|
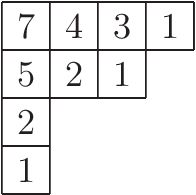
Hook Length Formula
In combinatorics, combinatorial mathematics, the hook length formula is a formula for the number of Young tableau, standard Young tableaux whose shape is a given Young diagram. It has applications in diverse areas of mathematics, areas such as representation theory, probability theory, probability, and algorithm analysis; for example, the problem of longest increasing subsequences. A related formula gives the number of semi-standard Young tableaux, which is a specialization of a Schur polynomial. Definitions and statement Let \lambda=(\lambda_1\geq \cdots\geq \lambda_k) be a integer partition, partition of n=\lambda_1+\cdots+\lambda_k. It is customary to interpret \lambda graphically as a Young diagram, namely a left-justified array of square cells with k rows of lengths \lambda_1,\ldots,\lambda_k. A (standard) Young tableau of shape \lambda is a filling of the n cells of the Young diagram with all the integers \, with no repetition, such that each row and each column form incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and as an end to obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science. Combinatorics is well known for the breadth of the problems it tackles. Combinatorial problems arise in many areas of pure mathematics, notably in algebra, probability theory, topology, and geometry, as well as in its many application areas. Many combinatorial questions have historically been considered in isolation, giving an ''ad hoc'' solution to a problem arising in some mathematical context. In the later twentieth century, however, powerful and general theoretical methods were developed, making combinatorics into an independent branch of mathematics in its own right. One of the oldest and most accessible parts of combinatorics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert De Beauregard Robinson
Gilbert de Beauregard Robinson, MBE (3 June 1906 – 8 April 1992) was a Canadian mathematician most famous for his work on combinatorics and representation theory of the symmetric groups, including the Robinson-Schensted algorithm. Biography Gilbert Robinson was born in Toronto in 1906. He then attended St. Andrew's College and graduated from the University of Toronto in 1927. He received his Ph.D. at Cambridge where his advisor was group theorist Alfred Young. He then joined the Mathematics Department in Toronto where he served until his retirement in 1971, except for a period of wartime service in Ottawa. Robinson specialized in the study of the symmetric groups on which he became a recognized authority. In 1938 he formulated, in a paper studying the Littlewood–Richardson rule, a correspondence that would later become known as the Robinson-Schensted correspondence. He wrote some forty papers on the topic of symmetric groups. He also published ''The Foundations of Geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corners Of Young
{{disambiguation ...
Corners may refer to: * A community formed at a crossroads or other intersection; a few examples include: ** Balcom Corners, New York ** Bells Corners in Ottawa ** Dixon's Corners, Ontario ** Five Corners, Wisconsin (other), any of three communities of that name ** Hales Corners, Wisconsin ** Hallers Corners, Michigan ** Layton Corners, Michigan * Corners, a variation on the Four Seasons card game * ''Corners'' (TV series), 1980s BBC children's television series * Corners, Perry County, Missouri, an unincorporated community See also * Corner (other) Corner may refer to: People *Corner (surname) *House of Cornaro, a noble Venetian family (''Corner'' in Venetian dialect) Places *Corner, Alabama, a community in the United States *Corner Inlet, Victoria, Australia *Corner River, a tributary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Knuth
Donald Ervin Knuth ( ; born January 10, 1938) is an American computer scientist and mathematician. He is a professor emeritus at Stanford University. He is the 1974 recipient of the ACM Turing Award, informally considered the Nobel Prize of computer science. Knuth has been called the "father of the analysis of algorithms". Knuth is the author of the multi-volume work '' The Art of Computer Programming''. He contributed to the development of the rigorous analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms and systematized formal mathematical techniques for it. In the process, he also popularized the asymptotic notation. In addition to fundamental contributions in several branches of theoretical computer science, Knuth is the creator of the TeX computer typesetting system, the related METAFONT font definition language and rendering system, and the Computer Modern family of typefaces. As a writer and scholar, Knuth created the WEB and CWEB computer programming systems des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor Pak
Igor Pak () (born 1971, Moscow, Soviet Union) is a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Los Angeles, working in combinatorics and discrete probability. He formerly taught at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the University of Minnesota, and he is best known for his bijective proof of the hook-length formula for the number of Young tableaux, and his work on random walks. He was a keynote speaker alongside George Andrews and Doron Zeilberger at the 2006 Harvey Mudd College Mathematics Conference on Enumerative Combinatorics. Pak is an Associate Editor for the journal ''Discrete Mathematics''. He gave a Fejes Tóth Lecture at the University of Calgary in February 2009. In 2018, he was an invited speaker at the International Congress of Mathematicians in Rio de Janeiro. Background Pak went to Moscow High School № 57. After graduating, he worked for a year at Bank Menatep. He did his undergraduate studies at Moscow State University. He was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Mathematics (journal)
''Discrete Mathematics'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal in the broad area of discrete mathematics, combinatorics, graph theory, and their applications. It was established in 1971 and is published by North-Holland Publishing Company. It publishes both short notes, full length contributions, as well as survey articles. In addition, the journal publishes a number of special issues each year dedicated to a particular topic. Although originally it published articles in French and German, it now allows only English language articles. The editor-in-chief is Douglas West ( University of Illinois, Urbana). History The journal was established in 1971. The first article it published was written by Paul Erdős, who went on to publish a total of 84 papers in the journal. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doron Zeilberger
Doron Zeilberger (; born 2 July 1950) is an Israeli-American mathematician, known for his work in combinatorics. Education and career He received his doctorate from the Weizmann Institute of Science in 1976, under the direction of Harry Dym, with the thesis "New Approaches and Results in the Theory of Discrete Analytic Functions." He is a Board of Governors Professor of Mathematics at Rutgers University. Mathematical work Zeilberger has made contributions to combinatorics, hypergeometric identities, and q-series. He gave the first proof of the alternating sign matrix conjecture, noteworthy not only for its mathematical content, but also for the fact that Zeilberger recruited nearly a hundred volunteer checkers to "pre-referee" the paper. In 2011, together with Manuel Kauers and Christoph Koutschan, Zeilberger proved the ''q''-TSPP conjecture, which was independently stated in 1983 by George Andrews and David P. Robbins. Zeilberger is an ultrafinitist. He is also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advances In Mathematics
''Advances in Mathematics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on pure mathematics. It was established in 1961 by Gian-Carlo Rota. The journal publishes 18 issues each year, in three volumes. At the origin, the journal aimed at publishing articles addressed to a broader "mathematical community", and not only to mathematicians in the author's field. Herbert Busemann writes, in the preface of the first issue, "The need for expository articles addressing either all mathematicians or only those in somewhat related fields has long been felt, but little has been done outside of the USSR. The serial publication ''Advances in Mathematics'' was created in response to this demand." Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert S
Herbert may refer to: People * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket, a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' * Herbert West, titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Nijenhuis
Albert Nijenhuis (November 21, 1926 – February 13, 2015) was a Dutch-American mathematician who specialized in differential geometry and the theory of deformations in algebra and geometry, and later worked in combinatorics. His high school studies at the gymnasium in Arnhem were interrupted by the evacuation of Arnhem by the Nazis after the failure of Operation Market Garden by the Allies. He continued his high school mathematical studies by himself on his grandparents’ farm, and then took state exams in 1945. His university studies were carried out at the University of Amsterdam, where he received the degree of Candidaat (equivalent to a Bachelor of Science) in 1947, and a Doctorandus (equivalent to a Masters in Science) in 1950, cum laude. He was a Medewerker (associate) at the Mathematisch Centrum (now the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica) in Amsterdam 1951–1952. He obtained a PhD in mathematics in 1952, cum laude (Theory of the geometric object). His thesis advisor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtis Greene
Curtis Greene is an American mathematician, specializing in algebraic combinatorics. He is the J. McLain King Professor of Mathematics at Haverford College in Pennsylvania.Faculty profile an , Haverford College, retrieved 2012-02-20. Greene did his undergraduate studies at , and earned his Ph.D. in 1969 from the under the supervision of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Combinatorial Theory
The ''Journal of Combinatorial Theory'', Series A and Series B, are mathematical journals specializing in combinatorics and related areas. They are published by Elsevier. ''Series A'' is concerned primarily with structures, designs, and applications of combinatorics. ''Series B'' is concerned primarily with graph and matroid theory. The two series are two of the leading journals in the field and are widely known as ''JCTA'' and ''JCTB''. The journal was founded in 1966 by Frank Harary and Gian-Carlo Rota.They are acknowledged on the journals' title pages and Web sites. SeEditorial board of JCTA Originally there was only one journal, which was split into two parts in 1971 as the field grew rapidly. In 2020, most of the editorial board of ''JCTA'' resigned to form a new, |