|
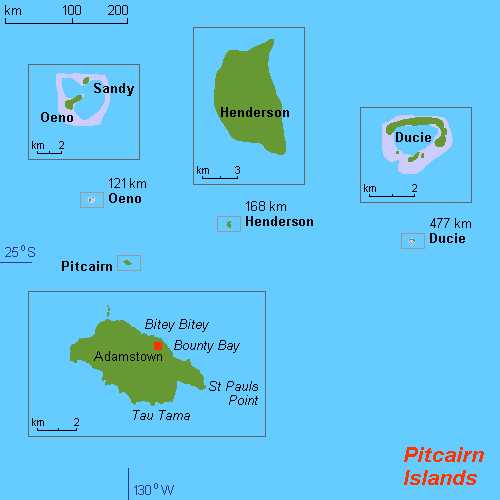
History Of The Pitcairn Islands
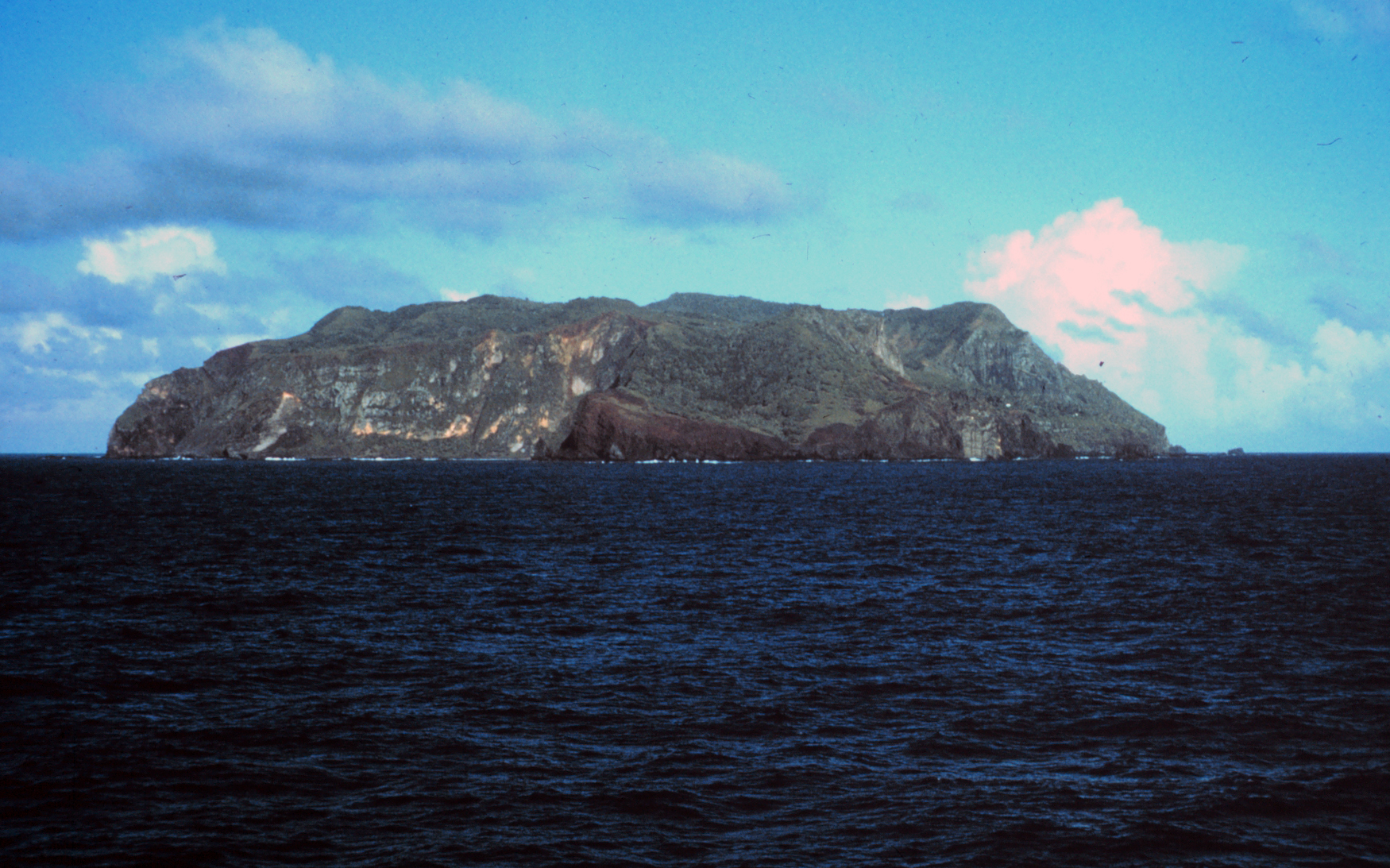
The history of the Pitcairn Islands begins with the colonization of the islands by Polynesians in the 11th century. Polynesian people established a culture that flourished for four centuries and then vanished. They lived on Pitcairn and Henderson Islands, and on Mangareva Island to the northwest, for about 400 years. In 1790, nine of the mutineers from HMS ''Bounty'', led by Fletcher Christian, abducted 18 native Tahitians and settled on Pitcairn Island, afterwards setting fire to the ''Bounty''. Christian's group continued under the auspices of Ned Young and John Adams until contacted by Mayhew Folger in 1808, by which time Adams was the only surviving mutineer. Polynesian society The earliest known settlers of the Pitcairn Islands were Polynesians who appear to have settled on Pitcairn and Henderson Islands by at least the 11th Century, and on the more populous Mangareva Island to the northwest, for several centuries. These first inhabitants may have maintained a tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
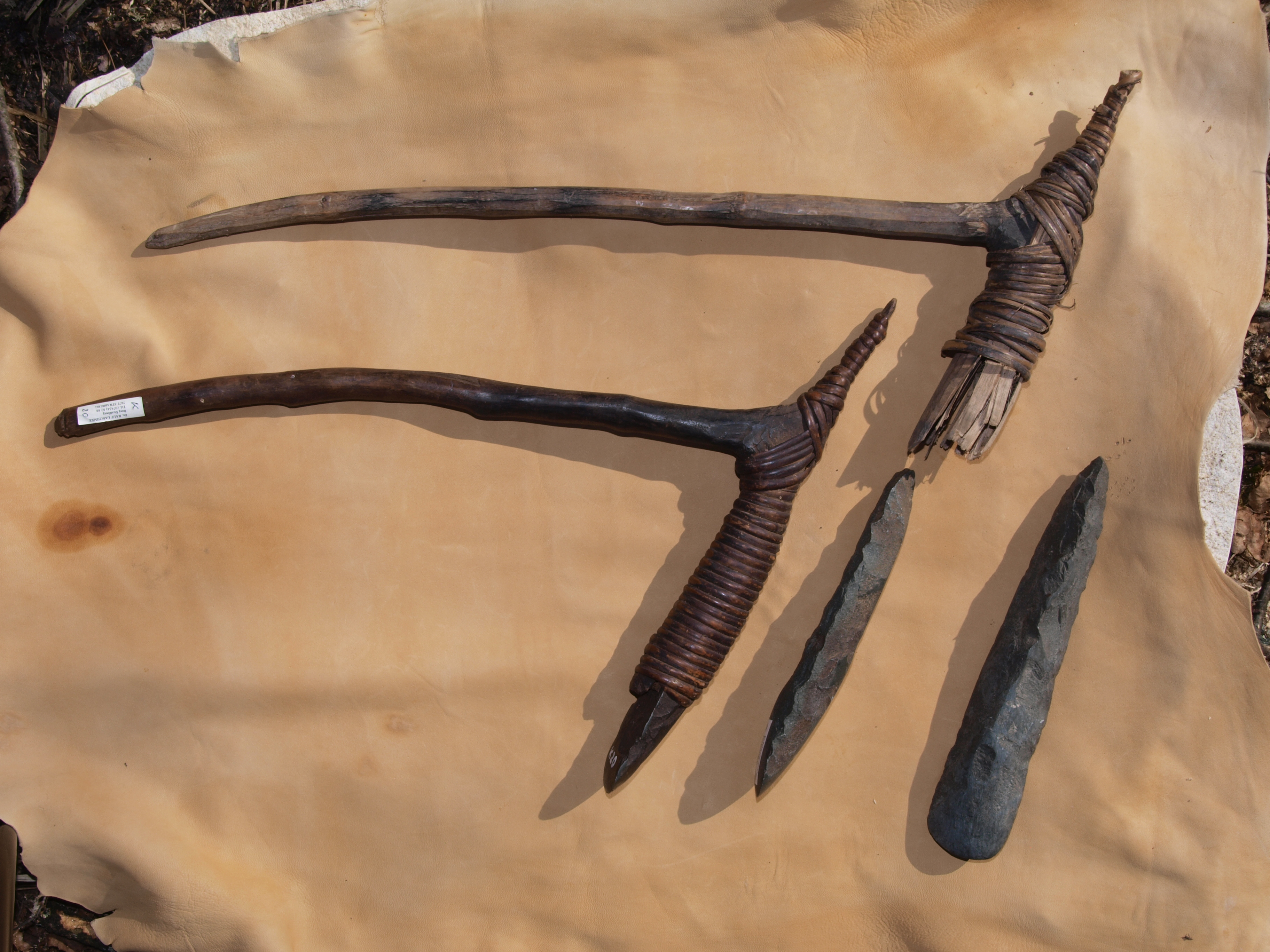
Adze
An adze () or adz is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing or carving wood in hand woodworking, and as a Hoe (tool), hoe for agriculture and horticulture. Two basic forms of an adze are the hand adze (short hoe)—a short-handled tool swung with one hand—and the foot adze (hoe)—a long-handled tool capable of powerful swings using both hands, the cutting edge usually striking at foot or shin level. A similar tool is called a mattock, which differs by having two blades, one perpendicular to the handle and one parallel. History Africa The adze is depicted in ancient Egyptian art from the Old Kingdom onward. Originally the adze blades were made of stone, but already in the Predynastic Egypt, Predynastic Period copper adzes had all but replaced those made of flint. Stone blades were fastened to the handle by tying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
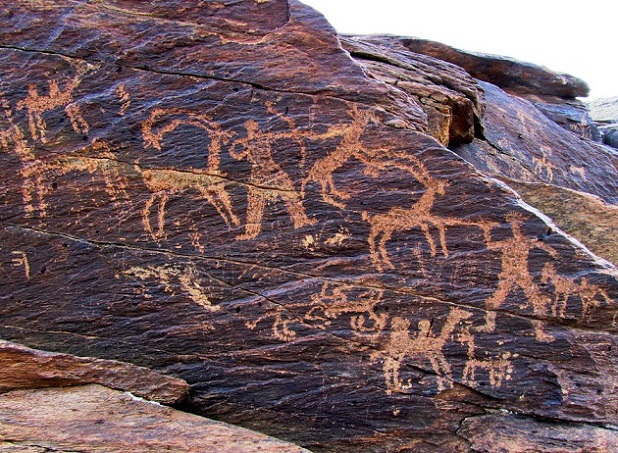
Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix , from meaning " stone", and meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as . In scholarly texts, a ''petroglyph'' is a rock engraving, whereas a '' petrograph'' (or ''pictograph'') is a rock painting. In common usage, the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
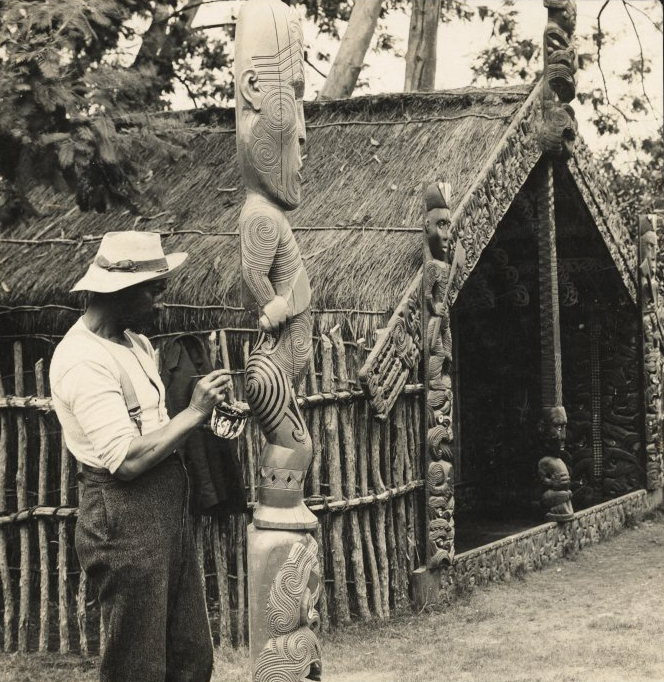
Tiki
In Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne. He found the first woman, Marikoriko, in a pond; she seduced him and he became the father of Hine-kau-ataata. By extension, a tiki is a large or small wooden, pounamu or other stone carving in humanoid form, although this is a somewhat archaic usage in the Māori language, where a tiki is usually a hei-tiki, a pendant worn around the neck. Hei-tiki are often considered taonga, especially if they are older and have been passed down throughout multiple generations. Carvings similar to tiki and coming to represent deified ancestors are found in most Polynesian cultures. They often serve to mark the boundaries of sacred or significant sites. The word has cognates in other Polynesian languages, such as ''tii'' in Tahitian and ''kii'' in Hawaiian. In the Western world, Tiki culture, a movement inspired by various Pacific cultures, has become popular in the 20th and 21st centuries. Religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marae
A ' (in Māori language, New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian language, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan language, Tongan), ' (in Marquesan language, Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan language, Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian culture, Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term also means cleared and free of weeds or trees. generally consist of an area of cleared land roughly rectangular (the itself), bordered with stones or wooden posts (called ' in Tahitian and Cook Islands Māori) perhaps with ' (terraces) which were traditionally used for ceremonial purposes; and in some cases, such as Easter Island, a central stone ' or ''a'u'' is placed. In the Easter Island Rapa Nui people, Rapa Nui culture, the term ''ahu'' or ''a'u'' has become a synonym for the whole marae complex. In some modern Polynesian societies, notably that of the Māori people, Māori of New Zealand, the marae is still a vital part of everyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are imaginary semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, south-east London on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Parallel (latitude), Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''Normal (geometry), normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the equatorial plane, plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Chronometer
A marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), and the time at the current location found from observations of celestial bodies. When first developed in the 18th century, it was a major technical achievement, as accurate knowledge of the time over a long sea voyage was vital for effective navigation, lacking electronic or communications aids. The first true chronometer was the life work of one man, John Harrison, spanning 31 years of persistent experimentation and testing that revolutionized naval (and later aerial) navigation. The term ''wikt:chronometer, chronometer'' was coined from the Greek words () (meaning time) and (meaning measure). The 1713 book ''Physico-Theology'' by the English cleric and scientist William Derham includes one of the earliest theoretical descriptions of a marine chronome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pitcairn
Major John Pitcairn (28 December 1722 – 17 June 1775) was a British military officer. Born in Dysart, Fife, he enlisted in the Chatham Marine Division of the British Naval Service at the age of 23. He served in North America during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. Arriving in Boston in 1774 with the rank of major, he fought in the 1775 battles of Lexington and Concord during the outbreak of the American War of Independence. Two months later in June, Pitcairn was killed in action during the Battle of Bunker Hill. Respected by both his men and his American opponents, he was buried at Boston's Old North Church. At the time of his death Pitcairn was serving alongside his son Thomas, also a marine officer in the same division, who helped to carry his mortally wounded father from the battlefield. Early life and education Pitcairn was born in 1722 in Dysart, a port town in Fife, Scotland. His parents were the Reverend David Pitcairn and Katherine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Pitcairn (Royal Navy Officer)
Robert Pitcairn (6 May 1752 – ) was a Scottish midshipman in the Royal Navy. Pitcairn Island was named after him; he was the first person to spot the island, on 2 July 1767 (ship's time), while serving in a voyage in the South Pacific on , captained by Philip Carteret. Early life and family Pitcairn was born in Burntisland, Fife, in 1752. His father, John Pitcairn (1722–75), was a major in the Royal Marines who commanded the British advance party at the Battle of Lexington where the "shot heard round the world" was fired, and who died from wounds after the Battle of Bunker Hill in 1775. His paternal grandfather, David Pitcairn, was a clergyman at Dysart, Fife, and his paternal grandmother Katherine was the daughter of William Hamilton. His mother Elizabeth (1724–1809) was the daughter of Robert Dalrymple. His uncle William Pitcairn (1712–91) was a doctor at St Bartholomew's Hospital in London. Among his eight siblings (four other sons and four daughters) were: * His br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Carteret
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret, Seigneur of Trinity (22 January 1733 – 21 July 1796) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer who participated in two of the British navy's circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69. Biography Carteret was the son of Charles de Carteret, Seigneur of Trinity, and his wife Frances-Mary S. Paul. Carteret entered the navy in 1747, serving aboard the , and then under Captain John Byron from 1751 to 1755. Between 1757 and 1758 he was in the on the Mediterranean Station. As a lieutenant in the he accompanied Byron during his voyage of circumnavigation, from June 1764 to May 1766. In 1766 he was made a commander and given the command of HMS ''Swallow'' to circumnavigate the world, as consort to the under the command of Samuel Wallis. The two ships were parted shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Carteret discovering Pitcairn Island and the Carteret Islands, which were subsequently named after him. In 1767, he also dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |