|
Indian National Committee For Space Research
The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by India's first prime minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the suggestion of the scientist Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. It committed to formulate the Indian Space Programme. At the time, the committee was part of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research. The committee took over the responsibilities of the Department of Atomic Energy in space science and research. The then director of the DAE, Homi Bhabha, was instrumental in creation of the committee. INCOSPAR decided to set up Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) at Thumba on the southern tip of India. IOFS officers were drawn from the Indian Ordnance Factories to harness their knowledge of propellants and advanced light materials used to build rockets. H.G.S. Murthy, an IOFS officer, was appointed the first director of the Thumba Equatorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Agency
Space is a three-dimensional In geometry, a three-dimensional space (3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a mathematical space in which three values (''coordinates'') are required to determine the position (geometry), position of a point (geometry), poi ... continuum containing position (geometry), positions and direction (geometry), directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional Continuum (theory), continuum known as ''spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Eucli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station
Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) is India's first rocket launching station and was established on 21 November 1963. Operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), it is located in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, which is near the southwestern tip of mainland India, very close to Earth's magnetic equator. It is currently used by ISRO for launching sounding rockets. The first rockets were assembled in the former St Louis High School, which now houses a space museum. The local Bishop of Trivandrum, Rev. Peter Bernard Periera, along with Vincent Victor Dereere (a Belgian) and district collector Madhavan Nair were instrumental in acquiring a large parcel of land measuring 600 acres from coastal community. Periera had given away the prayer hall and bishop's room in the local church. Minister of State for External Affairs, Lakshmi N. Menon helped to smooth bureaucratic hurdles facing the project in Delhi. H. G. S. Murthy was appointed as the first Director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Kalam
Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam ( ; 15 October 193127 July 2015) was an Indian Aerospace engineering, aerospace scientist and statesman who served as the president of India from 2002 to 2007. Born and raised in a Muslim family in Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu, Kalam studied physics and aerospace engineering. He spent the next four decades as a scientist and science administrator, mainly at the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and was intimately involved in India's civilian space programme and military Integrated Guided Missile Development Program, missile development efforts. He was known as the "Missile Man of India" for his work on the development of ballistic missile and launch vehicle technology. He also played a pivotal organisational, technical, and political role in ''Pokhran-II'' nuclear tests in 1998, India's second such test after the Smiling Buddha, first test in 1974. Kalam 2002 Indian presidential el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waman Dattatreya Patwardhan
Waman Dattatreya Patwardhan (30 January 1917 – 27 July 2007) was an IOFS officer, nuclear chemist, defence scientist and an expert in the science of Explosives engineering. He was the founder director of the Explosives Research and Development Laboratory (now known as the High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL)) of India. He is considered one of the distinguished scientists in India due to his contributions to Indian space program, Indian nuclear program and missile program in their early stages. He developed the solid propellant for India's first space rocket launched at Thumba. He was responsible for developing the detonation system of India's first nuclear device which was successfully tested in 1974, an operation codenamed Smiling Buddha. Other areas of work: Wrote a book on Hydroponics and developed a cost-effective method for producing parabolic mirrors for astronomical telescopes. He was awarded the Padma Shri in 1974 by the Government of India The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
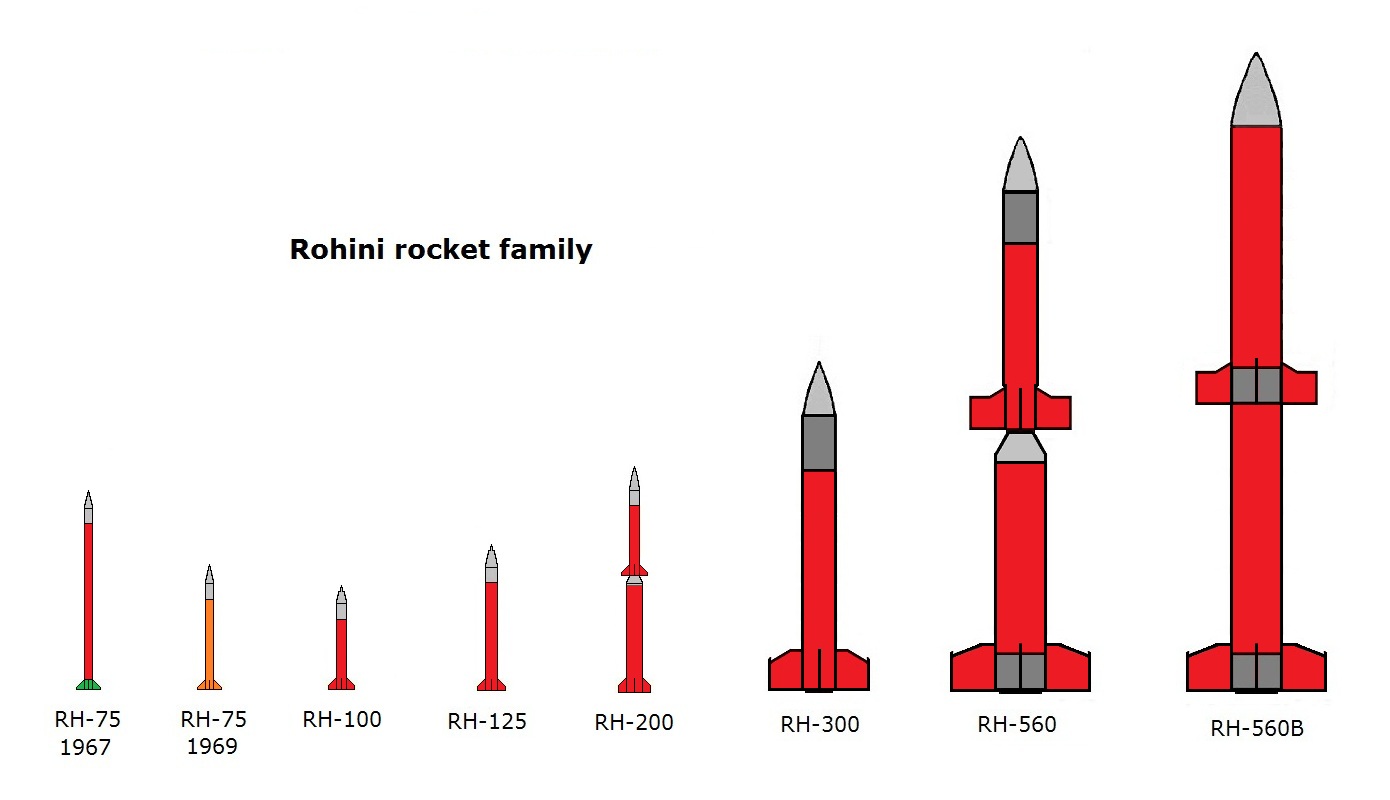
Rohini (rocket Family)
Rohini is a series of sounding rockets developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for meteorological and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads of between altitudes of . The ISRO currently uses RH-200, RH-300,Mk-II, RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets, which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Thumba and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota. Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological experiment and research. Currently, three versions are offered as operational sounding rockets , which cover a payload ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
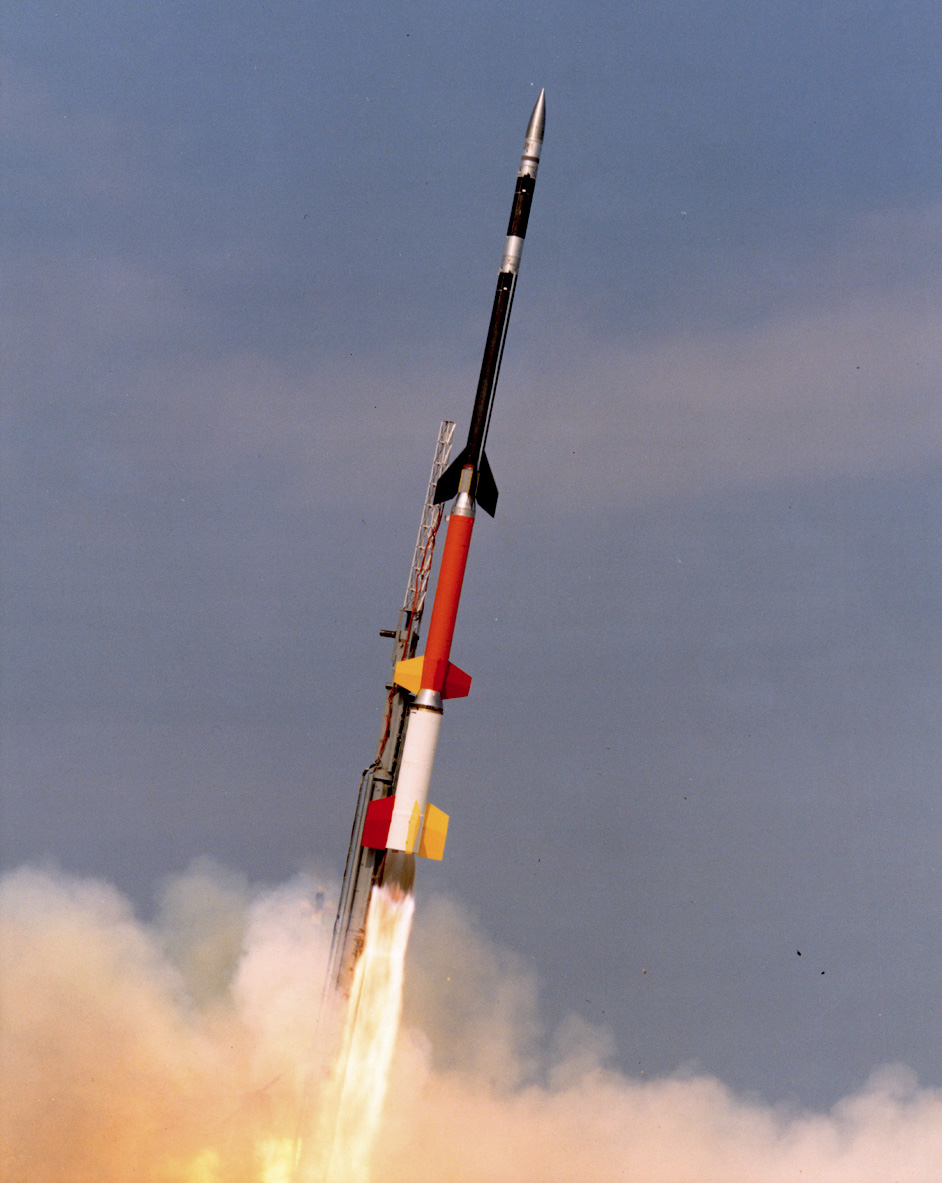
Sounding Rocket
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are often used to launch instruments from above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about and the minimum for satellites is approximately . Due to their suborbital flight profile, sounding rockets are often much simpler than their counterparts built for orbital flight. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between , such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. For certain purposes, sounding rockets may be flown to altitudes as high as to allow observing times of around 40 minutes to provide geophysical observations of the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and mesosphere. Etymology The origin of the term comes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ordnance Factories
The Directorate of Ordnance (Coordination & Services) (abbreviated: DOO(C&S)) is an authority under the Department of Defence Production (DDP) of Ministry of Defence (MoD), Government of India. Its primary work is to management, give instructions and make coordination of government ordnance production public companies. It is the main regulatory body of Indian Ordnance and its administration civil service, Indian Ordnance Factories Service (IOFS). The DOO(C&S) earlier known as Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), consisting of the Indian Ordnance Factories. In 2021, Government having corporatise the functions of the 41 Indian Ordnance Factories into 7 Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), the Government is merging them again in 2024, as the output of one factory serves as the input of the other. OFB was the 37th-largest defence equipment manufacturer in the world, 2nd-largest in Asia, and the largest in India. OFB was the world's largest government-operated production organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IOFS
The Indian Ordnance Factories Service (IOFS) is a civil service of the Government of India. IOFS officers are Gazetted (Group A) defence-civilian officers under the Ministry of Defence. They are responsible for the administration of the Indian Ordnance Factories, which provide the indigenous defence production capabilities of India. Composition During the colonial times, the administrative service of Ordnance was known as the Indian Ordnance Service. It was constituted in the year 1935. It had only European officers in the years that followed. Only engineering graduates from the University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, etc., were allowed to appear in the examination. They had to undergo specialised training prior to joining the service. In 1939, there was only one Indian officer and the remaining forty-four officers were of European origin. IOFS was reconstituted in its present form in 1954 with the cadre controlling authority of the Ministry of Defence – Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thumba
Thumba is a coastal area of Thiruvananthapuram city, the capital of Kerala, India. Location and geography Thumba is a vast village bordering Menamkulam in the east, St. Dominic's Vettucaud in the north, and Kochuthura in the south; towards its west is the Arabian Sea. While the border with Menamkulam is the Parvathi Puthannaar canal, the border with Kochuthura is the Rajiv Gandhi Nagar road. The entire village is flat at sea level, and the ground near to the coast is made of tan-coloured beach sand. This is in stark contrast to the rest of the village, where the ground is made of white sand, where, till the developments of the late 1990s, large amounts of a medicinal herb with white flowers called ''Thumba'' grew in abundance, hence the name. It is well connected by road and the closest railway stations are the Halt stop of Veli Railway station and the Major Junction of Kochuveli Railway station. Overview Thumba became well-known to the outsiders after the establishment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) is India's national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It serves as the principal research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), overseen by the Prime Minister of India, with the Chairman of ISRO also serving as the chief executive of the DoS. It is primarily responsible for space-based operations, space exploration, international space cooperation and the development of related technologies. The agency maintains a constellation of imaging, communications and remote sensing satellites. It operates the GAGAN and IRNSS satellite navigation systems. It has sent three missions to the Moon and one mission to Mars. Formerly known as the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR), ISRO was set up in 1962 by the Government of India on the recommendation of scientist Vikram Sarabhai. It was renamed as ISRO in 1969 and was subsumed into the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE). The establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |