|
Hoffnung Music Festival
The Hoffnung Music Festivals were a series of humorous classical music festivals created by cartoonist and amateur tuba player Gerard Hoffnung and held in the Royal Festival Hall in London. The concerts consisted of humorous works specially commissioned from well-known composers of the day. 1956 concert The 1956 concert was recorded, and is available in the American market on Angel Records 35500. Music from The Hoffnung Music Festival Concert, Royal Festival Hall, London. An Extravagant Evening of Symphonic Caricature devised by Gerald Hoffnung, Producer: Sam Wanamaker, Organizer: John Amis. It was recorded at the concert, 13 November 1956, by EMI and released in the U.S. by Angel Records. The orchestra was the Morley College Orchestra (billed as the Hoffnung Symphony Orchestra) The concert opens with Ernst Bean, the General Manager of the Festival Hall, announcing that “owing to circumstances over which the London County Council and the management of the hall have no contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to List of classical and art music traditions, non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and Harmony, harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century, it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated music notation, notational system, as well as accompanying literature in music analysis, analytical, music criticism, critical, Music history, historiographical, musicology, musicological and Philosophy of music, philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Reizenstein
Franz Theodor Reizenstein (7 June 191115 October 1968) was a Germany, German-born British composer and concert pianist. He left Germany for sanctuary in Britain in 1934 and went on to have his teaching and performing career there. As a composer, he successfully blended the equally strong but very different influences of his primary teachers, Hindemith and Vaughan Williams. Life Franz Reizenstein's parents were the well-known physician Dr. Albert Reizenstein (1871–1925) and his wife Lina Kohn (b. 1880), both of Nuremberg, Germany. The family was Jewish and counted many professionals, scientists, bankers, and musically inclined people among its members. Reizenstein grew up in Nuremberg and was considered a child prodigy. He composed his first pieces when he was 5, and by the age of 17 he had written a string quartet. His well-to-do and artistic family encouraged him to play chamber music at home. Eventually he was sent to study composition under Paul Hindemith and piano under Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphorn
The alphorn (; ; ) is a traditional lip-reed wind instrument. It consists of a very long straight wooden natural horn, with a length of , a conical bore and a wooden cup-shaped mouthpiece. Traditionally the alphorn was made in one piece from the trunk of a pine. Modern alphorns are usually made in three detachable sections for easier transport and handling, carved from blocks of spruce. The alphorn is used by rural communities in the Alps. Similar wooden horns were used for communication in most mountainous regions of Europe, from the Alps to the Carpathians. History The alphorn may have developed from instruments like the , a similarly shaped Etruscan instrument of classical antiquity, although there is little documented evidence of a continuous connection between them. A 2nd century Roman mosaic, found in Boscéaz, depicts a shepherd using a similar straight horn. The use of long signal horns in mountainous areas throughout Europe and Asia may indicate a long history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
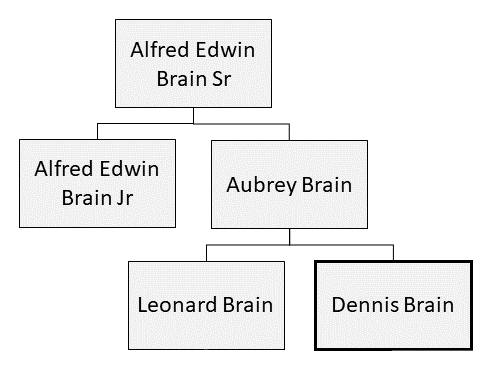
Dennis Brain
Dennis Brain (17 May 19211 September 1957) was a British French horn, horn player. From a musical family – his father and grandfather were horn players – he attended the Royal Academy of Music in London. During the Second World War he served in the Royal Air Force, playing in its Central Band of the Royal Air Force, band and orchestra. After the war, he was the principal horn of the Philharmonia Orchestra, Philharmonia and Royal Philharmonic Orchestra, Royal Philharmonic orchestras, and played in chamber ensembles. Among the works written for Brain is Benjamin Britten's ''Serenade for Tenor, Horn and Strings'' (1944). Other composers who wrote for him include Malcolm Arnold, Lennox Berkeley, Alan Bush, Gordon Jacob, Humphrey Searle and Mátyás Seiber. Brain was killed in a car crash at the age of 36. Life and career Early years Brain was born in Hammersmith, London on 17 May 1921 to a musical family. His mother, Marion, ''née'' Beeley (1887–1954), was a singer at Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Mozart
Johann Georg Leopold Mozart (November 14, 1719 – May 28, 1787) was a German composer, violinist, and music theorist. He is best known today as the father and teacher of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and for his violin textbook ''Versuch einer gründlichen Violinschule'' (1756). Life and career Childhood and youth He was born in Augsburg, son of Johann Georg Mozart, a bookbinding, bookbinder, and his second wife Anna Maria Sulzer. From an early age he sang as a choirboy. He attended a local Society of Jesus, Jesuit school, , where he studied logic, science, and theology, graduating ''magna cum laude'' in 1735. He studied then at the St. Salvator Lyzeum. While a student in Augsburg, he appeared in student theater productions as an actor and singer, and became a skilled violinist and organist. He also developed an interest, which he retained, in microscopes and telescopes. Although his parents had planned a career for Leopold as a Catholic priest, this apparently was not Leopold's own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Toch
Ernst Toch (; 7 December 1887 – 1 October 1964) was an Austrian composer of European classical music and film scores, who from 1933 worked as an émigré in Paris, London and New York. He sought throughout his life to introduce new approaches to music. Biography Toch was born in Leopoldstadt, Vienna, into the family of a humble Ashkenazi Jews, Jewish leather dealer when the city was at its 19th-century cultural zenith. He studied philosophy at the University of Vienna, medicine at University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg and music at the Hoch Conservatory (1909–1913) in Frankfurt. His main instrument was the piano, and he was a pianist of considerable stature, performing to acclaim throughout much of western Europe. Much of his writing was intended for the piano. Toch continued to grow as an artist and composer throughout his adult life, and in America came to influence whole new generations of composers. His first compositions date from c. 1900 and were pastiches in the style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Fugue
The ''Geographical Fugue'' or ''Fuge aus der Geographie'' is the most famous piece for spoken chorus by Ernst Toch. Toch was a prominent composer in 1920s Berlin who invented the idiom of the "Spoken Chorus". The work was composed as the third and final movement in Toch's suite ''Gesprochene Musik'' (Spoken Music). The suite was designed to be recorded by a chorus on gramophone records at 78 rpm, then "performed" in concert by replaying the records at a much higher speed. As Toch wrote in his original program notes: "increasing the tempo, and the resulting pitch level ... created a type of instrumental music, which leads the listener to forget that it originated from speaking". The piece was first performed, in its original German, at the Neue Musik Berlin festival in June 1930. The performance, in front of an audience that included experimental composer John Cage, was a sensational success. Wikipedia:Citations needed">citation needed''/sup> When Toch arrived in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer Barrel Polka
"Beer Barrel Polka", originally in Czech , also known as "The Barrel Polka", "Roll Out the Barrel", or "Rosamunde", is a 1927 polka composed by Czech musician Jaromír Vejvoda. Lyrics were added in 1934, subsequently gaining worldwide popularity during World War II as a drinking song. History In 1927, the music for the polka was composed by the Czech musician Jaromír Vejvoda. Eduard Ingriš wrote the first arrangement of the piece, after Vejvoda came up with the melody and sought Ingriš's help in refining it. At that time, it was played without lyrics as (). In 1934, the first text for the polka was written by Vašek Zeman – with the title () Around that same time, Shapiro Bernstein acquired the rights to the song and English lyrics were written by Lew Brown and Wladimir Timm. Zeman's original Czech lyrics framed the polka as a love song, whereas Brown and Timm's English version framed it as a song celebrating the repeal of Prohibition in the United States. At first the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Concerto (Grieg)
The Piano Concerto in A minor, Op. 16, composed by Edvard Grieg in 1868, was the only concerto Grieg completed. It is one of his most popular works, and is among the most popular of the genre. Grieg, who was only 24 years old at the time of the composition, had taken inspiration from Robert Schumann's piano concerto (Op.54), also in A minor. Structure The concerto is in three movements: Performance time of the whole concerto is usually about 30 minutes. Instrumentation Grieg scored the concerto for solo piano, 2 flutes, 2 oboes, 2 clarinets (in A and B), 2 bassoons, 4 horns in E and E, 2 trumpets in C and B, 3 trombones, timpani and strings (violins, violas, cellos and double basses). An earlier version called for only two horns and a tuba instead of a third trombone. History and influences The work is among Grieg's earliest important works, written by the 24-year-old composer in 1868 in Søllerød, Denmark, during one of his visits there to benefit from the cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edvard Grieg
Edvard Hagerup Grieg ( , ; 15 June 18434 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist. He is widely considered one of the leading Romantic music, Romantic era composers, and his music is part of the standard classical repertoire worldwide. His use of Music of Norway, Norwegian folk music in his own compositions brought the music of Norway to fame, as well as helping to develop a Norwegian romantic nationalism, national identity, much as Jean Sibelius did in Finland and Bedřich Smetana in Bohemia. Grieg is the most celebrated person from the city of Bergen, with numerous statues that depict his image and many cultural entities named after him: the city's largest concert building (Grieg Hall), its most advanced music school (Grieg Academy) and its professional choir (Edvard Grieg Kor). The Edvard Grieg Museum at Grieg's former home, Troldhaugen, is dedicated to his legacy. Background Edvard Hagerup Grieg was born in Bergen, Norway. His parents were Alexander Grieg (1806 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Concerto No
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an action mechanism where hammers strike strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a chromatic scale in equal temperament. A musician who specializes in piano is called a pianist. There are two main types of piano: the grand piano and the upright piano. The grand piano offers better sound and more precise key control, making it the preferred choice when space and budget allow. The grand piano is also considered a necessity in venues hosting skilled pianists. The upright piano is more commonly used because of its smaller size and lower cost. When a key is depressed, the strings inside are struck by felt-coated wooden hammers. The vibrations are transmitted through a bridge to a soundboard that amplifies the sound by coupling the acoustic energy to the air. When the key is released, a damper stops the string's vibration, ending the sound. Most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |