|
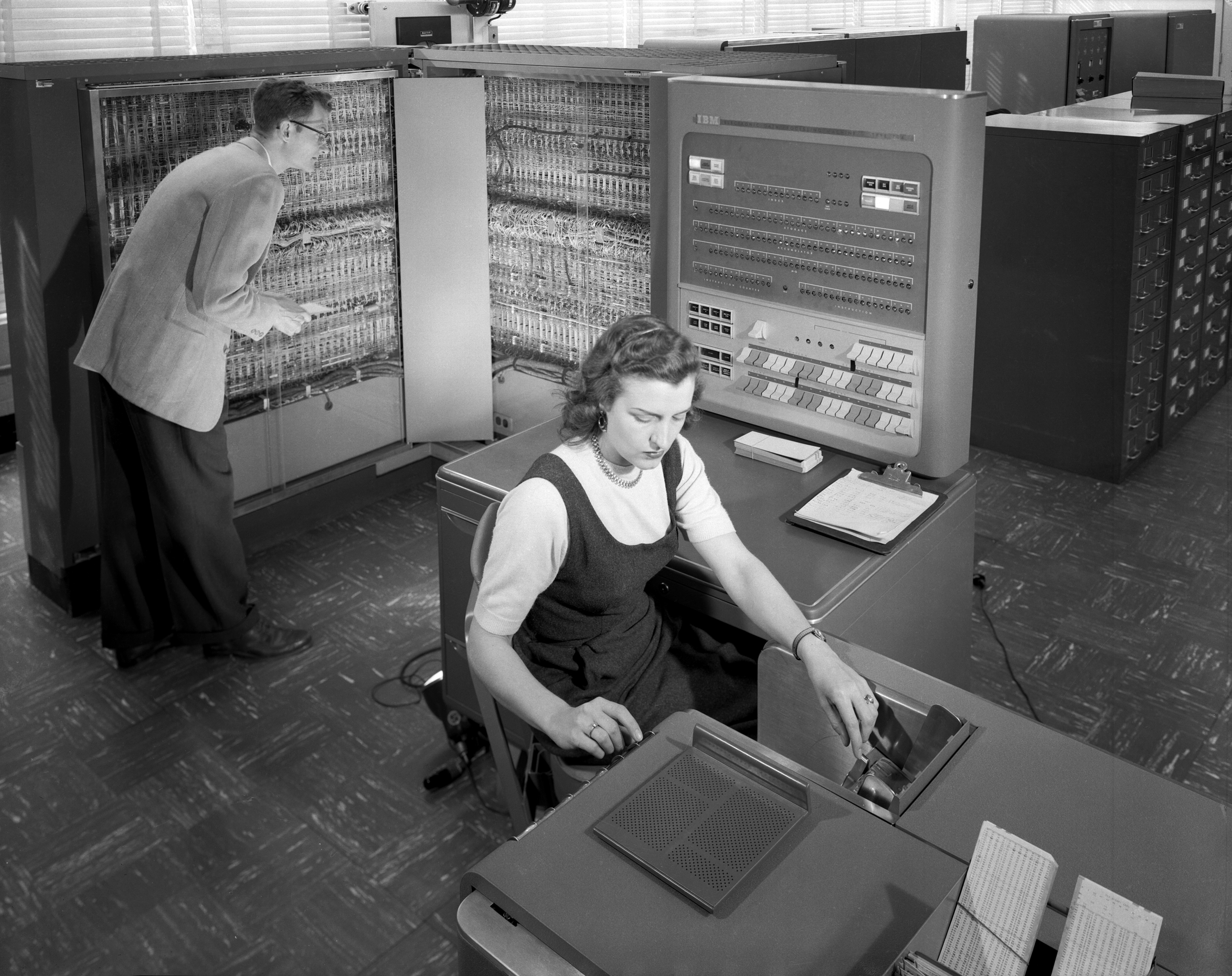
Ibm 7094
The IBM 7090 is a second-generation transistorized version of the earlier IBM 709 vacuum tube mainframe computer that was designed for "large-scale scientific and technological applications". The 7090 is the fourth member of the IBM 700/7000 series scientific computers. The first 7090 installation was in December 1959. In 1960, a typical system sold for $2.9 million (equivalent to $ million in ) or could be rented for $63,500 a month (). The 7090 uses a 36-bit word length, with an address space of 32,768 words (15-bit addresses). It operates with a basic memory cycle of 2.18 μs, using the IBM 7302 Core Storage core memory technology from the IBM 7030 (Stretch) project. With a processing speed of around 100 Kflop/s, the 7090 is six times faster than the 709, and could be rented for half the price. An upgraded version, the 7094, was up to twice as fast. Both the 7090 and the 7094 were withdrawn from sale on July 14, 1969, but systems remained in service for more than a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 7090 Console
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of Tabulating machine, punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the IBM System/360, System/360 and its successors, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input/output, input designed for such a system. Modifying a system in a way that does not allow backward compatibility is sometimes called "wikt:breaking change, breaking" backward compatibility. Such breaking usually incurs various types of costs, such as Switching barriers, switching cost. A complementary concept is ''forward compatibility''; a design that is forward-compatible usually has a Technology roadmap, roadmap for compatibility with future standards and products. Usage In hardware A simple example of both backward and forward compatibility is the introduction of FM broadcasting, FM radio in stereophonic sound, stereo. FM radio was initially monaural, mono, with only one audio channel represented by one signal (electrical engineerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Standard Modular System
The Standard Modular System (SMS) is a system of standard transistorized circuit boards and mounting racks developed by IBM in the late 1950s, originally for the IBM 7030 Stretch. They were used throughout IBM's second-generation computers, peripherals, the IBM 700/7000 series, 7000 series, the IBM 1400 series, 1400 series, and the IBM 1620, 1620. SMS was superseded by Solid Logic Technology (SLT) introduced with System/360 in 1964, however they remained in use with legacy systems through the 1970s. Overview Many IBM peripheral devices that are part of System/360, but were adapted from second-generation designs, continued to use SMS circuitry instead of the newer SLT. These included the IBM 2400, 240x-series tape drives and controllers, the IBM 2540, 2540 card reader/punch and IBM 1403, 1403N1 printer, and the IBM 2821 Control Unit, 2821 Integrated Control Unit for the 1403 and 2540. A few SMS cards used in System/360 peripheral devices even have SLT-type hybrid ICs mounted on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift-field Transistor
The drift-field transistor, also called the drift transistor or graded base transistor, is a type of high-speed bipolar junction transistor having a doping-engineered electric field in the base to reduce the charge carrier base transit time. Invented by Herbert Kroemer at the Central Bureau of Telecommunications Technology of the German Postal Service, in 1953, it continues to influence the design of modern high-speed bipolar junction transistors. Early drift transistors were made by diffusing the base dopant in a way that caused a higher doping concentration near the emitter reducing towards the collector. This graded base happens automatically with the double diffused planar transistor (so they aren't usually called drift transistors). Similar high speed transistors Another way to speed the base transit time of this type of transistor is to vary the band gap across the base, e.g. in the SiGe pitaxial baseBJT the base of Si1−ηGeη can be grown with η approx 0.2 by the colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy-junction Transistor
The germanium alloy-junction transistor, or alloy transistor, was an early type of bipolar junction transistor, developed at General Electric and RCA in 1951 as an improvement over the earlier grown-junction transistor. The usual construction of an alloy-junction transistor is a germanium crystal forming the base, with emitter and collector alloy beads fused on opposite sides. Indium and antimony were commonly used to form the alloy junctions on a bar of N-type germanium. The collector junction pellet would be about 50 mils (thousandths of an inch) in diameter, and the emitter pellet about 20 mils. The base region would be on the order of 1 mil (0.001 inches, 25 μm) thick. There were several types of improved alloy-junction transistors developed over the years that they were manufactured. All types of alloy-junction transistors became obsolete in the early 1960s, with the introduction of the planar transistor which could be mass-produced easily while alloy-junction transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a computer museum in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the Information Age, and explores the Digital Revolution, computing revolution and its impact on society. History The museum's origins date to 1968 when Gordon Bell began a quest for a historical collection and, at that same time, others were looking to preserve the Whirlwind (computer), Whirlwind computer. The resulting ''Museum Project'' had its first exhibit in 1975, located in a converted coat closet in a Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC lobby. In 1978, the museum, now ''The Digital Computer Museum'' (TDCM), moved to a larger DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts and opened to the public in September 1979. Maurice Wilkes presented the first lecture at TDCM in 1979 – the presentation of such lectures has continued to the present time. TDCM incorporated as ''The Computer Museum, Boston, The Computer Museum'' (TCM) in 1982. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, i/o, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, such as another computer system, peripherals, or a human operator. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by an interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Corporation
The Aerospace Corporation is an American nonprofit corporation that operates a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC). The corporation provides technical guidance and advice on all aspects of space missions to military, civil, and commercial customers. As the FFRDC for national-security space, Aerospace works closely with organizations such as the United States Space Force (USSF) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to provide "objective technical analyses and assessments for space programs that serve the national interest". Although the USSF and NRO are primary customers, Aerospace performs work for civil agencies such as NASA and NOAA as well as international organizations and governments in the national interest. Aerospace, as part of its charter, also provides expertise to commercial entities, both established companies and startups, domestically and abroad. History On July 1, 1954, the Western Development Division (WDD) of the United States Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 1400 Series
The IBM 1400 series are second-generation (transistor) mid-range business decimal computers that IBM marketed in the early 1960s. The computers were offered to replace tabulating machines like the IBM 407. The 1400-series machines stored information in magnetic cores as variable-length character strings separated on the left by a special bit, called a "wordmark," and on the right by a "record mark." Arithmetic was performed digit-by-digit. Input and output support included punched card, magnetic tape, and high-speed line printers. Disk storage Disc or disk may refer to: * Disk (mathematics) In geometry, a disk (Spelling of disc, also spelled disc) is the region in a plane (geometry), plane bounded by a circle. A disk is said to be ''closed'' if it contains the circle that constitut ... was also available. Many members of the series could be used as independent systems, as extensions to IBM punched-card equipment, or as auxiliary equipment to other computer systems. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
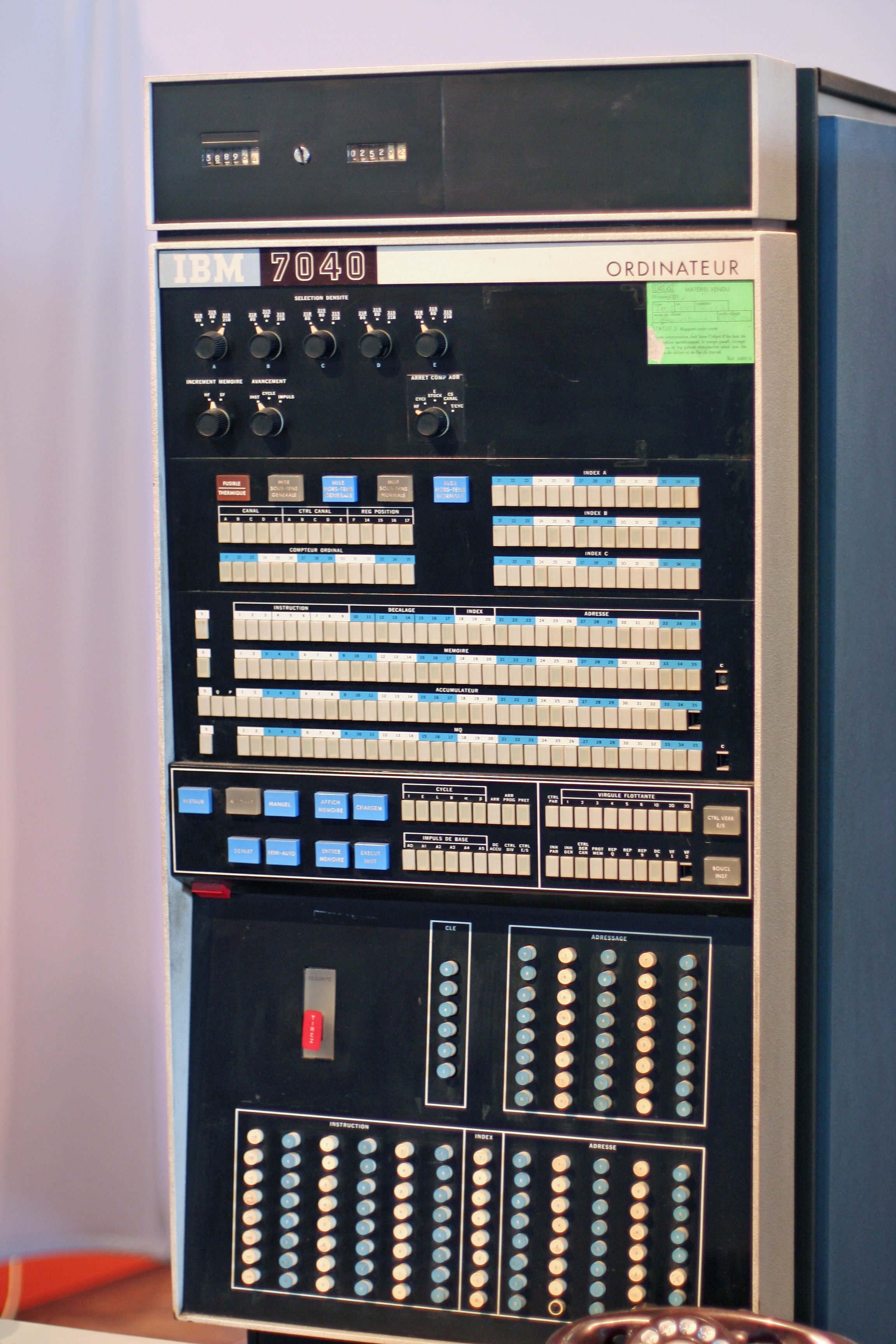
IBM 7040
The IBM 7040 was a historic but short-lived model of transistor computer built in the 1960s. History It was announced by IBM in December 1961, but did not ship until April 1963. A later member of the IBM 700/7000 series of scientific computers, it was a scaled-down version of the IBM 7090. It was not fully compatible with the 7090. Some 7090 features, including index registers, character instructions and floating point, were extra-cost options. It also featured a different input/output architecture, based on the IBM 1414 data synchronizer, allowing more modern IBM peripherals to be used. A model designed to be compatible with the 7040 with more performance was announced as the 7044 at the same time. Peter Fagg headed the development of the 7040 under executive Bob O. Evans. A number of IBM 7040 and 7044 computers were shipped, but it was eventually made obsolete by the IBM System/360 family, announced in 1964. The schedule delays caused by IBM's multiple incompatible archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Pipelining
In computer engineering, instruction pipelining is a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. Pipelining attempts to keep every part of the processor busy with some instruction by dividing incoming instructions into a series of sequential steps (the eponymous "pipeline") performed by different processor units with different parts of instructions processed in parallel. Concept and motivation In a pipelined computer, instructions flow through the central processing unit (CPU) in stages. For example, it might have one stage for each step of the von Neumann cycle: Fetch the instruction, fetch the operands, do the instruction, write the results. A pipelined computer usually has "pipeline registers" after each stage. These store information from the instruction and calculations so that the logic gates of the next stage can do the next step. This arrangement lets the CPU complete an instruction on each clock cycle. It is common for even-nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |