|
Indian Yellow
Indian yellow is a complex pigment consisting primarily of euxanthic acid salts (magnesium euxanthate and calcium euxanthate), euxanthone and sulphonated euxanthone. It is also known as purree, snowshoe yellow, gaugoli, gogili, Hardwari peori, Monghyr puri, peoli, peori, peri rung, pioury, piuri, purrea arabica, pwree, jaune indien (French, Dutch), Indischgelb (German), yìndù huáng (Chinese), giallo indiano (Italian), and amarillo indio (Spanish). The crystalline form dissolved in water or mixed with oil to produce a transparent yellow paint which was used in Indian frescoes, oil painting and watercolors. After application Indian yellow produced a clear, deep and luminescent orange-yellow color which, due to its fluorescence, appears especially vibrant and bright in sunlight. It was said to be of a disagreeable odour. It was most used in India in the Mughal period and in Europe in the nineteenth century, before becoming commercially unavailable circa 1921. The origin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Vermeer
Johannes Vermeer ( , ; see below; also known as Jan Vermeer; October 1632 – 15 December 1675) was a Dutch painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle-class life. He is considered one of the greatest painters of the Dutch Golden Age. During his lifetime, he was a moderately successful provincial genre painter, recognized in Delft and The Hague. He produced relatively few paintings, primarily earning his living as an art dealer. He was not wealthy; at his death, his wife was left in debt. Vermeer worked slowly and with great care, and frequently used very expensive pigments. He is particularly renowned for making masterful use of light in his work. "Almost all his paintings", Hans Koningsberger wrote, "are apparently set in two smallish rooms in his house in Delft; they show the same furniture and decorations in various arrangements and they often portray the same people, mostly women." The modest celebrity he enjoyed during his life gave way to obscurity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts ( cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include pain that lasts longer than five hours, fever, yellowish skin, vomiting, da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castor Oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans, the seeds of the plant ''Ricinus communis''. The seeds are 40 to 60 percent oil. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is and its density is 0.961 g/cm3. It includes a mixture of triglycerides in which about 90 percent of fatty acids are Ricinoleic acid, ricinoleates. Oleic acid and linoleic acid are the other significant components. Some 270,000–360,000 tonnes (600–800 million pounds) of castor oil are produced annually for a variety of uses. Castor oil and its derivatives are used in the manufacturing of soaps, lubricants, hydraulic and brake fluids, paints, dyes, coatings, inks, cold-resistant plastics, waxes and polishes, nylon, and perfumes. Etymology The name probably comes from a confusion between the ''Ricinus'' plant that produces it and another plant, the ''Vitex agnus-castus''. An alternative etymology, though, suggests that it was used as a replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Magazine
The ''Philosophical Magazine'' is one of the oldest scientific journals published in English. It was established by Alexander Tilloch in 1798;John Burnett"Tilloch, Alexander (1759–1825)" Dictionary of National Biography#Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 2006, accessed 17 Feb 2010 in 1822 Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor became joint editor and it has been published continuously by Taylor & Francis ever since. Early history The name of the journal dates from a period when "natural philosophy" embraced all aspects of science. The very first paper published in the journal carried the title "Account of Mr Cartwright's Patent Steam Engine". Other articles in the first volume include "Methods of discovering whether Wine has been adulterated with any Metals prejudicial to Health" and "Description of the Apparatus used by Lavoisier to produce Water from its component Parts, Oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stenhouse
John Stenhouse FRS FRSE FIC FCS (21 October 1809 – 31 December 1880) was a British chemist. In 1854, he invented one of the first practical respirators. He was a co-founder of the Chemical Society in 1841. Life John Stenhouse was born in Barrhead in Glasgow on 21 October 1809. He was the eldest son of William Stenhouse, a calico-printer in the family firm of John Stenhouse & Co of 302 High Street, Glasgow, and Elizabeth Currie; he was the only one of their children to survive beyond infancy. After education at the Glasgow Grammar School, he studied at the University of Glasgow from 1824 to 1828. Initially he intended to pursue a career in literature, but later his interests switched to chemistry, which he studied first under Professor Thomas Graham at the university and then under Dr. Thomas Thomson at Anderson's University in Glasgow (now part of the University of Strathclyde, one of whose buildings is named after him). During 1837–1839, he attended the chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memecylon
''Memecylon'' is a plant group in Melastomataceae. It consists of 350-400 species of small to medium-sized trees and shrubs occurring in the Old World tropics. ''Memecylon'' is a monophyletic group basal to the Melastomataceae clade. ''Memecylon'' taxa have more than 600 published basionyms. Diversity of this group is concentrated in tropical Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, India and Malaysia. Etymology The name ''Memecylon'' is derived from 'memaecylon' as used by ancient Greek philosophers Dioscorides and Pliny to describe the red fruits of ''Arbutus unedo'' (oriental strawberry tree), an unrelated plant group, alluding to the pink to reddish berries often produced by ''Memecylon''. Some vernacular names in different regions of the world are given below. English: "Blue mist plant", Hindi: ''Anjan''; Malayalam: ''Aattukanala'' ��റ്റുകനല ''Kaasaavu'': ��ാശാവ് ''Kaayaampoo'': ��ായാമ്പൂ Odia: ''Neymaru''; Olle Kudi, Alimar (ಒಳ್ಳ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
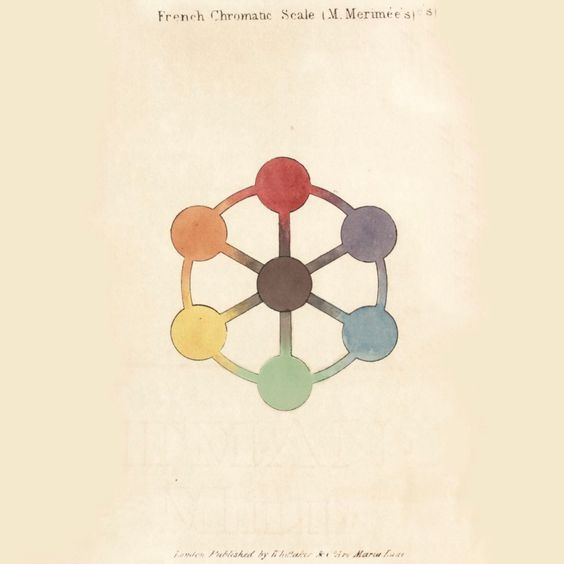
Léonor Mérimée
Jean-François Léonor Mérimée (16 September 1757, Broglie, Eure, Broglie - 26 September 1836, Paris) was a French writer, painter and chemist, specializing in pigment color in painting and decorative art. He was the father of the famous author Prosper Mérimée. Biography His father was François Merimée (c. 1715-1795), a lawyer at the Parlement de Rouen and author of ''"Treatise on fiefs and feudal rights in Normandy according to the natural order of matters and procedure divided into 5 parts'' (1760). He also served as a Steward (office), steward for the Victor-François de Broglie (1718-1804), Maréchal de Broglie. He studied at the Université de Caen, Collège de Caen before entering the Académie royale de peinture in 1778, where he studied with Gabriel-François Doyen and François-Élie Vincent. His fellow students included Charles Meynier, Jacques-Augustin-Catherine Pajou and Charles Thévenin. In 1787, he was awarded second place in the Prix de Rome and achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippuric Acid
Hippuric acid (Greek language, Gr. ''hippos'', horse, ''ouron'', urine) is a carboxylic acid and organic compound. It is found in urine and is formed from the combination of benzoic acid and glycine. Levels of hippuric acid rise with the consumption of Phenols, phenolic compounds (such as in Juice, fruit juice, tea, and wine). The phenols are first converted to benzoic acid, and then to hippuric acid and excreted in urine. Hippuric acid crystallizes in rhombus, rhombic prisms which are readily soluble in hot water, melt at 187 °C, and decompose at about 240 °C. High concentrations of hippuric acid may also indicate a Toluene (toxicology), toluene intoxication, however, scientists have called this correlation into question, because there are other variables that affect levels of hippuric acid. When many aromatic compounds such as benzoic acid and toluene are taken internally, they are converted to hippuric acid by reaction with the amino acid glycine. Synthesis A mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gräbe
Carl Graebe (; 24 February 1841 – 19 January 1927) was a German industrial and academic chemist from Frankfurt am Main who held professorships in his field at Leipzig, Königsberg, and Geneva. He is known for the first synthesis of the economically important dye, alizarin, with Liebermann, and for contributing to the fundamental nomenclature of organic chemistry. Biography Graebe was born in Frankfurt in 1841. He studied at a vocational high school in Frankfurt and Karlsruhe Polytechnic and in Heidelberg. Later he worked for the chemical company ''Meister Lucius und Brüning'' (today Hoechst AG). He supervised the production of Fuchsine and researched violet colorants made using iodine. The work with iodine resulted in eye problems, so he returned to academia. Carl Graebe received his Ph.D. from the University of Heidelberg in 1862 under the supervision of Robert Wilhelm Bunsen. In 1868 he wrote his habilitation, and became a professor in University of Leipzig. Graebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monghyr
Munger, formerly spelt as Monghyr, is a twin city and a Municipal Corporation situated in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the administrative headquarters of Munger district and Munger Division. Munger was one of the major cities in Eastern India and undivided Bengal during Mughal period and British Raj. It is one of the major political, cultural, educational and commercial centers of Bihar and Eastern India. Munger is situated about 180km east of capital city Patna, about 480km west of Eastern India's largest city Kolkata and 1200km from country's capital New Delhi. Historically, Munger is known for being an ancient seat of rule. The twin city comprises Munger and Jamalpur situated on the southern bank of the river Ganges. It is situated 8 km from Jamalpur Junction, 180 km east of capital city Patna and 430 Km from Kolkata the capital of West Bengal. Munger is said to have been founded by the Guptas (4th century CE) and contains a fort that houses the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Dalton Hooker
Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker (30 June 1817 – 10 December 1911) was a British botanist and explorer in the 19th century. He was a founder of geographical botany and Charles Darwin's closest friend. For 20 years he served as director of the Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew, succeeding his father, William Jackson Hooker, and was awarded the highest honours of British science. Biography Early years Hooker was born in Halesworth, Suffolk, England. He was the second son of Maria Sarah Turner, eldest daughter of the banker Dawson Turner and sister-in-law of Francis Palgrave, and the famous botanist Sir William Jackson Hooker, Regius Professor of Botany, Glasgow, Regius Professor of Botany. From the age of seven, Hooker attended his father's lectures at the University of Glasgow, taking an early interest in plant geography, plant distribution and the voyages of explorers like Captain James Cook. He was educated at the High School of Glasgow, Glasgow High School and went on to study med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |