|
Index Of Sustainable Economic Welfare
The Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare (ISEW) is an economic indicator intended to replace the gross domestic product (GDP), which is the main macroeconomic indicator of System of National Accounts (SNA). Rather than simply adding together all expenditures like the GDP, consumer spending is balanced by such factors as income distribution and cost associated with pollution and other unsustainable costs. The calculation excludes defence expenditures and considers a wider range of harmful effects of economic growth. It is similar to the genuine progress indicator (GPI). The Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare (ISEW) is roughly defined by the following formula: ''ISEW'' = ''personal consumption''+ ''public non-defensive expenditures''- ''private defensive expenditures''+ ''capital formation''+ ''services from domestic labour''- ''costs of environmental degradation''- ''depreciation of natural capital'' History GDP is misleading as an indicator or even as a proxy of the welfare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainability Measurement
Sustainability measurement is a set of frameworks or indicators used to measure how sustainable something is. This includes processes, products, services and businesses. Sustainability is difficult to quantify and it may even be impossible to measure as there is no fixed definition. To measure sustainability, frameworks and indicators consider environmental, social and economic domains. The metrics vary by use case and are still evolving. They include indicators, benchmarks and audits. They include sustainability standards and certification systems like Fairtrade and Organic. They also involve indices and accounting. They can include assessment, appraisal and other reporting systems. The metrics are used over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales.Bell, Simon and Morse, Stephen 2008. Sustainability Indicators Measuring the Immeasurable?'' 2nd edn. London: Earthscan. . For organizations, sustainability measures include corporate sustainability reporting and Triple Bottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happy Planet Index
The Happy Planet Index (HPI) is an Index (economics), index of human well-being and environmental impact that was introduced by the New Economics Foundation in 2006. Each country's HPI value is a function of its average subjective life satisfaction, life expectancy at birth, and ecological footprint per capita. The exact function is a little more complex, but conceptually it approximates multiplying life satisfaction and life expectancy and dividing that by the ecological footprint. The index is weighted to give progressively higher scores to nations with lower ecological footprints. The index is designed to challenge well-established indices of countries' development, such as the gross domestic product (GDP) and the Human Development Index (HDI), which are seen as not taking sustainability into account. In particular, GDP is seen as inappropriate, as the usual ultimate aim of most people is not to be rich, but to be happiness, happy and healthy. Furthermore, it is believed that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happiness Economics
The economics of happiness or happiness economics is the theoretical, qualitative and quantitative study of happiness and quality of life, including positive and negative Affect (psychology), affects, well-being, life satisfaction and related concepts – typically tying economics more closely than usual with other social sciences, like sociology and psychology, as well as physical health. It typically treats subjective happiness-related measures, as well as more objective quality of life indices, rather than wealth, income or profit, as something to be maximized. The field has grown substantially since the late 20th century, for example by the development of methods, surveys and indices to measure happiness and related concepts,• Carol Graham, 2008. "happiness, economics of," ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics'', 2nd EditionAbstract.Prepublicatio copy.br /> • _____, 2005. "The Economics of Happiness: Insights on Globalization from a Novel Approach," ''World Ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross National Well-being
Gross National Well-being (GNW), also known as Gross National Wellness, is a socioeconomic development and measurement framework. The GNW Index consists of seven dimensions: economic, environmental, physical, mental, work, social, and political. Most wellness areas include both subjective results (via survey) and objective data. The GNW Index is also known as the first Gross National Happiness Index, not to be confused with Bhutan's GNH Index. Both econometric frameworks are different in authorship, creation dates, and geographic scope. The GNW / GNH index is a global development measurement framework published in 2005 by the International Institute of Management in the United States. History The term "Gross National Happiness" was first coined by the Bhuntanese King Jigme Singye Wangchuck in 1972. However, no GNH Index existed until 2005. The GNH philosophy suggested that the ideal purpose of governments is to promote happiness. The philosophy remained difficult to implement du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross National Happiness
Gross National Happiness, (GNH; ) sometimes called Gross Domestic Happiness (GDH), is a philosophy that guides the government of Bhutan. It includes an index used to measure a population's collective happiness and well-being. The Gross National Happiness Index was instituted as the goal of the government of Bhutan in the Constitution of Bhutan, enacted on 18 July 2008. History The advent and concept of "Gross National Happiness" (GNH) germinated in the mind of Bodhisattva Druk Gyelpo, the 4th King of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuck, groomed with the evolution of "Gaki Phuensum" (Peace and Prosperity) and the modernization period of Bhutan during the reign of Druk Gyelpo, the 3rd King of Bhutan, Jigme Dorji Wangchuck. The term "Gross National Happiness" as conceptualized by the 4th King of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuck, in 1972 was declared, "more important than Gross Domestic Product." The concept implies that sustainable development should take a holistic approach towards noti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
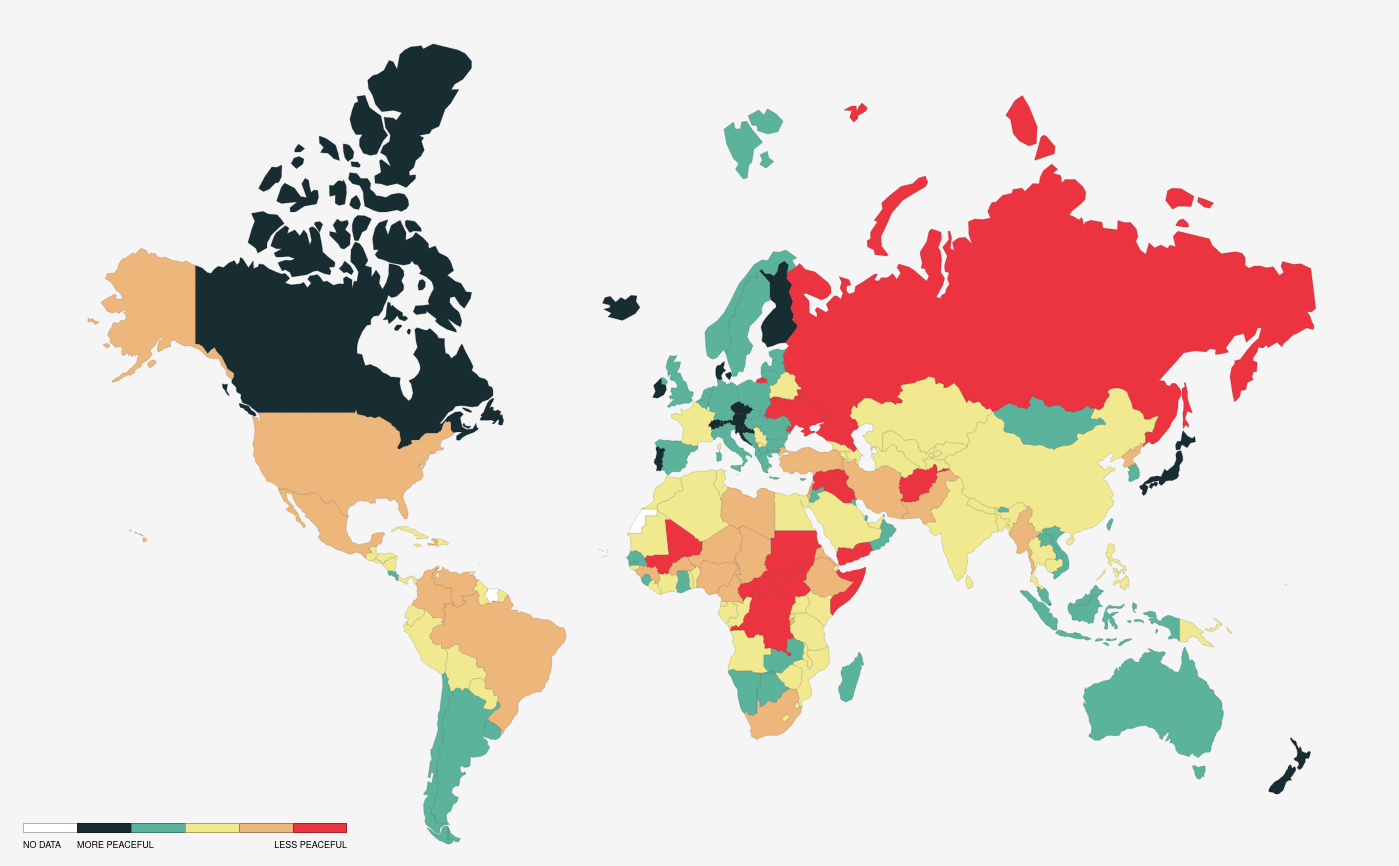
Global Peace Index
The Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Australia-based NGO Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) which measures the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. The GPI ranks 163 independent states and territories (collectively accounting for 99.7 per cent of the world's population) according to their levels of peacefulness. In the past decade, the GPI has presented trends of increased global violence and less peacefulness. The GPI (Global Peace Index) is developed in consultation with an international panel of peace experts from peace institutes and think tanks with data collected by the Economist Intelligence Unit. The Index was first launched in 2007, with subsequent reports being released annually. In 2015 it ranked 165 countries, up from 121 in 2007. The study was conceived by Australian technology entrepreneur Steve Killelea, and is endorsed by individuals such as former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan, the Dalai Lama, and 2008 Nobel Peace P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender-related Development Index
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is an index designed to measure gender equality. GDI, together with the Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM), was introduced in 1995 in the Human Development Report written by the United Nations Development Program. These measurements aimed to add a gender-sensitive dimension to the Human Development Index (HDI). The first measurement that they created as a result was the GDI. The GDI is defined as a "distribution-sensitive measure that accounts for the human development impact of existing gender gaps in the three components of the HDI" (Klasen 243). Distribution sensitivity means that the GDI takes into account not only the average or general level of well-being and wealth within a given country but focuses also on how this wealth and well-being is distributed between different groups within society. The HDI and the GDI (as well as the GEM) were created to rival the more traditional general income-based measures of development such as gross domest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Gross Domestic Product
The green gross domestic product (green GDP or GGDP) is an index of economic growth with the environmental consequences of that growth factored into a country's conventional GDP. Green GDP monetizes the loss of biodiversity, and accounts for costs caused by climate change. Some environmental experts prefer physical indicators (such as "waste per capita" or "carbon dioxide emissions per year"), which may be aggregated to indices such as the " Sustainable Development Index". Calculation Formula The environmental and related social costs to develop the economy are taken into consideration when calculating the green GDP, which can be expressed as: Green GDP = GDP − Environmental Costs − Social Costs where the environmental cost typically qualifies: * Depletion value of natural resources, e.g. oil, coal, natural gas, wood, and metals; * Degradation cost of ecological environment, e.g. underground water pollution, topsoil erosion, and extinction of wildlife; * Restoration co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green National Product
The green national product is an economic metric that seeks to include environmental features such as environmental degradation and resource depletion with a country's national product. Criticism of gross national product The gross national product (GNP) measures the welfare of a nation's economy through the aggregate of products and services produced in that nation. Although GNP is a proficient measurement of the magnitude of the economy, many economists, environmentalists and citizens have been arguing the validity of the GNP in respect to measuring welfare. Joseph Stiglitz, Nobel Prize–winning economist, states that this standard measurement for any national economy has become deficient as a measure of long-term economic health in the recently resource-driven and globalizing world. Critics suggest that GNP often includes the environment on the wrong side of the balance sheet because if someone first pollutes and then another person cleans the pollution, both activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Cost Accounting
True Cost Accounting (TCA) is an accounting approach that measures and values the hidden impacts of economic activities on the environment, society and health. TCA is also referred to as full cost accounting (FCA) or “multiple capital accounting (MCA)”. The approach moves beyond purely economic thinking with the aim of improving decision-making in commercial organizations and in public policy. It includes accounting for natural capital, human capital, social capital and produced capital. The True Cost Accounting approach can be applied to every sector of the economy. It aims to reveal the impacts of economic activities on society as a whole, in addition to the private costs directly incurred by producers and consumers. These can be environmental, health or social impacts that are not reflected in the market prices of products and services, i.e. not included in the operational profit and loss accounts, and so are regarded as hidden. True Cost Accounting is of particular relevanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |