|
Horizontal Plate
The horizontal plate of palatine bone is a quadrilateral part of the palatine bone, and has two surfaces and four borders. Surfaces The superior surface, concave from side to side, forms the back part of the floor of the nasal cavity. The inferior surface, slightly concave and rough, forms, with the corresponding surface of the opposite bone, the posterior fourth of the hard palate. Near its posterior margin may be seen a more or less marked transverse ridge for the attachment of part of the aponeurosis of the tensor veli palatini. Borders The anterior border is serrated. It articulates with the palatine process of maxilla. The posterior border is concave, free, and serves for the attachment of the soft palate. Its medial end is sharp and pointed, and, when united with that of the opposite bone, forms a projecting process, the posterior nasal spine for the attachment of the musculus uvulae. The lateral border is united with the lower margin of the perpendicular plate, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones (; derived from the Latin ''palatum'') are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate. Structure The palatine bones are situated at the back of the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. They contribute to the walls of three cavities: the floor and lateral walls of the nasal cavity, the roof of the mouth, and the floor of the orbits. They help to form the pterygopalatine and pterygoid fossae, and the inferior orbital fissures. Each palatine bone somewhat resembles the letter L, and consists of a horizontal plate, a perpendicular plate, and three projecting processes—the pyramidal process, which is directed backward and lateral from the junction of the two parts, and the orbital and sphenoidal processes, which surmount the vertical part, and are separated by a deep notch, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
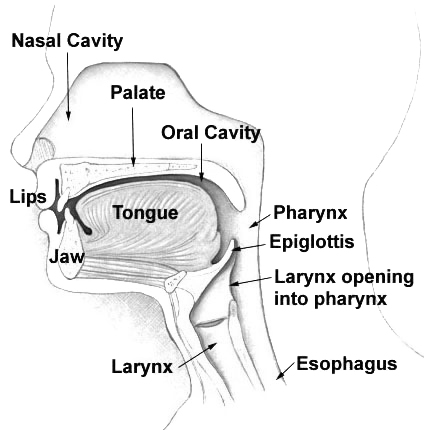
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia. Most of these ostia communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave
Concave or concavity may refer to: Science and technology * Concave lens * Concave mirror Mathematics * Concave function, the negative of a convex function * Concave polygon A simple polygon that is not convex is called concave, non-convex or reentrant. A concave polygon will always have at least one reflex interior angle—that is, an angle with a measure that is between 180° degrees and 360° degrees exclusive. ..., a polygon which is not convex * Concave set * The concavity of a function, determined by its second derivative See also * {{disambiguation, math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones of the facial skeleton, located in the roof of the mouth. The bones are the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of palatine bone. The hard palate spans the alveolar arch formed by the alveolar process that holds the upper teeth (when these are developed). Structure The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone. It forms a partition between the nasal passages and the mouth. On the anterior portion of the hard palate are the ''plicae'', irregular ridges in the mucous membrane that help hold food while the teeth are biting into it while also facilitating the movement of food backward towards the larynx once pieces have been bitten off. This partition is continued deeper into the mouth by a fleshy extension called the soft palate. On the ventral surface of the hard palate, some projections or transverse ridges are present which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; : aponeuroses) is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable to tensional or shear forces in other directions. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections. The primary regions with thick aponeuroses are in the ventral abdominal region, the dorsal lumbar region, the ventriculus in birds, and the palmar (palms) and plantar (soles) regions. Anatomy Anterior abdominal aponeuroses The anterior abdominal aponeuroses are located just superficial to the rectus abdominis muscle. It has for its borders the external oblique, pectoralis muscles, and the latissimus dorsi. Posterior lumbar aponeuroses The posterior lumbar aponeuroses are sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Veli Palatini
The tensor veli palatini muscle (tensor palati or tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) is a thin, triangular muscle of the head that tenses the soft palate and opens the Eustachian tube to equalise pressure in the middle ear. Structure The tensor veli palatini muscle is thin and triangular in shape. Origin It arises from the scaphoid fossa of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid anteriorly, the (medial aspect of the) spine of sphenoid bone posteriorly, and - between the aforementioned anterior and posterior attachments - from the anterolateral aspect of the membranous wall of the pharyngotympanic tube. At the muscle's origin, some of its muscle fibres may be continuous with those of the tensor tympani muscle. Insertion Inferiorly, the muscle converges to form a tendon of attachment. This tendon winds medially around the pterygoid hamulus (with a small bursa interposed between the two) to insert into the palatine aponeurosis and into the bony surface posterior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Process Of Maxilla
In human anatomy of the mouth, the palatine process of maxilla (palatal process), is a thick, horizontal process of the maxilla. It forms the anterior three quarters of the hard palate, the horizontal plate of the palatine bone making up the rest. It is the most important bone in the midface. It provides structural support for the viscerocranium.Dalgorf D, Higgins K. Reconstruction of the midface and maxilla. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Aug;16(4):303-11 Structure It is perforated by numerous foramina for the passage of the nutrient vessels; is channelled at the back part of its lateral border by a groove, sometimes a canal, for the transmission of the descending palatine vessels and the anterior palatine nerve from the spheno-palatine ganglion; and presents little depressions for the lodgement of the palatine glands. When the two maxillae are articulated, a funnel-shaped opening, the incisive foramen, is seen in the middle line, immediately behind the incisor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Structure Muscles The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: # Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing # Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing # Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing # Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing # Musculus uvulae, which moves the palatine uvula, uvula These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve, pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Nasal Spine
The posterior nasal spine is part of the horizontal plate of the palatine bone of the skull. It is found at the medial end of its posterior border. It is paired with the corresponding palatine bone to form a solid spine. It is the attachment of the uvula muscle. Structure The posterior nasal spine is found at the medial end of the posterior border of the horizontal plate of the palatine bone of the skull The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate. In the human, the skull comprises two prominent .... Function The posterior nasal spine is the attachment of the uvula muscle. Clinical applications The posterior nasal spine is an important cephalometric landmark. Additional images File:Gray187.png, Base of skull. Inferior surface. See also * anterior nasal spine References External links * Bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculus Uvulae
The musculus uvulae (also muscle of uvula, uvular muscle, or palatouvularis muscle) is a bilaterally muscle of the soft palate (one of five such muscles) that acts to shorten the uvula when both muscles contract. It forms most of the mass of the uvula. It is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve (cranial nerve X). Anatomy The muscle is situated in between the two laminae of the palatine aponeurosis. From its origin, it passes posterior-ward superior to the swing that is formed by the levator veli palatini muscle. The musculus uvulae and levator veli palatini muscle form a right angle so that their contraction elevates the levator eminence to aid in separating the oral cavity and the oropharynx. Origin The muscle arises from the posterior nasal spine of the palatine bone, and the (superior aspect of the) palatine aponeurosis. Insertion The muscle inserts into the mucous membrane of the uvula. Vasculature The muscle receives arterial blood from the asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Plate Of Palatine Bone
The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders. Surfaces The nasal surface exhibits at its lower part a broad, shallow depression, which forms part of the inferior meatus of the nose. Immediately above this is a well-marked horizontal ridge, the conchal crest, for articulation with the inferior nasal concha; still higher is a second broad, shallow depression, which forms part of the middle meatus, and is limited above by a horizontal crest less prominent than the inferior, the ethmoidal crest, for articulation with the middle nasal concha. Above the ethmoidal crest is a narrow, horizontal groove, which forms part of the superior meatus. The maxillary surface is rough and irregular throughout the greater part of its extent, for articulation with the nasal surface of the maxilla; its upper and back part is smooth where it enters into the formation of the pterygopalatine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Palatine Canal
The greater palatine canal (or pterygopalatine canal) is a passage in the skull that transmits the descending palatine artery, vein, and greater and lesser palatine nerves between the pterygopalatine fossa and the oral cavity. Structure The greater palatine canal starts on the inferior aspect of the pterygopalatine fossa. It goes through the maxilla and palatine bones to reach the palate, ending at the greater palatine foramen. From this canal, accessory canals branch off; these are known as the lesser palatine canals. The canal is formed by a vertical groove on the posterior part of the maxillary surface of the palatine bone; it is converted into a canal by articulation with the maxilla. The canal transmits the descending palatine vessels, the greater palatine nerve, and the lesser palatine nerve. See also * Greater palatine foramen * Pterygopalatine fossa In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa (sphenopalatine fossa) is a fossa in the skull. A human skull conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |