|
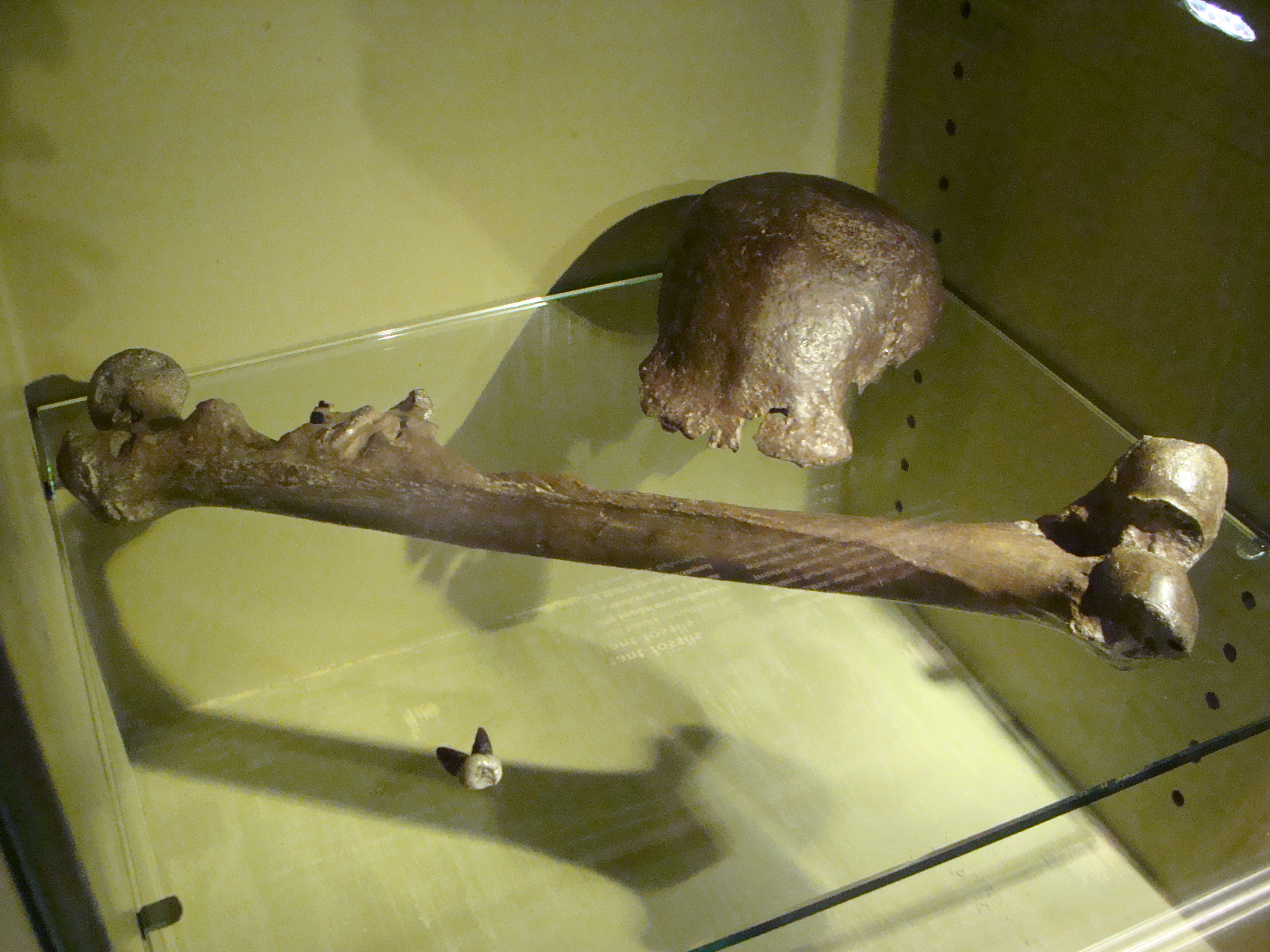
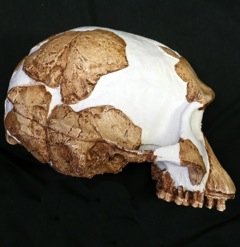
Homo Gautengensis
''Homo gautengensis'' is a species name proposed by anthropologist Darren Curnoe in 2010 for South African hominin fossils otherwise attributed to '' H. habilis'', ''H. ergaster,'' or, in some cases, ''Australopithecus'' or ''Paranthropus''. The fossils assigned to the species by Curnoe cover a vast temporal range, from about 1.8 million years ago to potentially as late as 0.8 million years ago, meaning that if the species is considered valid, ''H. gautengensis'' would be both one of the earliest and one of the longest lived species of ''Homo''. Since Curnoe's 2010 description, recognition of the species has been limited. The classification of most of the fossils referred to ''H. gautengensis'' was controversial before the description of the species and continue to be controversial to this day. Some palaeoanthropologists have gone as far as to declare that there is little reason to consider ''H. gautengensis'' a valid taxon. Research history Palaeoanthropologists vary in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6a00d8341bf67c53ef01348157067b970c-320wi
Six Apart Ltd., sometimes abbreviated 6A, is a software company known for creating the Movable Type blogware, TypePad blog hosting service, and Vox (the blogging platform). The company also is the former owner of LiveJournal. Six Apart is headquartered in Tokyo. The name is a reference to the six-day age difference between its married co-founders, Ben and Mena Trott. History The company was founded in September 2001 after Ben, during a period of unemployment, wrote what became Movable Type to allow Mena to easily produce her weblog. When version 1.0 was put on the web, it was downloaded over 100 times in the first hour. 2003–2006 In 2003, Six Apart received initial venture capital funding from a group led by Joi Ito and his Neoteny Co., which allowed the company to hire additional employees, acquire a French weblog publishing company, and unveil plans for what was to become its hosted weblog publishing system, TypePad. In 2004, Six Apart completed a second round of funding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning " upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as ''H. heidelbergensis'' and ''H. antecessor'' — with the former generally considered to have been the ancestor to Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans — appear to have evolved from ''H. erectus''. Its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus ''Homo''. ''H. erectus'' was the first human ancestor to spread throughout Eurasia, with a continental range extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Java. Asian populations of ''H. erectus'' may be ancestral to '' H. floresiensis'' and possibly to '' H. luzonensis''. The last known population of ''H. erectus'' is '' H. e. soloensis'' from Java, around 117,000–108,000 years ago. ''H. erectus'' had a more modern gait and body proportions, and was the first human species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million years ago (extinction of ''Paranthropus''), all fossils sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossil Sites
This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of the entries in this list are considered Lagerstätten (sedimentary deposits that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues). Lagerstätten are indicated by a note () in the noteworthiness column. Fossils may be found either associated with a geological formation A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock expo ... or at a single geographic site. Geological formations consist of rock that was deposited during a specific period of time. They usually extend for large areas, and som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KNM-ER 1813
KNM ER 1813 is a skull of the species ''Homo habilis''. It was discovered in Koobi Fora, Kenya by Kamoya Kimeu in 1973, and is estimated to be 1.9 million years old. Its characteristics include an overall smaller size than other ''Homo habilis'' finds, but with a fully adult and typical ''H. habilis'' morphology. It is an adult (the third molars were completely erupted and showed signs of wear) with an estimated cranial capacity of only 510 cc. The designation indicates specimen 1813, collected from the east shore of Lake Rudolf (now Lake Turkana) for the Kenya National Museums. See also * List of fossil sites ''(with link directory)'' * List of human evolution fossils The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roug ... ''(with images)'' References Further reading * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Rudolfensis
''Homo rudolfensis'' is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because ''H. rudolfensis'' coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confidently assigned to this species beyond the lectotype skull KNM-ER 1470 and other partial skull aspects. No bodily remains are definitively assigned to ''H. rudolfensis''. Consequently, both its genus, generic classification and validity are debated without any wide consensus, with some recommending the species to actually belong to the genus ''Australopithecus'' as ''A. rudolfensis'' or ''Kenyanthropus'' as ''K. rudolfensis'', or that it is synonym (taxonomy), synonymous with the contemporaneous and anatomically similar ''Homo habilis, H. habilis''. ''H. rudolfensis'' is distinguished from ''H. habilis'' by larger size, but it is also argued that this species actually consists of male ''H. habilis'' specimens, assuming that ''H. habilis'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Sediba
''Australopithecus sediba'' is an extinct species of australopithecine recovered from Malapa Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa. It is known from a partial juvenile skeleton, the holotype MH1, and a partial adult female skeleton, the paratype MH2. They date to about 1.98 million years ago in the Early Pleistocene, and coexisted with '' Paranthropus robustus'' and '' Homo ergaster'' / '' Homo erectus''. Malapa is interpreted as having been a natural death trap, the base of a long vertical shaft which creatures could accidentally fall into. ''A. sediba'' was initially described as being a potential human ancestor, and perhaps the progenitor of ''Homo'', but this is contested and it could also represent a late-surviving population or sister species of '' A. africanus'' which had earlier inhabited the area. MH1 has a brain volume of about 420–440 cc, similar to other australopithecines. The face of MH1 is strikingly similar to ''Homo'' instead of other australopithecines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Leakeyi
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably ''Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of ''Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus ''Paranthropus'', is probably sister to ''Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. ''Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed ''Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranthropus Robustus
''Paranthropus robustus'' is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 (or, more conservatively, 2 to 1) million years ago. It has been identified in Kromdraai, Swartkrans, Sterkfontein, Gondolin, Cooper's, and Drimolen Caves. Discovered in 1938, it was among the first early hominins described, and became the type species for the genus ''Paranthropus''. However, it has been argued by some that ''Paranthropus'' is an invalid grouping and synonymous with ''Australopithecus'', so the species is also often classified as ''Australopithecus robustus''. Robust australopithecines—as opposed to gracile australopithecines—are characterised by heavily built skulls capable of producing high stresses and bite forces, as well as inflated cheek teeth ( molars and premolars). Males had more heavily built skulls than females. ''P. robustus'' may have had a genetic susceptibility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype nor a syntype). Often there is more than one paratype. Paratypes are usually held in museum research collections. The exact meaning of the term ''paratype'' when it is used in zoology is not the same as the meaning when it is used in botany. In both cases however, this term is used in conjunction with ''holotype''. Zoology In zoological nomenclature, a paratype is officially defined as "Each specimen of a type series other than the holotype.", ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' In turn, this definition relies on the definition of a "type series". A type series is the material (specimens of organisms) that was cited in the original publication of the new species or subspecies, and was not excluded from being type material by the author (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

