Balasinor, also known as Vadasinor, is a city located in the Mahisagar district of Gujarat, India. The city was formerly part of Balasinor State, a princely state ruled by the Babi dynasty, from September 1758 until its accession to India in June 1948. History Balasinor State was founded in the 18th century. The rulers were titled Nawab Babi. Once a princely state under Presidencies and provinces of British India, it was ruled by the Babi dynasty, descendants of the Pathan rulers of Gujarat, who played a significant role in the region's politics. Balasinor is internationally famous for its Dinosaur Fossil Park in Raiyoli village, which houses one of the largest collections of dinosaur fossils in India, including eggs and bones from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Often referred to as the "Jurassic Park of India, Indroda Dinosaur and Fossil Park" the site has fossils of species like the Rajasaurus narmadensis. The town’s cultural fabric reflects a confluence of Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himatnagar
Himatnagar or Himmatnagar is a city and the headquarters of Sabarkantha district in the Indian state of Gujarat. The city is on the bank of the river Hathmati. History Himatnagar was founded in by Ahmad shah of Gujarat Sultanate and named it Ahmednagar after himself. He founded the town to keep Raos of Idar State in check. In 1658, Aurangzeb became emperor and reintroduced jizya. Through his ferman of 1665 he prohibited Jains and Hindus from closing their shops on 'Pachusan' ( paryushan), last day of the month and eleventh day; ordered that arrangements be made to ensure that Kolis of Himmatnagar do not disturb Muslims when they recite their Friday prayers. When the Marwar dynasty took Idar in 1728, Ahmednagar soon fell into their hands. After the death of Maharaja Shivsing, in 1792, his brother Sangramsing took Ahmednagar and the country around; and, in spite of the efforts of his nephew Gambhirsing, became an independent chief. Sangramsing was succeeded by his son Karan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species found worldwide have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic revision in the early 21st century has defined ''Iguanodon'' to be based on one well-substantiated species: ''I. bernissartensis'', which lived during the Barremian to early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous in Belgium, Germany, England, and Spain, between about 126 and 122 million years ago. ''Iguanodon'' was a large, bulky herbivory, herbivore, measuring up to in length and in body mass. Distinctive features include large thumb spikes, which were possibly used for defense against predation, predators, combined with long prehensile fifth fingers able to forage for food. The genus was named in 1825 by English geologist Gideon Mantell, based on fossil specimens found in England and was given the species name ''I. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |