|
History Of The Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (201 BCE220 CE) was the second imperial dynasty of China. It followed the Qin dynasty, which had unified the Warring States of China by conquest. It was founded by Liu Bang (Emperor Gaozu). The dynasty is divided into two periods: the Western Han (202 BCE9 CE) and the Eastern Han (25–220 CE), interrupted briefly by the Xin dynasty (9–23 CE) of Wang Mang. These appellations are derived from the locations of the capital cities Chang'an and Luoyang, respectively. The third and final capital of the dynasty was Xuchang, where the court moved in 196 CE during a period of political turmoil and civil war. The Han dynasty ruled in an era of Chinese cultural consolidation, political experimentation, relative economic prosperity and maturity, and great technological advances. There was unprecedented territorial expansion and exploration initiated by struggles with non-Chinese peoples, especially the nomadic Xiongnu of the Euras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Civilisation
Han may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Han", a fifth season episode of ''The West Wing'' * Han (musician), born Han Ji-sung, a South Korean singer-songwriter, rapper, and record producer, member of Stray Kids * Han Lue, a character in the ''Fast & Furious'' franchise * Han Solo, a character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise Education * Han school, Japan, Edo period * HAN University of Applied Sciences, in the Netherlands People Ethnic groups * Han Chinese, or Han people (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group ** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese people who are fully or partially of Han Chinese descent * Han Minjok, or Han people (): the Korean native name referring to Koreans * Hän: one of the First Nations peoples of Canada Names * Han (name), a given name and surname ** Han (Chinese surname), also Haan, Hahn or Hann, the Romanized spelling of many Chinese family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xin Dynasty
The Xin dynasty (; ), also known as Xin Mang () in Chinese historiography, was a short-lived Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty which lasted from 9 to 23 AD, established by the Han dynasty consort kin Wang Mang, who usurped the throne of the Emperor Ping of Han and the infant "crown prince" Ruzi Ying, Liu Ying. The Xin dynasty ruled for over a decade before it was overthrown by rebels. After Wang's death, the Han dynasty was restored by Emperor Guangwu of Han, Liu Xiu, a distant descendant of the Emperor Jing of Han; therefore, the Xin dynasty is often considered an interregnum of the Han, dividing it into the Western Han and the Eastern Han. Etymology Chinese dynasties were typically named after the fief of their founders, and this reading is consistent with Wang Mang's pre-imperial position as Marquess of Xin. In 1950, C.B. Sargent suggested that the name of the dynasty should be read as meaning "new", which J. J. L. Duyvendak rejected out of hand. Chauncey S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 AD. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Tujue leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentrala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Emperors Of The Han Dynasty
The Emperor of China, emperors of the Han dynasty were the supreme heads of government during the second Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China; the Han dynasty (202 BC220 AD) followed the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and preceded the Three Kingdoms (220–265 AD). The era is conventionally periodised into the Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and Eastern Han (25–220 AD). The Han dynasty was founded by the peasant rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han, Emperor Gao (). The longest reigning emperor of the dynasty was Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu (), who reigned for 54 years. The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang, but he was killed during a rebellion on 6 October 23 AD. The Han dynasty was reestablished by Liu Xiu, known posthumously as Emperor Guangwu of Han, Emperor Guangwu () or Guangwu Di, who claimed the throne on 5 August 25 AD. The last Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, European Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary and Slovakia. Since the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age, the Steppe Route has been the main overland route between Eastern Europe, North Asia, Central Asia and East Asia economically, politically, and culturally. The Steppe route is a predecessor not only of the Silk Road, which developed during Classical antiquity, antiquity and the Middle Ages, but also of the Eurasian Land Bridge in the modern era. It has been home to nomadic empires and many large tribal confederations and ancient states throughout history, such as the Xiongnu, Scythia, Cimmerians, Cimmeria, Sarmatians, Sarmatia, Hunnic Empire, Sogdia, Xianbei, Mongol Empire, Magyar tribes, and Göktürk Khaganate. Geography Divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology Of The Han Dynasty
Many significant developments in the history of science and technology in China took place during the Han dynasty (202 BCE – 220 CE). The Han period saw great innovations in metallurgy. Following the inventions of the blast furnace and cupola furnace during the Zhou dynasty (256 BCE) to make pig iron and cast iron respectively, the Han period saw the development of steel and wrought iron by use of the finery forge and Puddling (metallurgy), puddling process. With the drilling of deep boreholes into the earth, the Chinese used not only derricks to lift brine up to the surface to be boiled into salt, but also set up bamboo-crafted pipeline transport systems which brought natural gas as fuel to the furnaces. Smelting techniques were enhanced with inventions such as the waterwheel-powered bellows; the resulting widespread distribution of iron tools facilitated the growth of agriculture. For Tillage, tilling the soil and planting straight rows of crops, the improved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society And Culture Of The Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (202 BCE220 CE) was a period of Imperial China divided into the Western Han (202 BCE9 CE) and Eastern Han (25–220 CE) periods, when the capital cities were located at Chang'an and Luoyang, respectively. It was founded by Emperor Gaozu of Han and briefly interrupted by the regime of Wang Mang (r. 9–23 CE) who usurped the throne from a child Han emperor. The Han dynasty was an age of great economic, technological, cultural, and social progress in China. Its society was governed by an emperor who shared power with an official bureaucracy and semi-feudal nobility. Its laws, customs, literature, and education were largely guided by the philosophy and ethical system of Confucianism, yet the influence of Legalism and Daoism (from the previous Zhou dynasty) could still be seen. Members of the scholarly-gentry class who aspired to hold public office were required to receive a Confucian-based education. A new synthetic ideology of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
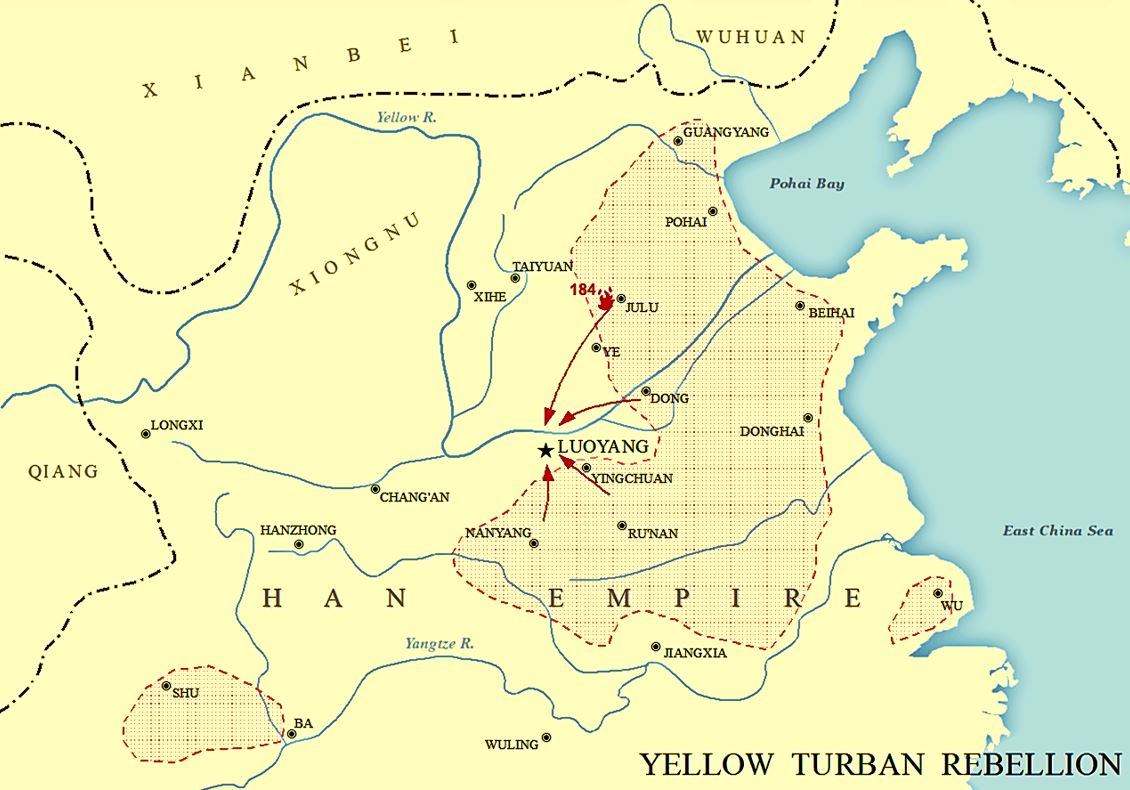
End Of The Han Dynasty
The end of the (Eastern) Han dynasty was the period of History of China, Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms era (220–280 CE). During the end of the Han dynasty, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow Turban Rebellion (184–205). Meanwhile, the Han Empire's institutions were destroyed by the warlord Dong Zhuo and fractured into regional regimes ruled by various warlords, some of whom were nobles and officials of the Han imperial court. The warlord Cao Cao took control of Emperor Xian and his court in 196 and began gradually reunifying the empire. Cao Cao ostensibly operated under Emperor Xian's rule, though in reality the emperor was a hostage. Cao Cao's efforts to reunify China were rebuffed at the Battle of Red Cliffs in 208-209, when his armies were defeated by the allied forces of Sun Quan and Liu Bei. The Han d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuchang
Xuchang ( zh, s=, t= ; postal: Hsuchang) is a prefecture-level city in central Henan province in Central China. It is bordered by the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the northwest, Kaifeng to the northeast, Zhoukou to the east, Luohe to the southeast, and Pingdingshan to the southwest. Its population was 4,307,488 inhabitants at the final 2010 census, of whom 1,952,666 lived in the built-up (or "metro") area made up of Weidu and Jian'an districts (named from Emperor Xian of Han’s era name) and Changge City largely being urbanized. In 2007, the city was named as one of China's top ten livable cities by Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum. Administration The prefecture-level city of Xuchang administers 2 districts, 2 county-level cities and 2 counties. * Weidu District () * Jian'an District () * Yuzhou City () * Changge City () * Yanling County () * Xiangcheng County () History During the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |