|
Iberian Language
The Iberian language is the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Ancient Greece, Greek and ancient Rome, Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre-Migration Era (before about AD 375). An ancient Iberians, Iberian culture can be identified as existing between the 7th and 1st centuries BC, at least. Iberian, like all the other Paleohispanic languages except Basque language, Basque, was extinct language, extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD. It had been replaced gradually by Latin, following the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula. The Iberian language is unclassified language, unclassified: while the scripts used to write it have been deciphered to various extents, the language itself remains largely unknown. Links with other languages have been suggested, especially the Basque language, based largely on the observed similarities between the numeral system, numerical systems of the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unclassified Language
An unclassified language is a language whose genetic affiliation to other languages has not been established. Languages can be unclassified for a variety of reasons, mostly due to a lack of reliable data but sometimes due to the confounding influence of language contact, if different layers of its vocabulary or morphology point in different directions and it is not clear which represents the ancestral form of the language. Some poorly known extinct languages, such as Gutian and Cacán, are simply unclassifiable, and it is unlikely the situation will ever change. A supposedly unclassified language may turn out not to be a language at all, or even a distinct dialect, but merely a family, tribal or village name, or an alternative name for a people or language that is classified. If a language's genetic relationship has not been established after significant documentation of the language and comparison with other languages and families, as in the case of Basque in Europe, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
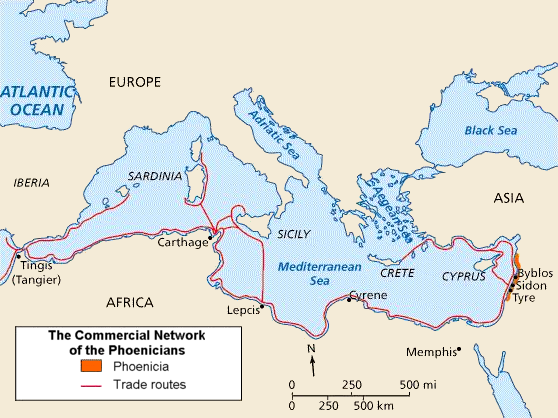
Carthaginian Iberia
Carthaginian Iberia was a province of the larger Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginians conquered the Mediterranean part of Iberia and remained there until the Second Punic war and the Roman conquest of the peninsula. Background The Phoenicians were a people from the eastern Mediterranean who were mainly traders from the cities of Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. They established many trading colonies around the Mediterranean Sea, including colonies in Spain. In the year 814 BC, they founded the city of Carthage on the north African coast in what is now Tunisia. After the fall of Phoenicia to the Babylonians and then the Persians, Carthage became the most powerful Phoenician city in the Mediterranean and the Carthaginians annexed many of the other Phoenician colonies around the coasts of the western Mediterranean, such as Hadrumetum and Thapsus. They also annexed territory in Sicily, Africa, and Sardinia. The city of '' Qart Hadasht'' (; meaning 'New Town', the same name as the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narbonne
Narbonne ( , , ; ; ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and was historically a prosperous port. From the 14th century it declined following a change in the course of the river Aude. While it is the largest commune in Aude, the capital of the Aude department is the smaller commune of Carcassonne. Etymology The source of the town's original name of Narbo is lost in antiquity, and it may have referred to a hillfort from the Iron Age close to the location of the current settlement or its occupants. The earliest known record of the area comes from the Greek Hecataeus of Miletus in the fifth century BC, who identified it as a Celtic harbor and marketplace at that time, and called its inhabitants the ''Ναρβαῖοι''. In ancient inscriptions the name is sometimes rendered in Latin and sometimes transl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppidum D'Ensérune
The Oppidum d'Ensérune is an ancient hill-town (or ''oppidum'') near the village of Nissan-lez-Ensérune, France, located between Béziers and Narbonne close to the D609 (formerly RN9) and Canal du Midi. It has been listed since 1935 as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture. Oppidum d'Ensérune The settlement was occupied without interruption between the 6th century BC and 1st century AD on a hill with good views over the coastal plain, being close to the |
Hérault (river)
The Hérault (; ) is a river in southern France. Its length is . Its source is on the slopes of Mont Aigoual in the Cévennes mountains. It reaches the Mediterranean Sea near Agde. Name The river was known in Latin as ''Arauris'' (or ''Araura'' by Strabo). The name is sometimes considered Pre-Celtic although the element ''Ara-'' suggests a Celtic root. Towns The Hérault flows through the following departments and towns: *Gard: Valleraugue. *Hérault (named after the river): Ganges, Hérault, Ganges, Pézenas (nearby), Agde. Tributaries Navigation The lower reaches of the Hérault, from Bessan to the sea at Agde, are navigable. The lowest are tidal, whilst the next forms part of the Canal du Midi. These two sections of the river are linked to each other, and to the Canal du Midi to the west, by short junction canals and the famous Agde Round Lock. At the upper end of the section of the Hérault used by the Canal du Midi, the Prades Lock provides access to the Canal du Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Coast
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important route for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapa Llengües Paleohispàniques-ang
Mapa or MAPA may refer to: People * Alec Mapa (born 1965), American actor, comedian and writer * Dennis Mapa (born 1969), Filipino economist and statistician * Jao Mapa (born 1976), Filipino actor * Placido Mapa Jr. (born 1932), Filipino businessman, economist, and government official * Suraj Mapa (born 1980), Sri Lankan actor * Victorino Mapa (1855–1927), Filipino chief justice and government official Other uses * "Mapa" (song), a 2021 song by SB19 * Mexican American Political Association * Mapa (publisher), an Israeli subsidiary of Ituran * Mapa Group, a Turkish conglomerate * Mapa, a company producing latex gloves that merged with Hutchinson SA in 1973 * Most Affected People and Areas Most Affected People and Areas, also known by its acronym MAPA, is a term that represents groups and territories disproportionately affected by climate change, such as women, indigenous communities, racial minorities, LGBTQIA+ people, young, older ..., a climate justice concept * Mapa (gir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Romance Languages
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languages Iberian languages is also used as a more inclusive term for all languages spoken on the Iberian Peninsula, which in antiquity included the non-Indo-European Iberian language. are a group of Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar, Andorra and French Catalonia. They are today more commonly separated into West Iberian, East Iberian ( Catalan/ Valencian) and Mozarabic language groups. East Iberian's classification is a subject of ongoing scholarly debate, as some argue that the Occitano-Romance languages composed of Occitan along with the aforementioned two are better classified as Gallo-Romance languages. Evolved from the Vulgar Latin of Iberia, the most widely spoken Iberian Romance languages are Spanish and Portuguese, followed by Catalan-Valencian-Balear and Galician. These languages also have their own regional and local va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Latin
Latin is a member of the broad family of Italic languages. Its alphabet, the Latin alphabet, emerged from the Old Italic alphabets, which in turn were derived from the Etruscan, Greek and Phoenician scripts. Historical Latin came from the prehistoric language of the Latium region, specifically around the River Tiber, where Roman civilization first developed. How and when Latin came to be spoken has long been debated. Various influences on Latin of Celtic speeches in northern Italy, the non-Indo-European Etruscan language in Central Italy, and the Greek in some Greek colonies of southern Italy have been detected, but when these influences entered the native Latin is not known for certain. Surviving Roman-era Latin literature consists almost entirely of Classical Latin pieces usually chosen for their importance as help for people learning to write in Latin. Survivals emphasise polished and sometimes highly stylized literary language texts sometimes termed Golden Latin, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Greek
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Central Ionic), and from BC onward in Asiatic Ionia (East Ionic), where Ionian colonists from Athens founded their cities. Ionic was the base of several literary language forms of the Archaic and Classical periods, both in poetry and prose. The works of Homer and Hesiod are among the most popular poetic works that were written in a literary form of the Ionic dialect, known as Epic or Homeric Greek. The oldest Greek prose, including that of Heraclitus, Herodotus, Democritus, and Hippocrates, was also written in Ionic. By the end of the 5th century BC, Ionic was supplanted by Attic, which had become the dominant dialect of the Greek world. History The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland across the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusitanian Language
Lusitania Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province encompassing most of modern-day Portugal (south of the Douro River) and a large portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and Province of Salamanca). Romans named the region after th ... was an ancient Roman province corresponding to most of modern Portugal. Lusitania, Lusitanian, and Lusitanic may also refer to: Cultures and peoples * Lusitanian language * Lusitanian mythology * Lusitanians, the original Indo-European inhabitants of Lusitania (Proto-Celt) * Lusitanic, the shared linguistic and cultural traditions of the Portuguese-speaking nations Places * Kingdom of Northern Lusitania, proposed by Napoleon for the king of Etruria in Northwestern Portugal * New Lusitania, a Portuguese colony in Brazil Science * Lusitania (alga), a genus of green algae * Lusitanian distribution, a disjunct distribution of a species * HD 45652, a star named Lusitania Sport * S.C. Lusitânia (basketball), an Azorean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtiberian Language
Celtiberian or Northeastern Hispano-Celtic is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula between the headwaters of the Douro, Tagus, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river. This language is directly attested in nearly 200 inscriptions dated from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century AD, mainly in Celtiberian script, a direct adaptation of the northeastern Iberian script, but also in the Latin alphabet. The longest extant Celtiberian inscriptions are those on three Botorrita plaques, bronze plaques from Botorrita near Zaragoza, dating to the early 1st century BC, labeled Botorrita I, III and IV (Botorrita II is in Latin). Shorter and more fragmentary is the Novallas bronze tablet. Overview Under the P/Q Celtic hypothesis, and like its Iberian relative Gallaecian, Celtiberian is classified as a Q Celtic language, putting it in the same category as Goidelic and not P-Celtic like Gaulish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |