|
Holmes' Marine Life Protection Association
The Holmes' Marine Life Protection Association was a United Kingdom company set up in the 19th century to produce Marine (ocean), marine signal lights and foghorns. It was founded by Nathaniel John Holmes, a telegraphy, telegraph engineer from Middlesex; and it passed to his son Joseph R. Holmes. The company was taken over by Albright and Wilson in 1919. Holmes' patents In 1875 Holmes obtained a British Patent for a marine audible alarm signal (B.P. 2564 of 1875); and in 1877 he bought, for £80 Pound Sterling, a half-share of John Grey's Patent (B.P. 2564 of 1868) for ''Improvements in fog alarms''. In 1876 he obtained, with J.H. Player as co-applicant, a provisional application for ''Improvements in self-igniting and inextinguishable signal lights for marine and other purposes''; it became British Patent 4215 of 1876. Further patents were taken out by Holmes in 1885 and 1887; and his company up to 1906. Marine markers and signals In July 1873 he demonstrated his Patent Signal Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many List of islands of the United Kingdom, smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercator03
__NOTOC__ Mercator ( Latin for "merchant") may refer to: People * Marius Mercator (c. 390–451), a Catholic ecclesiastical writer * Arnold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer * Gerardus Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer ** Mercator 1569 world map ** Mercator projection, a cartographic projection devised by Gerardus Mercator * Rumold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer * Nicholas Mercator, a 17th-century mathematician ** Mercator series, a representation of the natural logarithm Companies and universities * Mercator (retail), a Slovenian supermarket chain * Mercator-S, a retail company in Serbia, part of Agrokor Group * Mercator School of Management, University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany * Mercator Limited, a shipping company in India * Mercator Corporation, a consulting firm and investment bank formed by James Giffen, involved with Kazakhgate Vehicles * ''Mercator'' (ship), a barquentine museum ship in Oostende, Belgium * P4M Mercator, a reconnaissance ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifebuoy
A lifebuoy is a life-saving buoy designed to be thrown to a person in water, to provide buoyancy and prevent drowning. Some modern lifebuoys are fitted with one or more seawater-activated lights, to aid rescue at night. Other names Other names for "lifebuoy" include safety wheel, lifebelt, water wheely, ring buoy, lifering, lifesaver, life donut, life preserver, Perry buoy, or Kisbee ring. The "Kisbee ring", sometimes "kisby ring" or "kisbie ring", is thought to be named after inventor Thomas Kisbee (1792–1877), a British naval officer. Description The lifebuoy is usually ring- or horseshoe-shaped personal flotation device with a connecting line allowing the casualty to be pulled to the rescuer in a boat. They are carried by ships and are also located beside bodies of water that have the depth or potential to drown someone. They are often subjected to vandalism which, since the unavailability of lifebuoys could lead to death, may be punished by fines (up to £5,000 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foghorn
A foghorn or fog signal is a device that uses sound to warn vehicles of navigational hazards such as rocky coastlines, or boats of the presence of other vessels, in foggy conditions. The term is most often used in relation to marine transport. When visual navigation aids such as lighthouses are obscured, foghorns provide an audible warning of rock outcrops, shoals, headlands, or other dangers to shipping. Description All foghorns use a vibrating column of air to create an audible tone, but the method of setting up this vibration differs. Some horns, such as the Daboll trumpet, used vibrating plates or metal reeds, a similar principle to a modern electric car horn. Others used air forced through holes in a rotating cylinder or disk, in the same manner as a siren. Semi-automatic operation of foghorns was achieved by using a clockwork mechanism (or "coder") to sequentially open the valves admitting air to the horns; each horn was given its own timing characteristics to help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of Ca C2. Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide. The pure material is colorless, while pieces of technical-grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of about 80–85% of CaC2 (the rest is CaO (calcium oxide), Ca3P2 ( calcium phosphide), CaS ( calcium sulfide), Ca3N2 (calcium nitride), SiC (silicon carbide), etc.). In the presence of trace moisture, technical-grade calcium carbide emits an unpleasant odor reminiscent of garlic. Applications of calcium carbide include manufacture of acetylene gas, generation of acetylene in carbide lamps, manufacture of chemicals for fertilizer, and steelmaking. Production Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately . This is an endothermic reaction requiring per mole and high temperatures to drive off the carbon monoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast (sailing)
The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, and giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed. Until the mid-19th century, all vessels' masts were made of wood formed from a single or several pieces of timber which typically consisted of the trunk of a conifer tree. From the 16th century, vessels were often built of a size requiring masts taller and thicker than could be made from single tree trunks. On these larger vessels, to achieve the required height, the masts were built from up to four sections (also called masts). From lowest to highest, these were called: lower, top, topgallant, and royal masts. Giving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
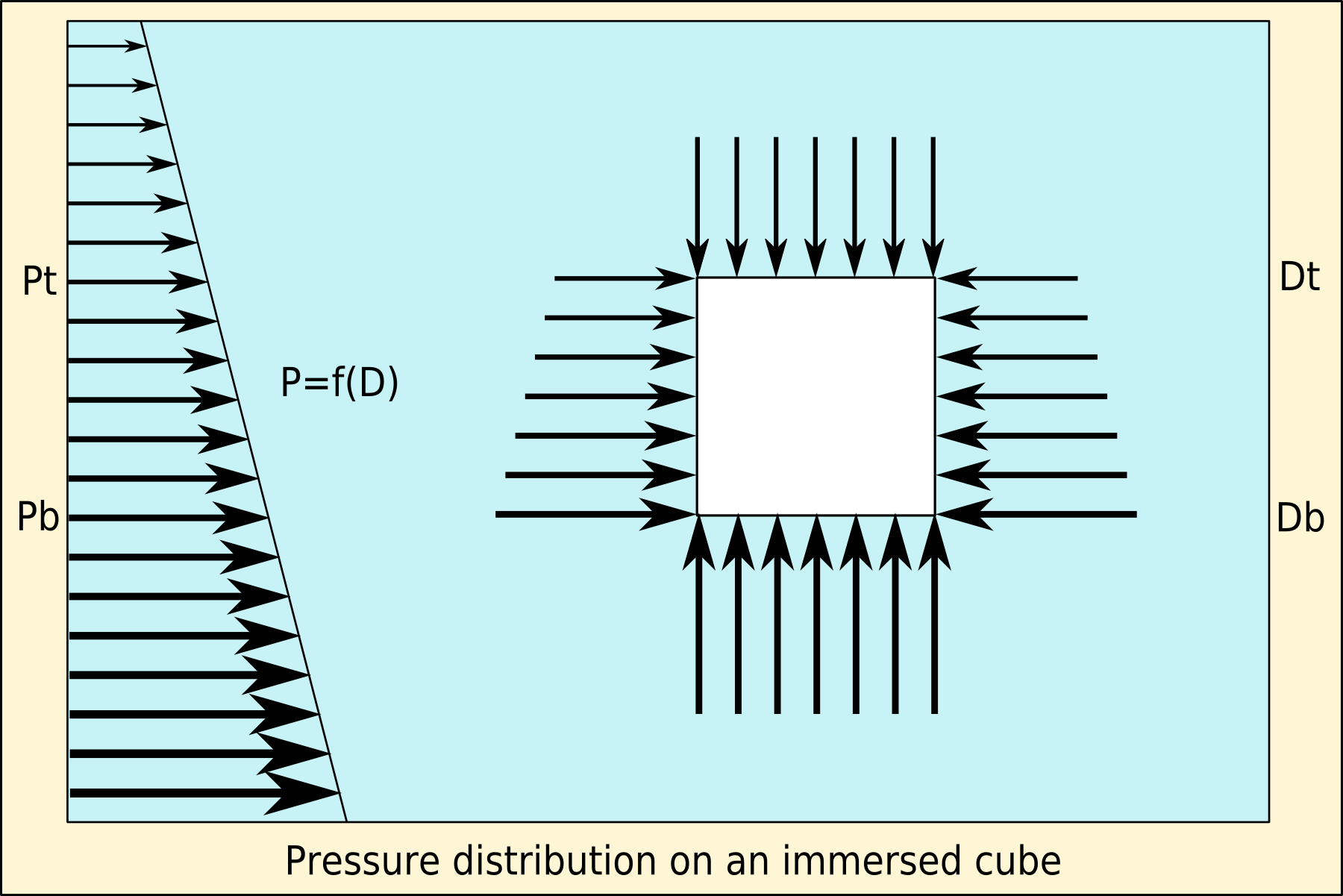
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine ( IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Phosphide
Calcium phosphide (CP) is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3P2. It is one of several phosphides of calcium, being described as the salt-like material composed of Ca2+ and P3−. Other, more exotic calcium phosphides have the formula CaP, CaP3, Ca2P2, and Ca5P8. Ca3P2 has the appearance of red-brown crystalline powder or grey lumps. Its trade name is Photophor for the incendiary use or Polytanol for the use as rodenticide. Preparation and structure It may be formed by reaction of the elements, but it is more commonly prepared by carbothermal reduction of calcium phosphate: :Ca3(PO4)2 + 8 C → Ca3P2 + 8 CO The structure of the room temperature form of Ca3P2 has not been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. A high temperature phase has been characterized by Rietveld refinement. Ca2+ centers are octahedral. Uses Metal phosphides are used as a rodenticide. A mixture of food and calcium phosphide is left where the rodents can eat it. The acid in the digestive syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene ( systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet of hydrogen". It was an accidental discovery while attempting to isolate potassium metal. By heating potassium carbonate with carbon at very high temperatures, he pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of Ca C2. Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide. The pure material is colorless, while pieces of technical-grade calcium carbide are grey or brown and consist of about 80–85% of CaC2 (the rest is CaO (calcium oxide), Ca3P2 ( calcium phosphide), CaS ( calcium sulfide), Ca3N2 (calcium nitride), SiC (silicon carbide), etc.). In the presence of trace moisture, technical-grade calcium carbide emits an unpleasant odor reminiscent of garlic. Applications of calcium carbide include manufacture of acetylene gas, generation of acetylene in carbide lamps, manufacture of chemicals for fertilizer, and steelmaking. Production Calcium carbide is produced industrially in an electric arc furnace from a mixture of lime and coke at approximately . This is an endothermic reaction requiring per mole and high temperatures to drive off the carbon monoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)