|
Hindu Cosmology
Hindu cosmology is the description of the universe and its states of matter, cycles within time, physical structure, and effects on living entities according to Hindu texts. Hindu cosmology is also intertwined with the idea of a creator who allows the world to exist and take shape. Matter All matter is based on three inert '' gunas'' (qualities or tendencies):James G. Lochtefeld, Guna, in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Vol. 1, Rosen Publishing, , pages 224, 265, 520Theos Bernard (1999), ''Hindu Philosophy'', Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 74–76 * '' sattva'' (goodness) * '' rajas'' (passion) * '' tamas'' (darkness) There are three states of the ''gunas'' that make up all matter in the universe: * ''pradhana'' (root matter): ''gunas'' in an unmixed and unmanifested state (equilibrium). * '' prakriti'' (primal matter): ''gunas'' in a mixed and unmanifested state (agitated). * '' mahat-tattva'' (matter or universal womb): ''gunas'' in a mixed and manifested stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Texts
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These include the Puranas, Itihasa and Vedas. Scholars hesitate in defining the term "Hindu scriptures" given the diverse nature of Hinduism,Dominic Goodall (1996), Hindu Scriptures, University of California Press, , page ix-xliii but many list the Bhagavad Gita and the Agamas as Hindu scriptures,Klaus Klostermaier (2007), A Survey of Hinduism: Third Edition, State University of New York Press, , pages 46–52, 76–77 and Dominic Goodall includes Bhagavata Purana and Yajnavalkya Smriti in the list of Hindu scriptures as well. History There are two historic classifications of Hindu texts: ''Śruti'' – that which is heard, and ''Smriti'' – that which is remembered. The ''Shruti'' refers to the body of most authoritative, ancient religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kurukshetra War and the fates of the Kaurava and the Pāṇḍava princes and their successors. It also contains philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the '' Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an abbreviated version of the '' Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyāsa. There have been many attempts to unravel its historical gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
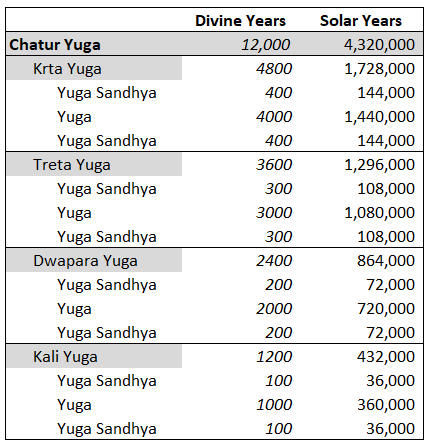
Treta Yuga
''Treta Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the second and second best of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'' and followed by ''Dvapara Yuga''. ''Treta Yuga'' lasts for 1,296,000 years (3,600 divine years). ''Treta'' means 'a collection of three things' in Sanskrit, and is so called because during the ''Treta Yuga'', there were three Avatars of Vishnu that were seen, the fifth, sixth and seventh incarnations as Vamana, Parashurama and Rama, respectively. The bull of Dharma symbolizes that morality stood on three legs during this period. It had all four legs in the ''Satya Yuga'' and two in the succeeding ''Dvapara Yuga''. Currently, in the immoral age of '' Kali'', it stands on one leg. Etymology '' Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satya Yuga
''Satya Yuga'' ( ''Krita Yuga''), in Hinduism, is the first and best of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Kali Yuga'' of the previous cycle and followed by ''Treta Yuga''. ''Satya Yuga'' lasts for 1,728,000 years (4,800 divine years). ''Satya Yuga'' is known as the age of truth, when humanity is governed by gods, and every manifestation or work is close to the purest ideal and humanity will allow intrinsic goodness to rule supreme. It is sometimes referred to as the "Golden Age". The god ''Dharma'' (depicted in the form of a bull), which symbolizes morality, stood on all four legs during this period. The legs of ''Dharma'' reduce by one in each ''yuga'' that follows. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived from ' (Proto-Indo-European: 'to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ''dharma'' in European languages, it is commonly translated as "righteousness", "merit" or "religious and moral duties" governing individual conduct.Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. (9 April 2019)Dharma. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Accessed 14 September 2021. In Hinduism, dharma is one of the four components of the ''Puruṣārtha'', the aims of life, and signifies behaviours that are considered to be in accord with '' Ṛta'', the order that makes life and universe possible. It includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living".see: *"Dharma", ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th Ed. (2013), Columbia University Press, Gale, ; *Steven Rosen (2006), Essential Hinduism, Praeger, , Chapter 3. It had a transtempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuga Cycle
A ''Yuga'' Cycle ( ''chatur yuga'', ''maha yuga'', etc.) is a cyclic age (epoch) in Hindu cosmology. Each cycle lasts for 4,320,000 years (12,000 divine years) and repeats four ''yugas'' (world ages): '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', ''Dvapara Yuga'', and ''Kali Yuga''. As a ''Yuga'' Cycle progresses through the four ''yugas'', each '' yuga's'' length and humanity's general moral and physical state within each ''yuga'' decrease by one-fourth. ''Kali Yuga'', which lasts for 432,000 years, is believed to have started in 3102 BCE. Near the end of ''Kali Yuga'', when virtues are at their worst, a cataclysm and a re-establishment of ''dharma'' occur to usher in the next cycle's ''Satya Yuga'', prophesied to occur by Kalki. There are 71 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''manvantara'' (age of Manu) and 1,000 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a '' kalpa'' (day of Brahma). Lexicology A ''Yuga'' Cycle has several names. Age or ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग, , an age of the gods): : "Age" and "''Yuga''", some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manu (Hinduism)
Manu ( sa, मनु) is a term found as various meanings in Hinduism. In early texts, it refers to the archetypal man, or to the first man ( progenitor of humanity). The Sanskrit term for 'human', मानव ( IAST: mānava) means 'of Manu' or 'children of Manu'. In later texts, Manu is the title or name of fourteen rulers of earth, or alternatively as the head of dynasties that begin with each cyclic '' kalpa'' (aeon) when the universe is born anew. The title of the text ''Manusmriti'' uses this term as a prefix, but refers to the first Manu – Svayambhuva, the spiritual son of Brahma. In the earliest mention of Manu, in the Rigveda, Manu is only the ancestor of the "Five Peoples", or "Páñca Jánāḥ" (the five tribes being the Anu, Druhyus, Yadus, Turvashas, and Purus). The Aryans considered all other peoples to be a-manuṣa. Later, in the Hindu cosmology, each ''kalpa'' consists of fourteen Manvantaras, and each Manvantara is headed by a different Manu. The curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manvantara
A ''manvantara'', in Hindu cosmology, is a cyclic period of time identifying the duration, reign, or age of a Manu, the progenitor of mankind. In each ''manvantara'', seven Rishis, certain deities, an Indra, a Manu, and kings (sons of Manu) are created and perish. Each ''manvantara'' is distinguished by the Manu who rules/reigns over it, of which we are currently in the seventh ''manvantara'' of fourteen, which is ruled by Vaivasvata Manu.Account of the several Manus and Manwantaras , translated by Horace Hayman Wilson, 1840, Book III: Chapter I. p. 259, The first Manu was [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pralaya
Pralaya ( sa, प्रलय, , Apocalypse or the Annihilation of the Universe, translit=Pralaya) is a concept in Hindu eschatology. Generally referring to four different phenomena, it is most commonly used to indicate the event of the dissolution of the entire universe that follows a ''kalpa'' (a period of 4.32 billion years) called the ''Brahmapralaya''. Pralaya also refers to ''Nityapralaya'', the continuous destruction of all animate and inanimate beings that occurs on a daily basis, ''Prakritapralaya'', the great flood produced by Prakriti (Nature) that ends all of creation after the completion of the Chaturyuga (four-age) cycle, and ''Atyantikapralaya'', the dissolution of one's Atman (Self) due to its union with Brahman (Ultimate Reality). A concept that has been referenced in literature since the Upanishads, the concept of pralaya has been widely discussed in Hindu cosmology as well as philosophy. Description Hindu cosmology posits an endless cycle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212–226. He is associated with creation, knowledge, and the ''Vedas''. Brahma is prominently mentioned in creation legends. In some ''Puranas'', he created himself in a golden embryo known as the Hiranyagarbha. Brahma is frequently identified with the Vedic god Prajapati.;David Leeming (2005), The Oxford Companion to World Mythology, Oxford University Press, , page 54, Quote: "Especially in the Vedanta Hindu Philosophy, Brahman is the Absolute. In the Upanishads, Brahman becomes the eternal first cause, present everywhere and nowhere, always and never. Brahman can be incarnated in Brahma, in Vishnu, in Shiva. To put it another way, everything that is, owes its existence to Brahman. In this sense, Hinduism is ultimately monotheistic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalpa (aeon)
A ''kalpa'' is a long period of time (aeon) in Hindu and Buddhist cosmology, generally between the creation and recreation of a world or universe. Etymology ''Kalpa'' ( sa, कल्प, , a formation or creation) in this context, means "a long period of time (aeon) related to the lifetime of the universe (creation)." It is derived from ''कॢप्'' (kḷp) + -अ (-a, nominalizing suffix) ( sa, कॢप्, kḷp, to create, prepare, form, produce, compose, invent). Hinduism In Hinduism, a ''kalpa'' is equal to 4.32 billion years, a "day of Brahma" (12-hour day proper) or one thousand '' mahayugas'', measuring the duration of the world. Each ''kalpa'' is divided into 14 '' manvantara'' periods, each lasting 71 ''Yuga Cycles'' (306,720,000 years). Preceding the first and following each ''manvantara'' period is a juncture (''sandhya'') equal to the length of a '' Satya Yuga'' (1,728,000 years). A ''kalpa'' is followed by a '' pralaya'' (dissolution) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakthi Group
The Sakthi Group is an Indian multinational conglomerate with operational areas in India, China, Europe, Middle East and United States. The group has operations in Sugar, Dairy, Industrial Alcohol, Automobile distribution and components, Transportation, Energy, Textiles, IT, Education and Healthcare. N. Mahalingam is the Founder. The group has automotive dealerships for leading brands of Maruti Suzuki and Tata vehicles in various places in South India. The group is also involved in Petrol Pump Operations, Indane LPG Distribution and the sale of consumer products and electronics. It also has a footprint in the textiles industries with Sri Sakthi Textiles Ltd. Industries Sugar In 1961, Sakthi Sugars Limited was established and commenced its commercial production in 1964. It has sugar plants at Sakthi Nagar, Sivaganga, Modakurichi and Dhenkanal. With the aggregate capacity of 19,500 tonnes of cane Crush Per Day it is one of the largest producers of sugar in India. It diversifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |