|
Ince And Mayhew
Ince and Mayhew were a partnership of furniture designers, upholsterers and cabinetmakers, founded and run by William Ince (1737–1804) and John Mayhew (1736–1811) in London, from 1759 to 1803; Mayhew continued alone in business until 1809. Their premises were located in Marshall Street but were listed in London directories in Broad Street, Soho, 1763–83, and in Marshall Street, Carnaby Market, 1783–1809. The partnership's volume of engraved designs, ''The Universal System of Household Furniture'', dedicated to the Duke of Marlborough General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 O.S.) was a British army officer and statesman. From a gentry family, he ... (published in parts, 1759–63), was issued in imitative rivalry with Thomas Chippendale; Ince, who was a subscriber to the first edition of Chippendale's ''Director'', was chiefly responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideboard By Ince And Mayhew, 1786, Mahogany, With Silver By Richard Crossley, 1796 - Dining Room - Kingston Lacy - Dorset, England - DSC03438
A sideboard, also called a buffet, is an item of furniture traditionally used in the dining room for serving food, for displaying serving dishes, and for storage. It usually consists of a set of cabinets, or cupboards, and one or more drawers, all topped by a wooden surface for conveniently holding food, serving dishes, or lighting devices. The words ''sideboard'' and ''buffet'' are somewhat interchangeable, but if the item has short legs, or a base that sits directly on the floor with no legs, it is more likely to be called a ''sideboard''; if it has longer legs, it is more likely to be called a ''buffet''. The earliest versions of the sideboard familiar today made their appearance in the 18th century, but they gained most of their popularity during the 19th century, as households became prosperous enough to dedicate a room solely to dining. Sideboards were made in a range of decorative styles and were frequently ornamented with costly veneers and inlays. In later years, side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crichel House
Crichel House is a Grade I listed Classical Revival country house near the village of Moor Crichel in Dorset, England. The house has an entrance designed by Thomas Hopper (architect), Thomas Hopper and interiors by James Wyatt. It is surrounded by of parkland, which includes a crescent-shaped lake covering . The parkland is Grade II listed in the National Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. History The original Tudor style architecture, Tudor house, owned by the Napier baronets, Napier family, was largely destroyed in an accidental fire in 1742 and was rebuilt in English Baroque style for Sir William Napier by Bastard brothers, John Bastard of Blandford and Francis Cartwright, probably the contractor.John Martin Robinson"The magnificent puzzle of Crichel, one of Dorset's grandest Georgian houses" ''Country Life'' [2017] 30 April 2019. Humphrey Sturt, of Horton, Dorset, Horton, acquired the estate in 1765 on his marriage with Diana, the aunt and heir of Sir Gerard Napier, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphry Sturt
Humphrey Sturt (''c.'' 1724 – 20 October 1786) was a British landowner, architect and politician who sat in the British House of Commons, House of Commons from 1754 to 1784. Early life and family Sturt was the son of Humphrey Sturt (1687-1740) of Horton and Diana Napier (died 1740), daughter of Sir Nathaniel Napier, 3rd Baronet of Critchell More. He matriculated at Queen's College, Oxford on 27 April 1741, aged 16. He married Mary Pitfield, daughter of Charles Pitfield and Dorothy Ashley, on 27 April 1756 at St James, Westminster, London. He owed his wealth to his grandfather, Sir Anthony Sturt, who had been a successful business man and City of London alderman and Victualler to the Navy. Diana Napier, his mother, was the great great granddaughter of Sir Nathaniel Napier the builder of Crichell House, and it was through her that the house passed to the Sturts. Political career Sturt was the Lord of Horton Manor. He was returned unopposed as the Member of Parliament for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
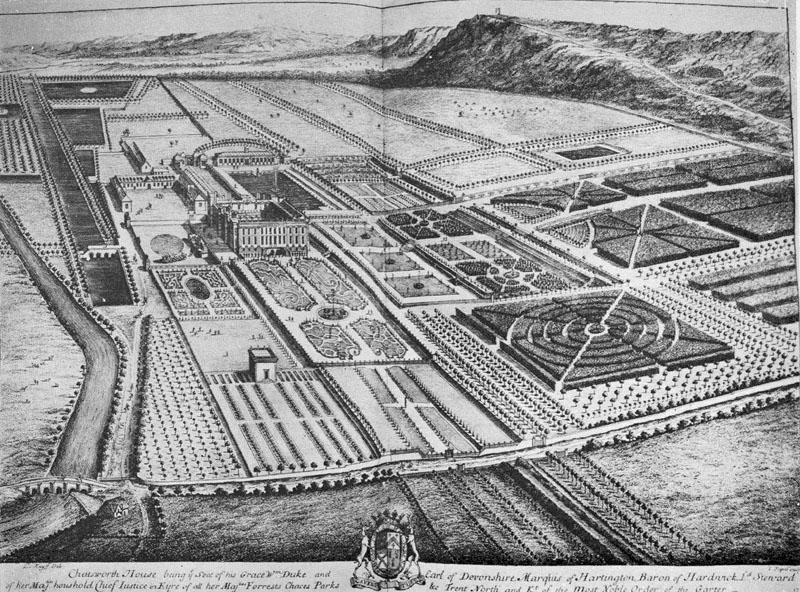
Chatsworth House
Chatsworth House is a stately home in the Derbyshire Dales, north-east of Bakewell and west of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, England. The seat of the Duke of Devonshire, it has belonged to the House of Cavendish, Cavendish family since 1549. It stands on the east bank of the River Derwent, Derbyshire, River Derwent, across from hills between the Derwent and River Wye, Derbyshire, Wye valleys, amid parkland backed by wooded hills that rise to Moorland, heather moorland. The house holds major collections of paintings, furniture, Old Master drawings, neoclassical sculptures and books. Chosen several times as Britain's favourite country house, it is a Grade I listed property from the 17th century, altered in the 18th and 19th centuries. In 2011–2012 it underwent a £14-million restoration. The owner is the Chatsworth House Trust, an independent charitable foundation formed in 1981, on behalf of the Cavendish family. History 11th–16th centuries The name 'Chatsworth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton ( ; 3 September 172817 August 1809) was an English businessman, inventor, mechanical engineer, and silversmith. He was a business partner of the Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton and Watt, Boulton & Watt steam engines, which were a great advance on the state of the art, making possible the mechanisation of factories and mills. Boulton applied modern techniques to the minting of coins, striking millions of pieces for Britain and other countries, and supplying the Royal Mint with up-to-date equipment. Born in Birmingham, he was the son of a Birmingham manufacturer of small metal products who died when Boulton was 31. By then Boulton had managed the business for several years, and thereafter expanded it considerably, consolidating operations at the Soho Manufactory, built by him near Birmingham. At Soho, he adopted the latest techniques, branching into silver plate, ormolu ("gilt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria And Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (abbreviated V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.8 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and named after Queen Victoria and Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert. The V&A is in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, in an area known as "Albertopolis" because of its association with Prince Albert, the Albert Memorial, and the major cultural institutions with which he was associated. These include the Natural History Museum, London, Natural History Museum, the Science Museum (London), Science Museum, the Royal Albert Hall and Imperial College London. The museum is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. As with other national British museums, entrance is free. The V&A covers and 145 galleries. Its collection spans 5,000 years of art, from ancient history to the present day, from the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietra Dura
''Pietra dura'' (), ''pietre dure'' () or intarsia lapidary ( see below), called ''parchin kari'' or ''parchinkari'' () in the Indian subcontinent, is a term for the inlay technique of using cut and fitted, highly polished colored stones to create images. It is considered a decorative art. The stonework, after the work is assembled loosely, is glued stone-by-stone to a substrate after having previously been "sliced and cut in different shape sections, and then assembled together so precisely that the contact between each section was practically invisible". Stability was achieved by grooving the undersides of the stones so that they interlocked, rather like a jigsaw puzzle, with everything held tautly in place by an encircling 'frame'. Many different colored stones, particularly marbles, were used, along with semiprecious, and even precious stones. It first appeared in Rome in the 16th century, reaching its full maturity in Florence. ''Pietra dura'' items are generally crafted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimbolton Cabinet
The Kimbolton Cabinet is an ornate wooden cabinet on a stand, designed by Robert Adam and completed in 1775. It is in the collection of the Victoria and Albert Museum. The cabinet is made from mahogany and oak, decorated with marquetry of satinwood and rosewood, with gilt-bronze ormolu mounts and inlaid with eleven Italian ''pietra dura'' plaques. It was made for the Dukes of Manchester and formerly displayed at their house at Kimbolton Castle. It has been in the collection of the Victoria and Albert Museum since 1949, acquired using funds from the James Rose Vallentin Bequest. Cabinets are box-shaped items of furniture which were usually designed with many cupboards and drawers, to store small objects. The Kimbolton Cabinet was designed as a display object in its own right, and as a mount for the ''pietra dura'' plaques. The front panels suggest doors, but they are false: the cabinet is empty inside, with just one door at each end. The box is mounted on four legs. It measures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audley End
Audley End House is a largely early 17th-century country house outside Saffron Walden, Essex, England. It is a prodigy house, known as one of the finest Jacobean houses in England. Audley End is now one-third of its original size, but is still large, with much to enjoy in its architectural features and varied collections. The house shares some similarities with Hatfield House, except that it is stone-clad as opposed to brick.Hadfield, J. (1970). ''The Shell Guide to England''. London: Michael Joseph. It is currently in the stewardship of English Heritage but long remained the family seat of the Barons Braybrooke, heirs to the estate of whom retain a portion of the contents of the house, the estate, and the right to repurchase as an incorporeal hereditament. Audley End railway station is named after the house. History Audley End was the site of Walden Abbey, a Benedictine monastery that was dissolved and granted to the Lord Chancellor Sir Thomas Audley in 1538 by Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Griffin, 4th Baron Howard De Walden
Field Marshal John Griffin Griffin, 4th Baron Howard de Walden, KB (13 March 1719 – 25 May 1797), was a British Army officer, politician and peer. He served as a junior officer with the Pragmatic Army in the Dutch Republic and Germany during the War of the Austrian Succession. After changing his surname to Griffin in 1749, he commanded a brigade at the Battle of Corbach in July 1760 during the Seven Years' War. He also commanded a brigade at the Battle of Warburg and was wounded at the Battle of Kloster Kampen. Early life He was born John Griffin Whitwell, the son of William Whitwell by his wife Anne Griffin, sister and sole heiress of Edward Griffin, 3rd Baron Griffin of Braybrooke, and granddaughter of James Howard, 3rd Earl of Suffolk and 3rd Baron Howard de Walden (1619–1689). Career Whitwell was educated at Winchester College and commissioned as an ensign in the 3rd regiment of Foot Guards and lieutenant in the Army in 1739. He served with the Pragmatic Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquetry
Marquetry (also spelled as marqueterie; from the French ''marqueter'', to variegate) is the art and craft of applying pieces of wood veneer, veneer to a structure to form decorative patterns or designs. The technique may be applied to case furniture or even seat furniture, to decorative small objects with smooth, veneerable surfaces or to freestanding pictorial panels appreciated in their own right. Marquetry differs from the more ancient craft of inlay, or intarsia, in which a solid body of one material is cut out to receive sections of another to form the surface pattern. The word derives from a Middle French word meaning "inlaid work". Materials The veneers used are primarily woods, but may include bone, ivory, turtle-shell (conventionally called "Tortoiseshell material, tortoiseshell"), mother-of-pearl, pewter, brass or fine metals. Marquetry using colored Straw marquetry, straw was a specialty of some European spa resorts from the end of the 18th century. Many exotic wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |