|
House Of Andechs
The House of Andechs was a feudal line of Bavarian princes in the 12th and 13th centuries. The counts of Dießen-Andechs (1100 to 1180) obtained territories in northern Dalmatia on the Adriatic seacoast, where they became Margraves of Istria and ultimately dukes of a short-lived imperial state named Merania from 1180 to 1248. They were also self-styled lords of Carniola. History The noble family originally resided in southwestern Bavaria at the castle of Ambras near Innsbruck, controlling the road to the March of Verona across the Brenner Pass, at Dießen am Ammersee and Wolfratshausen. One Count Rasso (''Rath'') is documented in Dießen, who allegedly fought against the invading Magyars in the early 10th century and established the monastery of Grafrath. By their ancestor Count Palatine Berthold of Reisensburg, a grandson of the Bavarian duke Arnulf the Bad, the Andechser may be affiliated with the Luitpolding dynasty. Berthold appears a fierce enemy of King Otto I of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Austria
The Duchy of Austria (; ) was a medieval principality of the Holy Roman Empire, established in 1156 by the '' Privilegium Minus'', when the Margraviate of Austria ('' Ostarrîchi'') was detached from Bavaria and elevated to a duchy in its own right. After the ruling dukes of the House of Babenberg became extinct in male line, there was as much as three decades of rivalry on inheritance and rulership, until the German king Rudolf I took over the dominion as the first monarch of the Habsburg dynasty in 1276. Thereafter, Austria became the patrimony and ancestral homeland of the dynasty and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. In 1453, the archducal title of the Austrian rulers, invented by Duke Rudolf IV in the forged '' Privilegium Maius'' of 1359, was officially acknowledged by the Habsburg emperor Frederick III. Geography Initially, the duchy was comparatively small in area, roughly comprising the modern-day Austrian state of Lower Austria. As a former border march, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasso
Saint Rasso of Andechs (also ''Rasso of Grafrath, Graf Ratt, Ratho, Grafrath, Rasso von Andechs'') () was a Bavarian count and military leader, pilgrim, and saint. He was the count (''Graf'') of Dießen-Andechs, leading the Bavarians against invading Magyars in the tenth century. No contemporary ''Vita'' of Rasso has survived and various legends arose around his cult in the late Middle Ages. However, there is no reason to doubt that there existed a count named Rasso who fought against the Magyars in the 950s.Charles R. Bowlus, ''The Battle of Lechfeld And Its Aftermath, August 955: The End'' (Ashgate Publishing, 2006), 143n. As a middle-aged man, he went on a pilgrimage to the Holy Land and Rome, where he collected relics, returning to found a Benedictine abbey at Wörth, later named Grafrath after him.Ott, Michael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
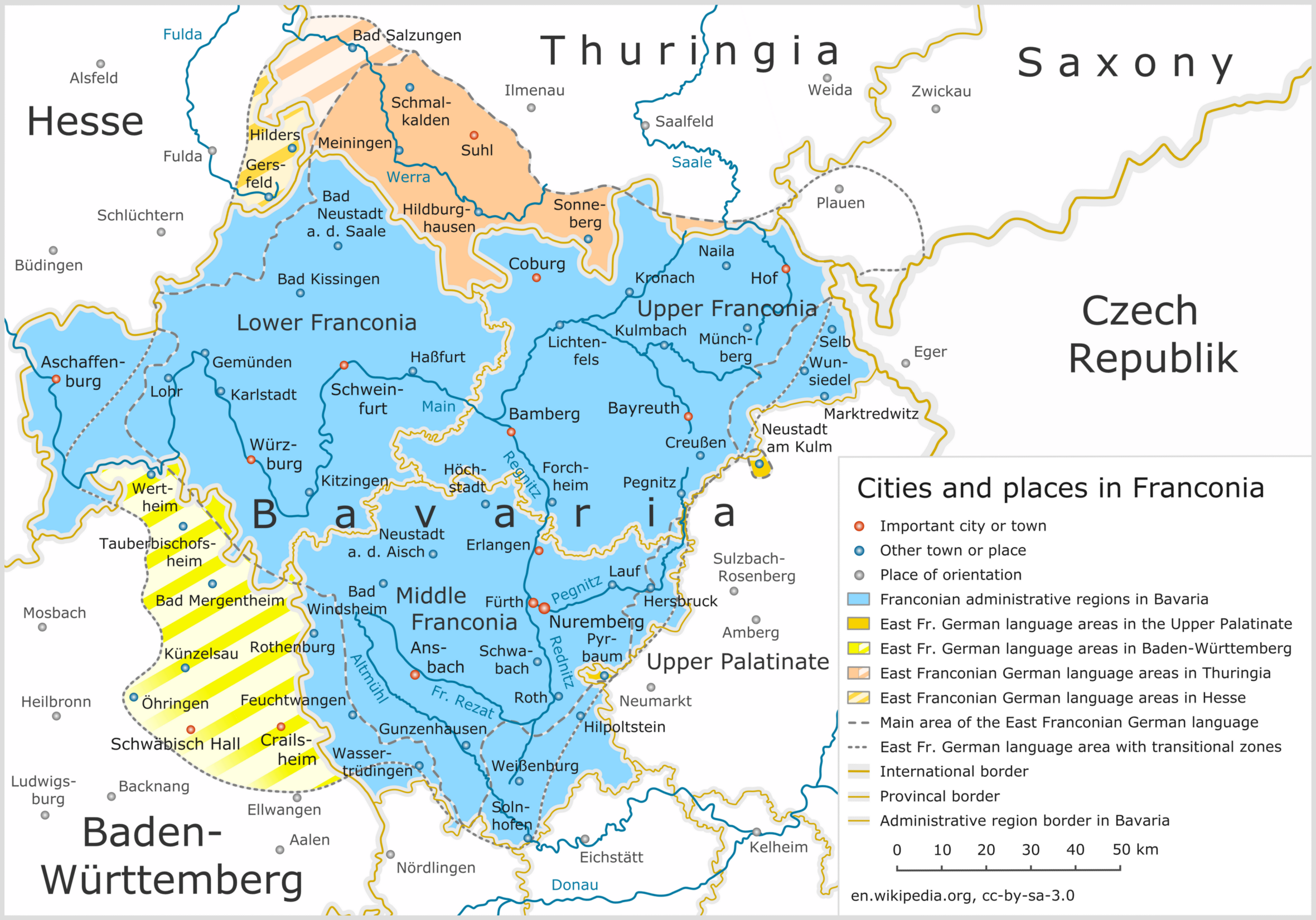
Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of Upper Franconia and has a population of 72,148 (2015). It hosts the annual Bayreuth Festival, at which performances of operas by the 19th-century German composer Richard Wagner are presented. History Middle Ages and Early Modern Period The town is believed to have been founded by the counts of County of Andechs, Andechs probably around the mid-12th century,Mayer, Bernd and Rückel, Gert (2009). ''Bayreuth – Tours on Foot'', Heinrichs-Verlag, Bamberg, p.5, . but was first mentioned in 1194 as ''Baierrute'' in a document by Bishop Otto VI of Andechs, Otto II of Bishopric of Bamberg, Bamberg. The syllable ''-rute'' may mean ''Rodung'' or "clearing", whilst ''Baier-'' indicates immigrants from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plassenburg
Plassenburg is a castle in the city of Kulmbach in Bavaria. It is one of the most impressive castles in Germany and a symbol of the city. It was first mentioned in 1135. The Plassenberg family were Ministerialis, ministerial of the counts of Andechs (later the dukes of Duchy of Merania, Andechs-Meranien) and used as their seat the Plassenburg. The House of Guttenberg, a prominent Franconian noble family, traces its origins back to 1149 with a Gundeloh v. Blassenberg (Plassenberg). The name Guttenberg is derived from Guttenberg, Bavaria, Guttenberg and was adopted by a Heinrich von Blassenberg around 1310. From 1340, the Hohenzollerns governed from Plassenburg castle their territories in Franconia till 1604. The Plassenburg was fortress and residence for the Hohenzollerns. It was destroyed in 1554 at the end of the second Margravian war (1552–1554) of margrave Albert Alcibiades. The Plassenburg was later rebuilt by the architect Caspar Vischer as an impressive stronghold and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andechs
Andechs is a municipality in the district of Starnberg in Bavaria in Germany. It is renowned in Germany and beyond for Andechs Abbey, a Benedictine The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ... monastery that has brewed beer since 1455. The monastery brewery offers tours to visitors. The 20th century German composer Carl Orff is buried in the chapel of Andechs Abbey. This town was the capital of one of the States of the Counts of Andechs, one of the most important families in Europe. References External links * * Starnberg (district) {{Starnberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthold II, Count Of Andechs
Berthold II of Andechs (also known as ''Berthold IV'', ''Berchtold'', or ''Bertholf''; before 1099 – 27 June 1151), a member of the Counts of Andechs, House of Andechs, was a Kingdom of Germany, German nobleman. He was a ruling count of Dießen am Ammersee, Dießen and Andechs in the Duchy of Bavaria, of Plassenburg and Kulmbach in Franconia, as well as bailiff of Benediktbeuern Abbey. Life Berthold's ancestry has not been conclusively established. According to the ''Europäische Stammtafeln'' genealogy, he was probably the elder son and heir of Count Arnold of Dießen (d. 1098) and his wife Gisela of Schweinfurt, a daughter of Duke Otto III, Duke of Swabia, Otto III of Swabia. He thereby was a grandson of Count Frederick II, Count of Diessen, Frederick II of Dießen (d. 1075). In 1098, he inherited his father's Bavarian possessions around the Ammersee and Lake Starnberg, as well as those in Upper Franconia. Around 1120, he could succeed the comital Sigimar dynasty as bail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Duke Of Upper Lorraine
Frederick I (c. 912 – 18 May 978) was the count of Bar and duke of Upper Lorraine. He was a son of Wigeric, count of Bidgau, also count palatine of Lorraine, and Cunigunda, and thus a sixth-generation descendant of Charlemagne. In 954, he married Beatrice, daughter of Hugh the Great, count of Paris, and Hedwig of Saxony. He received in dowry the revenues of the abbey of Saint-Denis in Lorraine. To stop incursions from the duchy of Champagne, Frederick constructed a castle over the Ornain River in 960, and later occupied the confiscated lands of Saint-Mihiel. He exchanged fiefs with the bishop of Toul. Thus, he created his feudal domain, the county of Bar. So he became the founder of the House of Bar or the House of Ardennes–Bar, a cadet branch of the House of Ardennes. The duchy of Lorraine was at that time governed by the archbishop of Cologne, Bruno, who was called the '' archduke'' on account of his dual title. In 959, Bruno, in concert with his brother, Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lechfeld
The Battle of Lechfeld also known as the Second Battle of Lechfeld was a series of military engagements over the course of three days from 10–12 August 955 in which the Kingdom of Germany, led by King Otto I the Great, annihilated the Hungarian army led by ''Horka (title), Harka ''Bulcsú (chieftain), Bulcsú and the chieftains Lehel, Lél and Súr (chieftain), Súr. With the German victory, further invasions by the Magyars into Western Christianity, Latin Europe were ended. The Hungarians invaded the Duchy of Bavaria in late June or early July 955 with 8,000–10,000 horse archers, infantry, and siege engines, intending to draw the main German army, under Otto I, into battle in the open field and destroy it. The Hungarians laid siege to Augsburg on the river Lech (river), Lech. Otto I advanced to relieve the city with an army of 8,000 heavy cavalry, divided into eight legions. As Otto I approached Augsburg on 10 August, a Hungarian surprise attack destroyed the Duchy of Bohem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto I Of Germany
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), known as Otto the Great ( ) or Otto of Saxony ( ), was East Frankish (German) king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the eldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim. Otto inherited the Duchy of Saxony and the kingship of the Germans upon his father's death in 936. He continued his father's work of unifying all German tribes into a single kingdom and greatly expanded the king's powers at the expense of the aristocracy. Through strategic marriages and personal appointments, Otto installed members of his family in the kingdom's most important duchies. This reduced the various dukes, who had previously been co-equals with the king, to royal subjects under his authority. Otto transformed the church in Germany to strengthen royal authority and subjected its clergy to his personal control. After putting down a brief civil war among the rebellious duchies, Otto defeated the Magyars at the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luitpolding
The Luitpoldings were an East Frankish dynasty that ruled the German stem duchy of Duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria in the ninth century. They are named after their descent from Luitpold, Margrave of Bavaria, Margrave Luitpold (or ''Liutpold'') of Bavaria, who reasserted Bavarian autonomy in the early 10th century. His son Arnulf, Duke of Bavaria, Arnulf the Bad first assumed the List of Bavarian monarchs, title of Duke of Bavaria. The Luitpoldings would remain dukes until 947, when the king ceded the Bavarian duchy to his own brother Henry I, Duke of Bavaria, Henry I instead. The Luitpoldings disappear from history after the 10th century, but several houses that are thought to be descending from them (such as the House of Wittelsbach, Wittelsbach and the Babenberg, Babenberger) would continue to thrive. History Historical context After the last Agilolfings, Agilolfing duke of Bavaria, Tassilo III, Duke of Bavaria, Tassilo III, was deposed in 788, Charlemagne and his Carolingian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnulf The Bad
Arnulf II (birth unknown; died 14 July 937), also known as the Bad (), the Evil () or the Wicked, a member of the Luitpolding dynasty, held the title of Duke of Bavaria from about 907 until his death in 937. He is numbered in succession to Arnulf of Carinthia, counted as Arnulf I. Life The year of Arnulf's birth is unknown, but it is said that he was the namesake of other Arnulfs born around the time of the reign of the seventh-century bishop Arnulf of Metz and the Carolingian king Arnulf of Carinthia. Arnulf was the son of Margrave Luitpold of Bavaria and Cunigunde, herself a member of the Ahalolfing dynasty, daughter of Berthold I, the count palatine of Swabia. Her brother Erchanger assumed the Swabian ducal title in 915. Under the weak rule of the East Frankish king Louis the Child, Margrave Luitpold had already achieved a strong position in the Bavarian lands, succeeding the Wilhelminer margraves. He ruled over extended estates along the Danube with Regensburg (Rati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |