|
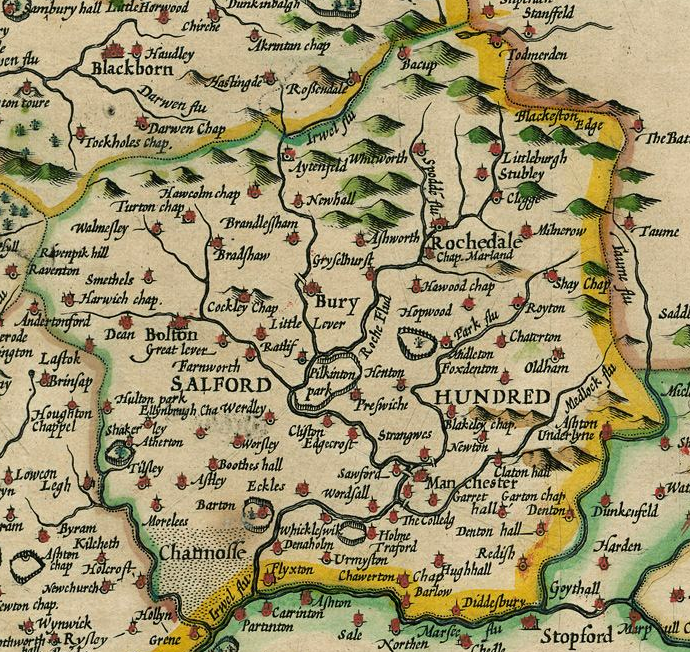
Hulme Locks
Hulme () is an inner city area and electoral ward of Manchester, in Greater Manchester, England, immediately south of Manchester city centre. It has a significant industrial heritage. Historically in Lancashire, the name Hulme is derived from the Old Norse word for a small island, or land surrounded by water or marsh, indicating that it may have been first settled by Norse invaders in the period of the Danelaw. History Hulme was formerly a township in the parish of Manchester, in 1866 Hulme became a separate civil parish, on 26 March 1896 the parish was abolished to form South Manchester. In 1891 the parish had a population of 71,96. Toponymy Hulme derives its name from the Old Norse ''holmr, holmi'', through Old Danish ''hulm'' or ''hulme'' meaning small islands or land surrounded by streams, fen or marsh. Ekwall, Eilert ''The Place-Names of Lancashire'' (1922, The University Press, Lime Grove, Manchester) The area may have fitted this description at the time of the Scand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester City Council
Manchester City Council is the Local government in England, local authority for the City status in the United Kingdom, city of Manchester in Greater Manchester, England. Manchester has had an elected local authority since 1838, which has been reformed several times. Since 1974 the council has been a metropolitan borough council. It provides the majority of local government services in the city. The council has been a member of the Greater Manchester Combined Authority since 2011. The council has been under Labour Party (UK), Labour majority control since 1971. It is based at Manchester Town Hall. History Manchester had been governed as a Ancient borough, borough in the 13th and 14th centuries, but its borough status was not supported by a royal charter. An inquiry in 1359 ruled that it was only a market town, not a borough. It was then governed by manorial courts and the parish vestry until the 18th century. In 1792 a body of improvement commissioners known as the 'Manchester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester (ancient Parish)
Manchester was an ancient ecclesiastical parish of the hundred of Salford, in Lancashire, England. It encompassed several townships and chapelries, including the then township of Manchester (now Manchester city centre). Other townships are now parts of the Anglican Diocese of Manchester and/or Greater Manchester. In the Domesday Book the parish of Manchester is recorded as including St Michael's Church in Ashton-under-Lyne as well as the mother church of St Mary's in Manchester. Although by the 13th century Ashton had formed its own separate parish, the advowson was held by Manchester as late as 1458. Townships In 1866 the townships became recognised as separate civil parishes. Part, but not all, of this area was in the municipal borough of Manchester, which expanded with the decades. In 1896 the parishes of the City of Manchester outside the remaining Manchester parish were re-organised as North Manchester and South Manchester parishes, which were themselves re-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salford (hundred)
The Salford Hundred (also known as Salfordshire) was one of the Hundred (county division), subdivisions (a hundred) of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire in Northern England. Its name alludes to its judicial centre being the township of Salford, Greater Manchester, Salford (the suffix ''-shire'' meaning the territory was appropriated to the prefixed settlement). It was also known as the Royal Manor of Salford and the Salford wapentake.. Origins The Manor or Hundred of Salford had Anglo-Saxon origins. The ''Domesday Book'' recorded that the area was held in 1066 by Edward the Confessor. Salford was recorded as part of the territory of ''Inter Ripam et Mersam'' or "Between Ribble and Mersey", and it was included with the information about Cheshire, though it cannot be said clearly to have been part of Cheshire. The area became a subdivision of the County Palatine of Lancaster (or Lancashire) on its creation in 1182. Salford Hundred Court In spite of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a Barony (Ireland), barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas, 2nd Earl Of Lancaster
Thomas, 2nd Earl of Lancaster ( 1278 – 22 March 1322) was an English nobleman of the first House of Lancaster of the royal Plantagenet Dynasty. He was Earl of Lancaster, Leicester, and Derby from 1296 to 1322, and Earl of Lincoln and Salisbury '' jure uxoris'' from 1311 to 1322. As one of the most powerful barons of England, Thomas was one of the leaders of the baronial opposition to his first cousin, King Edward II. Early life and, marriage Thomas was the eldest son of Edmund Crouchback and Blanche of Artois, Queen Dowager of Navarre and niece of King Louis IX of France. Crouchback was the son of King Henry III of England. Through his mother, Thomas was a half-brother of Queen Joan I of Navarre. His marriage to Alice de Lacy was not successful. They had no children together, while he fathered, illegitimately, two sons named John and Thomas. In 1317, Alice was abducted from her manor at Canford, Dorset, by Richard de St Martin, a knight in the service of John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Mersey
The River Mersey () is a major river in North West England. Its name derives from Old English and means "boundary river", possibly referring to its having been a border between the ancient kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria. For centuries it has formed part of the boundary between the historic counties of Lancashire and Cheshire. The Mersey starts at the confluence of the River Tame and River Goyt in Stockport. It flows westwards through south Manchester, then into the Manchester Ship Canal near Irlam Locks, becoming a part of the canal and maintaining its water levels. After it exits the canal, flowing towards Warrington where it widens. It then narrows as it passes between Runcorn and Widnes. The river widens into a large estuary, which is across at its widest point near Ellesmere Port. The course of the river then turns northwards as the estuary narrows between Liverpool and Birkenhead on the Wirral Peninsula to the west, and empties into Liverpool Bay. In total the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Medlock
The River Medlock in Greater Manchester, England rises in east Oldham and flows south and west for to join the River Irwell in Manchester city centre. Sources Rising in the hills that surround Strinesdale just to the eastern side of Oldham MBC, the Medlock flows through the steep-sided wooded gorge that separates Lees from Ashton-under-Lyne and the Daisy Nook Country Park with its 19th century aqueduct carrying the disused Hollinwood Branch Canal over the shallow river. Lower reaches The final miles of the river flowing to the River Irwell have been extensively modified. The river is culverted underneath the car park of the City of Manchester Stadium (the site of a former gasworks). It is visible flowing through Mayfield Park and under a bridge on Baring Street, close to Piccadilly station, before running again in a culvert beneath the former University of Manchester Institute of Science & Technology campus (London Road (A6) to Princess Street), then under Hulme Stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Irwell
The River Irwell ( ) is a tributary of the River Mersey in north-west England. It rises at Irwell Springs on Deerplay Moor, approximately north of Bacup and flows southwards for to meet the Mersey near Irlam Locks. The Irwell marks the boundary between Manchester and Salford, Greater Manchester, Salford, and its lower reaches have been canalised and now form part of the Manchester Ship Canal. In the 17th and 18th centuries, the Irwell's lower reaches were a trading route that became part of the Mersey and Irwell Navigation. In the 19th century, the river's course downstream of Manchester was permanently altered by the construction of the Manchester Ship Canal which opened in 1896. The canal turned Manchester and Salford into a major inland seaport and led to the development of Trafford Park, which became the largest industrial estate in Europe. Further changes were made in the 20th and 21st centuries to prevent flooding in Manchester and Salford, including the construction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes a part of northern Finland). In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and cultural similarities. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eilert Ekwall
Bror Oscar Eilert Ekwall (8 January 1877 in Vallsjö – 23 November 1964 in Lund) was a Swedish academic, Professor of English at Sweden's Lund University from 1909 to 1942 and one of the outstanding scholars of the English language in the first half of the 20th century. He wrote works on the history of English, but he is best known as the author of numerous important books on English place-names (in the broadest sense) and personal names. Scholarly works His chief works in this area are ''The Place-Names of Lancashire'' (1922), ''English Place-Names in -ing'' (1923, new edition 1961), ''English River Names'' (1928), ''Studies on English Place- and Personal Names'' (1931), ''Studies on English Place-Names'' (1936), ''Street-Names of the City of London'' (1954), ''Studies on the Population of Medieval London'' (1956), and the monumental ''Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-Names'' (1936, new editions 1940, 1947/51 and the last in 1960). The ''Dictionary'' remained the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Danish
The Danish language developed during the Middle Ages out of Old East Norse, the common predecessor of Danish and Swedish. It was a late form of common Old Norse. The Danish philologist Johannes Brøndum-Nielsen divided the history of Danish into "Old Danish" from 800 AD to 1525 and "Modern Danish" from 1525 and onwards. He subdivided Old Danish into "Runic Danish" (800–1100), Early Middle Danish (1100–1350) and Late Middle Danish (1350–1525). Runic Danish Old East Norse is in Sweden called '' Runic Swedish'' and in Denmark ''Runic Danish'', but until the 12th century, the dialect was the same in the two countries. The dialects are called ''runic'' because the main body of text appears in the runic alphabet. Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark alphabet, Old Norse was written with the Younger Futhark alphabet, which only had 16 letters. Due to the limited number of runes, some runes were used for a range of phonemes, such as the rune for the vowel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse Language
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia, and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid- to late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not precise, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse (Old West Nordic, often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse (Old East Nordic), and Old Gutnish. Old West Norse and Old East Norse formed a dialect continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |