|
Howard Stansbury
Howard Stansbury (February 8, 1806 – April 17, 1863) was a major in the U.S. Army Corps of Topographical Engineers. One of his most notable achievements was leading a two-year expedition (1849–1851) to survey the Great Salt Lake and its surroundings. The expedition report entitled ''Exploration and survey of the valley of the Great Salt Lake of Utah, including a reconnaissance of a new route through the Rocky Mountains'' was published in 1852 providing the first serious scientific exploration of the flora and fauna of the Great Salt Lake Valley as well as a favorable impression of the members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, who had settled there beginning in 1847. Career Stansbury was born in 1806 in New York City. He was trained as a civil engineer and joined the Topographical Bureau in 1828. In the service of the bureau he surveyed the James River in 1836, and the Illinois and Kaskaskia Rivers in 1837. In 1838 he oversaw the construction of a road from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
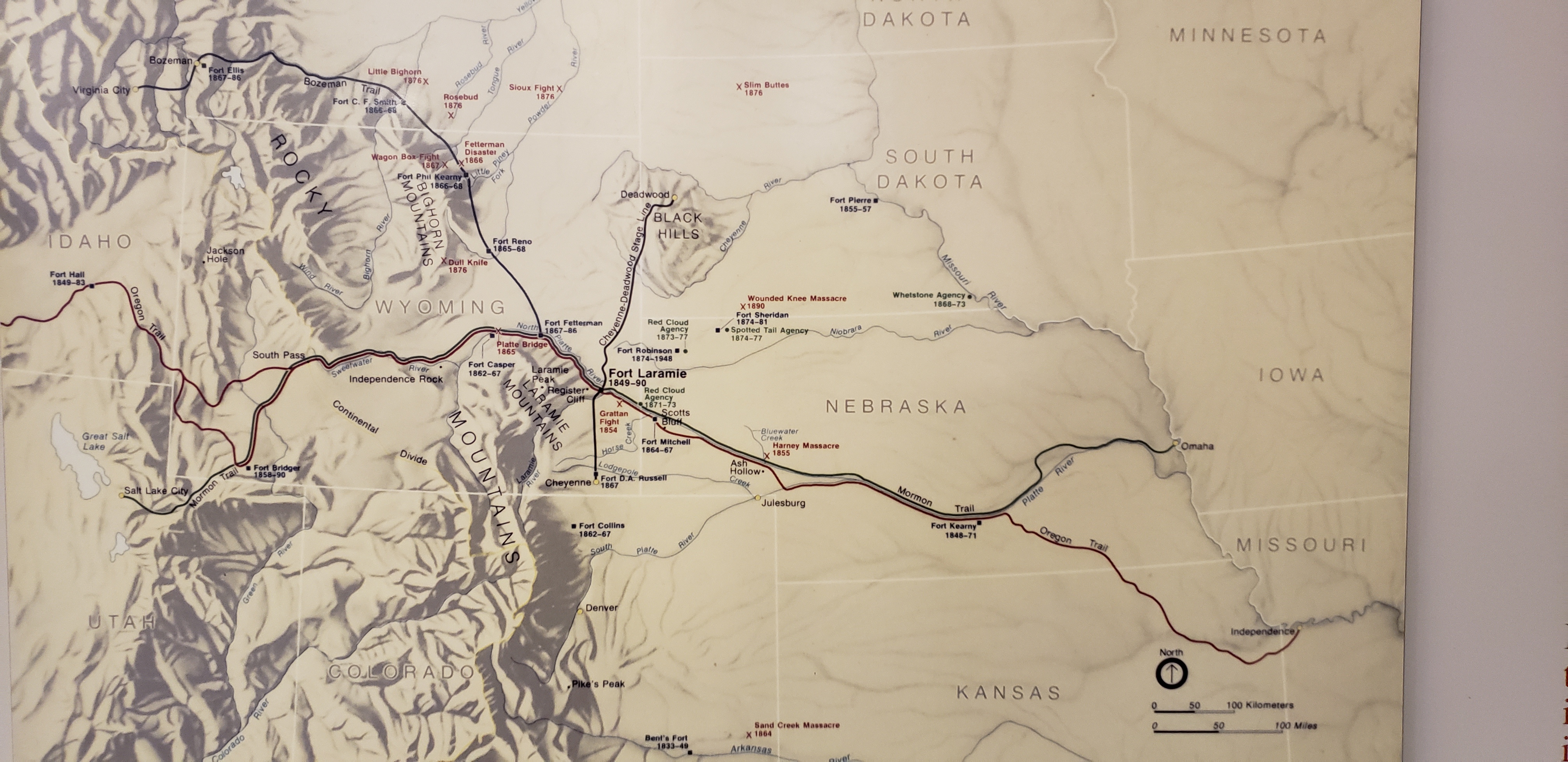
Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in North America that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon Territory. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail crossed what is now the states of Kansas, Nebraska, and Wyoming. The western half crossed the current states of Idaho and Oregon. The Oregon Trail was laid by fur traders and trappers from about 1811 to 1840 and was initially only passable on foot or horseback. By 1836, when the first migrant wagon train was organized in Independence, Missouri, a wagon trail had been cleared to Fort Hall, Idaho. Wagon trails were cleared increasingly farther west and eventually reached the Willamette Valley in Oregon, at which point what came to be called the Oregon Trail was complete, though further improvements in the forms of bridges, cutoffs, ferries, and roads would make the trip faster and safer. From various starting points in Iowa, Missouri, or Nebraska Territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
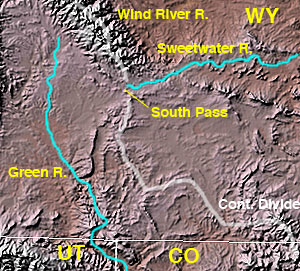
Sweetwater River (Wyoming)
The Sweetwater River is a long tributary of the North Platte River,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed March 21, 2011 in the U.S. state of Wyoming. As a part of the Mississippi River system, its waters eventually reach the Gulf of Mexico. Course The Sweetwater rises in southwestern Fremont County, at the continental divide near South Pass Wyoming, on the southern end of the Wind River Range. It flows ENE along the north side of the Antelope Hills, then ESE, through Fremont County, past Jeffrey City, between the Granite Mountains to the north and the Green Mountains (Wyoming) to the south, through what are now cattle-raising areas. In southern Natrona County, it passes Devil's Gate and Independence Rock along the Oregon, California and Mormon Trails, and empties into the North Platte as the Sweetwater arm of Pathfinder Reservoir. History The Sweetwater River valley provided a route used by fur tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pass (Wyoming)
South Pass (elevation and ) is a route across the Continental Divide, in the Rocky Mountains in southwestern Wyoming. It lies in a broad high region, wide, between the nearly Wind River Range to the north and the over Oregon Buttes and arid, saline near-impassable Great Divide Basin to the south. The Pass lies in southwestern Fremont County, approximately SSW of Lander. Though it approaches a mile and a half high, South Pass is the lowest point on the Continental Divide between the Central and Southern Rocky Mountains. The passes furnish a natural crossing point of the Rockies. The historic pass became the route for emigrants on the Oregon, California, and Mormon trails to the West during the 19th century. It was designated as a U.S. National Historic Landmark on January 20, 1961. History Though well known to Native Americans, South Pass was first traversed in 1812 by European American explorers who were seeking a safer way to return from the West Coast than they had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Bridger
Fort Bridger was originally a 19th-century fur trading outpost established in 1842, on Blacks Fork of the Green River, in what is now Uinta County, Wyoming, United States and was then part of Mexico. It became a vital resupply point for wagon trains on the Oregon, California, and Mormon Trails. The US Army established a military post here in 1858 during the Utah War, until it was finally closed in 1890. A small town, Fort Bridger, Wyoming, remains near the fort and takes its name from it. Bridger's trading post The post was established by the mountain man Jim Bridger, after whom it is named, and Louis Vasquez. In December 1843, Bridger wrote to Pierre Chouteau Jr., "I have established a small fort, with a blacksmith shop and a supply of iron in the road of emigrants on Black Fork of Green River, which promises fairly." According to Stanley Vestal, "His fort consisted simply of an eight-foot stockade, with a corral adjoining on the north. Within that stockade stood four log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle At Fort Utah
The Provo River Massacre (also known as the Battle at Fort Utah, or Fort Utah Massacre) was a violent attack and massacre in 1850 in which 90 Mormon militiamen surrounded an encampment of Timpanogos families on the Provo River, and laid siege for two days. They eventually shot between 40 and 100 Native American men and one woman with guns and a cannon during the siege and subsequent pursuit, capture, and execution of the two groups that fled during the last night. One militiaman died and eighteen were wounded from return fire during the siege. Of the Timpanogos people who fled in the night, one group escaped southward, and the other ran east to Rock Canyon. Both groups were captured, however, and the men were executed. Over 40 Timpanogos children, women, and a few men were taken as prisoners to nearby Fort Utah. They were later taken northward to the Salt Lake Valley and sold as slaves to church members there. The bodies of up to 50 Timpanogos men were beheaded by some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timpanogos
The Timpanogos (Timpanog, Utahs or Utah Indians) are a tribe of Native Americans who inhabited a large part of central Utah, in particular, the area from Utah Lake east to the Uinta Mountains and south into present-day Sanpete County. Most Timpanogos live on the Uintah Valley Reservation. They are not enrolled in the Ute Indian Tribe of the Uintah and Ouray Reservation. During the mid-19th century, when Mormon pioneers entered Utah territory, the Timpanogos were one of the principal tribes in the region based on population, area occupied, and influence. Linguists have had difficulty identifying (or classifying) their language. Historically, most communication was carried out in Spanish or English, and many of their leaders spoke several dialects of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. While the Timpanogos are typically classified as Ute people, they are a Shoshone band. Other Shoshone bands occupied parts of Utah, and historian Hubert Howe Bancroft wrote i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Carrington
Albert Carrington (January 8, 1813 – September 19, 1889) was an apostle and member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles and First Presidency of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). Early life Carrington was born in Royalton, Vermont. He graduated from Dartmouth College in 1833 and taught school and studied law in Pennsylvania. Andrew Jenson, '' Latter-day Saint Biographical Encyclopedia''. (Salt Lake City, Utah: Jenson Historical Company, 1901) vol. 1pp. 126http://contentdm.lib.byu.edu/cdm/ref/collection/BYUIBooks/id/3396 –27]. In 1839, he married Rhoda Maria Woods. The Carringtons were baptized into the Church of Christ (Latter Day Saints), Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints in Wiota, Wisconsin, on July 18, 1841, and in 1844 moved to Nauvoo, Illinois, to join the gathering of Latter Day Saints. In January 1846, Carrington took Mary Rock as a plural wife. Following the death of Joseph Smith, Carrington followed Brigham Young to the Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigham Young
Brigham Young ( ; June 1, 1801August 29, 1877) was an American religious leader and politician. He was the second President of the Church (LDS Church), president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) from 1847 until his death in 1877. He also served as the first List of governors of Utah, governor of the Utah Territory from 1851 until his resignation in 1858. Young was born in 1801 in Vermont and raised in Upstate New York. After working as a painter and carpenter, he became a full-time LDS Church leader in 1835. Following a short period of service as a missionary, he moved to Missouri in 1838. Later that year, Missouri governor Lilburn Boggs signed the Mormon Extermination Order, and Young organized the migration of the Latter Day Saints from Missouri to Illinois, where he became an inaugural member of the Council of Fifty. In 1844, while he was traveling to gain support for Joseph Smith 1844 presidential campaign, Joseph Smith's presidential campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several groups following different leaders; the majority followed Brigham Young, while smaller groups followed Joseph Smith III, Sidney Rigdon, and James Strang. Most of these smaller groups eventually merged into the Community of Christ, and the term ''Mormon'' typically refers to members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), as today, this branch is far larger than all the others combined. People who identify as Mormons may also be independently religious, secular, and non-practicing or belong to other denominations. Since 2018, the LDS Church has expressed the desire that its followers be referred to as "members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints", or more simply as "Latter-day Saints". Mormons ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Hall
Fort Hall was a fort in the Western United States that was built in 1834 as a fur trading post by Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth. It was located on the Snake River in the eastern Oregon Country, now part of present-day Bannock County in southeastern Idaho. Wyeth was an inventor and businessman from Boston, Massachusetts, who also founded a post at Fort William, in present-day Portland, Oregon, as part of a plan for a new trading and fisheries company. In 1837, unable to compete with the powerful British Hudson's Bay Company, based at Fort Vancouver, Wyeth sold both posts to it. Great Britain and the United States both operated in the Oregon Country in these years. After being included in United States territory in 1846 upon settlement of the northern boundary with Canada, Fort Hall developed as an important station for emigrants through the 1850s on the Oregon Trail; it was located at the end of the common stretch from the East shared by the three far west emigrant trails. Soon a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Valley
Cache Valley ''( Shoshoni: Seuhubeogoi, “Willow Valley”)'' is a valley of northern Utah and southeast Idaho, United States, that includes the Logan metropolitan area. The valley was used by 19th century mountain men and was the site of the 1863 Bear River Massacre of 250 to 400 Shoshone people. The name, Cache Valley is often used synonymously to describe the Logan Metropolitan Area, one of the fastest growing metro areas in the US per capita — both in terms of economic GDP and population. History Alongside habitation by the Shoshone and other indigenous peoples, European explorer Michel Bourdon discovered Cache Valley 1818 during a MacKenzie fur expedition. The valley was subsequently used for the second of the annual gatherings of mountain men. Many of the trappers who worked in the valley came from the Hudson's Bay Company, the Northwest Fur Company, and the Rocky Mountain Fur Company. The name "Cache Valley" was derived by the fur trappers who hid their tradin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |