|
History Of Virology
The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Edward Jenner and Louis Pasteur developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a "virus" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. The subsequent discovery and partial characterization of bacteriophages by Frederick Twort and Félix d'Herelle further catalyzed the field, and by the early 20th century many viruses had been discovered. In 1926, Thomas Milton Rivers defined viruses as obliga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivanovsky
Ivanovsky (; masculine), Ivanovskaya (; feminine), or Ivanovskoye (; neuter), are forms of a Russian adjective derived from the first name Ivan. It may refer to: People * Ivanovsky (surname) (feminine: Ivanovskaya), Russian surname Places * Ivanovsky District, name of several districts in Russia * Ivanovsky Municipal Okrug, a municipal okrug of Nevsky District of St. Petersburg, Russia * Ivanovsky (rural locality) (Ivanovskaya, Ivanovskoye), name of several rural localities in Russia *Ivanovo Oblast Ivanovo Oblast () is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It had a population of 927,828 as of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Russian Census. Its three largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, cities are Ivanovo (the administrat ... (), a federal subject of Russia * Ivanovskoye District, a district of Eastern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, Russia * Ivanovsky Waterfall, a waterfall in Sochi National Park, Russia See also * Ivanivske (other) * Ivanovski [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
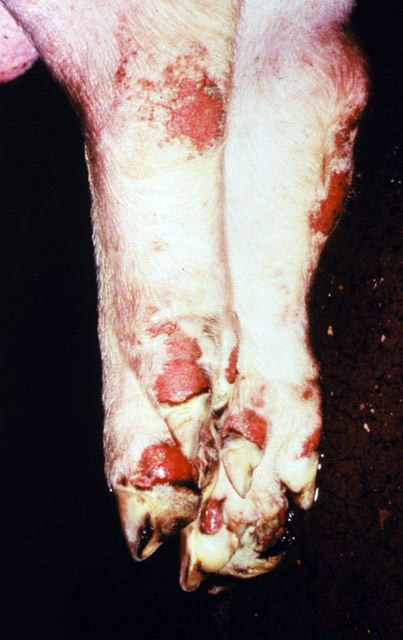
Foot-and-mouth Disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious disease, infectious and sometimes fatal virus (biology), viral disease that primarily affects even-toed ungulates, including domestic and wild Bovidae, bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, followed by vesicle (dermatology), blisters inside the mouth and near the hoof that may rupture and cause lameness. FMD has very severe implications for animal farming, since it is highly infectious and can be spread by infected animals comparatively easily through contact with contaminated farming equipment, vehicles, clothing, and feed, and by domestic and wild predators. Its containment demands considerable efforts in vaccine, vaccination, strict monitoring, trade restrictions, quarantines, and the culling of both infected and healthy (uninfected) animals. Susceptible animals include cattle, domestic water buffalo, water buffalo, domestic sheep, sheep, goats, pigs, antelope, deer, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Frosch
Paul may refer to: People * Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people * Paul (surname), a list of people * Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament * Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo Paul & Paula * Paul Stookey, one-third of the folk music trio Peter, Paul and Mary * Billy Paul, stage name of American soul singer Paul Williams (1934–2016) * Vinnie Paul, drummer for American Metal band Pantera * Paul Avril, pseudonym of Édouard-Henri Avril (1849–1928), French painter and commercial artist * Paul, pen name under which Walter Scott wrote ''Paul's letters to his Kinsfolk'' in 1816 * Jean Paul, pen name of Johann Paul Friedrich Richter (1763–1825), German Romantic writer Places *Paul, Cornwall, a village in the civil parish of Penzance, United Kingdom *Paul (civil parish), Cornwall, United Kingdom *Paul, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community *Paul, Idaho, United States, a city *Paul, Nebraska, United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Loeffler
Friedrich August Johannes Loeffler (; 24 June 18529 April 1915) was a German bacteriologist at the University of Greifswald. Biography He obtained his M.D. degree from the University of Berlin in 1874. He worked with Robert Koch from 1879 to 1884 as an assistant in the Imperial Health Office in Berlin. In 1884, he became staff physician at the Friedrich Wilhelm Institute in Berlin, and four years later became professor at the University of Greifswald. His development of original methods of staining rendered an important and lasting service to bacteriology. Early in his career, he began a study of parasitic diseases. Among his discoveries was the organism causing diphtheria (''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'') and the cause of foot-and-mouth disease ( Aphthovirus). His description of the diphtheria bacillus, published in 1884, was the originating cause of an antitoxin treatment. He also created Löffler's serum, a coagulated blood serum used for the detection of the bacteria. In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contagium Vivum Fluidum
''Contagium vivum fluidum'' (Latin: "contagious living fluid") was a phrase first used to describe a virus, and underlined its ability to slip through the finest ceramic filters then available, giving it almost liquid properties. Martinus Beijerinck (1851–1931), a Dutch microbiologist and botanist, first used the term when studying the tobacco mosaic virus, becoming convinced that the virus had a liquid nature. The word "virus", from the Latin for "poison", was originally used to refer to any infectious agent, and gradually became used to refer to infectious particles. Bacteria could be seen under microscope, and cultured on agar plates. In 1890, Louis Pasteur declared "tout virus est un microbe": "all infectious diseases are caused by microbes". In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky discovered that the cause of tobacco mosaic disease could pass through Chamberland's porcelain filter. Infected sap, passed through the filter, retained its infectious properties. Ivanovsky thought the diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from '' toxic''. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. They vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Less strict understandings embrace naturally occurring inorganic toxins, such as arsenic. Other understandings embrace synthetic analogs of naturally occurring organic poisons as toxins, and may or may not embrace naturally oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus '' Tobamovirus'' that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves (hence the name). TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus. The virus was crystallised by Wendell Meredith Stanley. It has a similar size to the largest synthetic molecule, known as PG5 with comparable length and diameter. History In 1886, Adolf Mayer first described the tobacco mosaic disease that could be transferred between plants, similar to bacterial infections. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky gave the first concrete e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wageningen
Wageningen () is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a historic city in the central Netherlands, in the province of Gelderland. It is famous for Wageningen University, which specialises in life sciences. The municipality had a population of in , of which many thousands are students from over 150 countries. Demographics Inhabitants by nationality 71,68% is Dutch, 28,32% has a migration background. Geography Wageningen is situated on the north bank of the Nederrijn (the Dutch portion of the Lower Rhine) part of the and the Veluwe, of which the southwest hill is called the ''Wageningse Berg''. Wageningen can be reached by car from highways A12 via the N781, A15 via the N233 and N225, and A50 via the N225, and from the Ede-Wageningen railway station via a 20-minute bus drive to the Wageningen central terminal (see below)., ''Topographic map of the municipality of Wageningen, July 2013 (click to enlarge)'' History The oldest known settlements in the Wageni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Mayer
Adolf Eduard Mayer (9 August 184325 December 1942) was a German agricultural biologist whose work on tobacco mosaic disease played an important role in the discovery of tobacco mosaic virus and viruses in general. Mayer was born in 1843 into the family of a high school teacher in Oldenburg. His mother was a daughter of renowned German chemist Leopold Gmelin. From 1860 to 1862 he studied biology, geology and chemistry at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. In 1862 he enrolled at the University of Heidelberg, where in 1864 he graduated summa cum laude with a Ph.D. in biology. In 1879, while Mayer held the position of the director of the Agricultural Experiment Station at Wageningen in the Netherlands, he was asked by Dutch farmers to study a peculiar disease affecting the tobacco plant. Mayer published a paper in 1886 on the disease, which he named "mosaic disease of tobacco", and described its symptoms in detail. He demonstrated that the disease can be transmitted by using t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamberland Filter
A Chamberland filter, also known as a Pasteur–Chamberland filter, is a porcelain water filter invented by Charles Chamberland in 1884. It was developed after Henry Doulton's ceramic water filter of 1827. It is similar to the Berkefeld filter in principle. Design The filter consists of a permeable unglazed porcelain tube (called bisque) that contains a ring of enameled porcelain through which the inflow pipe fits. The core of the porcelain is made up of a metal pipe with holes through which water flows out and is collected. Inflow is pressurized so filtration occurs under force. There are 13 types: ''L1'' to ''L13''. L1 filters have the coarsest pore size while L13 have the finest. Usefulness The Pasteur-Chamberland filter is as useful as other ceramic and porcelain filters. It is a good bacterial water filter used mainly as a high volume water filter.Textbook of Microbiology by Ananthanarayan and Panikar, The filter works more quickly when the water supplied is und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Chamberland
Charles Edouard Chamberland (; 12 March 1851 – 2 May 1908) was a French microbiologist from Chilly-le-Vignoble in the department of Jura who worked with Louis Pasteur. Chamberland was present at Pouilly-le-Fort when the efficacy of the anthrax vaccine, which he had made with Emile Roux, was validated. Following this success, Chamberland was put in charge of mass-producing the anthrax vaccine. In 1884 he developed a type of filtration known today as the Chamberland filter or Chamberland-Pasteur filter, a device that made use of an unglazed porcelain bar. The filter had pores that were smaller than bacteria, thus making it possible to pass a solution containing bacteria through the filter, and having the bacteria completely removed from the solution. Chamberland was also credited for starting a research project that led to the invention of the autoclave An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |