|
Homophony (other)
Homophony and Homophonic are from the Greek language, Greek ὁμόφωνος (''homóphōnos''), literally 'same sounding,' from ὁμός (''homós''), "same" and φωνή (''phōnē''), "sound". It may refer to: *Homophones − words with the same pronunciation. *Homophony − in music is a texture in which multiple voices move together in harmony. *Homophony (writing) − in a theory of writing systems is one of the forms of phonogram (linguistics), phonogram. * Homophonic substitution cipher − a cipher that disguises plaintext letter frequencies by homophony: 'e' is given more homophonic ciphertext symbols than 'z'. {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophone
A homophone () is a word that is pronounced the same (to varying extent) as another word but differs in meaning. A ''homophone'' may also differ in spelling. The two words may be spelled the same, for example ''rose'' (flower) and ''rose'' (past tense of "rise"), or spelled differently, as in ''rain'', ''reign'', and ''rein''. The term ''homophone'' may also apply to units longer or shorter than words, for example a phrase, letter, or groups of letters which are pronounced the same as another phrase, letter, or group of letters. Any unit with this property is said to be ''homophonous'' (). Homophones that are spelled the same are also both homographs and homonyms, e.g. the word ''read'', as in "He is well ''read''" (he is very learned) vs. the sentence "I ''read'' that book" (I have finished reading that book). Homophones that are spelled differently are also called heterographs, e.g. ''to'', ''too'', and ''two''. Etymology "Homophone" derives from Greek ''homo-'' (ὁμο� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
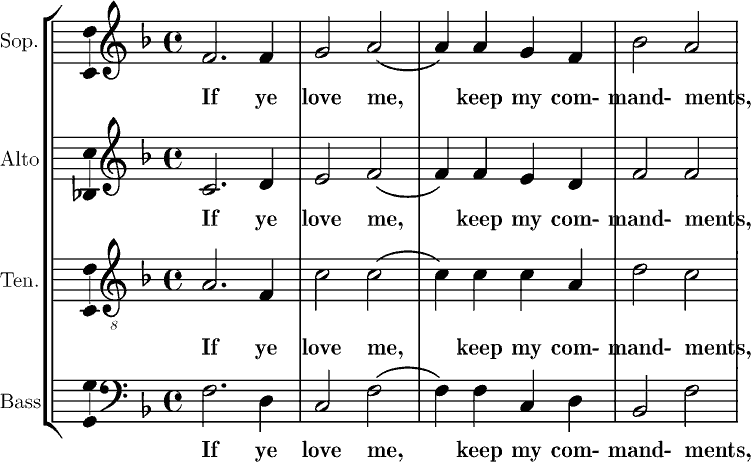
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh out the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However, harmony is generally understood to involve both vertical harmony (chords) and horizontal harmony (melody). Harmony is a perceptual property of music, and, along with melody, one of the building blocks of Western music. Its perception is based on consonance, a concept whose definition has changed various times throughout Western music. In a physiological approach, consonance is a continuous variable. Consonant pitch relationships are described as sounding more pleasant, euphonious, and beautiful than dissonant relationships which sound unpleasant, discordant, or rough. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Counterpoint, which refers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony (writing)
In the theory of writing systems, homophony (from the el, ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and el, φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound") refers to the presence or use of different signs ( phonograms) for the same syllabic value, i.e. the same sound combination may be represented by different signs. Akkadian In Chapter 4 of 'Akkadian language', a book on the origin and development of cuneiform, John Heise gives the following example (see cuneiform transliteration): Heise comments: “In transliterations the same sounds that are represented by different cuneiform signs are distinguished with an accent or an index. The signs for ni, ní (i with accent aigu), nì (i with accent grave The grave accent () ( or ) is a diacritical mark used to varying degrees in French, Dutch, Portuguese, Italian and many other western European languages, as well as for a few unusual uses in English. It is also used in other languages using th ...), ni4, ni5, ... are all different cuneiform symbols. n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonogram (linguistics)
A phonogram is a grapheme (written character) which represents a phoneme (speech sound) or combination of phonemes, such as the letters of the Latin alphabet or Korean letter Hangul. For example, "igh" is an English-language phonogram that represents the sound in "high". Whereas the word ''phonemes'' refers to the sounds, the word ''phonogram'' refers to the letter(s) that represent that sound. Phonograms contrast with logograms, which represent words and morphemes (meaningful units of language), and determinatives, silent characters used to mark semantic categories. See also * Emoji * Logo * Symbol * Syllabogram * Wingdings * Rebus A rebus () is a puzzle device that combines the use of illustrated pictures with individual letters to depict words or phrases. For example: the word "been" might be depicted by a rebus showing an illustrated bumblebee next to a plus sign (+) ..., the use of pictures to represent words or parts of words External links 古代文字資 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |