|
History Of Rail Transport In Chile
:''This article is part of the history of rail transport by country series'' The history of rail transport in Chile has gone through several periods of boom and bust. It began in 1840, with the construction by William Wheelwright of the first branch in the north (from Copiapo Caldera; see below). Further construction proceeded apace linking cities from Pisagua, Chile, Pisagua all the way to Puerto Montt. In addition, there was a network on the big island of Chiloé railway, Chiloe, and a host of now completely abandoned branches. Four cross border lines were also built: * Arica to La Paz in Bolivia, * another from Antofagasta to La Paz (currently operated only to Cochabamba), * Antofagasta to Salta (Argentina) * Valparaíso to Buenos Aires. The majority of rail infrastructure in Chile was constructed by private enterprise for freight transport, particularly for mining and to some extent forestry. The state did construct and operate some railways, first as FFCC del Estado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Rail Transport By Country
The history of rail transport began before the beginning of the common era. It can be divided into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of track material and motive power used. Ancient systems The Post Track, a prehistoric causeway in the valley of the River Brue in the Somerset Levels, England, is one of the oldest known constructed trackways and dates from around 3838 BCE, making it some 30 years older than the Sweet Track from the same area. Various sections have been designated as scheduled monuments. Evidence indicates that there was a ''Diolkos'' paved trackway, which transported boats across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece from around 600 BCE.Cook, R. M.: "Archaic Greek Trade: Three Conjectures 1. The Diolkos", ''The Journal of Hellenic Studies'', vol. 99 (1979), pp. 152–155 (152)Lewis, M. J. T."Railways in the Greek and Roman world", in Guy, A. / Rees, J. (eds), ''Early Railways. A Selection of Papers from the First International Early Railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Energy In Chile
Renewable energy in Chile is classified as Conventional and Non Conventional Renewable Energy (NCRE), and includes biomass, hydro-power, geothermal, wind and solar among other energy sources. Usually, when referring to Renewable Energy in Chile, it will be the Non Conventional kind. Chile has considerable geothermal, solar and wind energy resources while fossil fuel resources are limited. Chile has been described as "a world leader in renewable energy development." In 2016 Non Conventional Renewable Energy provided 7,794 GWh, or 11.4% of the country's total electricity generation. NCRE accounted for 17.2% of the installed electricity generation capacity by the end of 2016. On 2022, for the first time solar and wind energy generated more power than coal-based energy (27.5% vs. 26.5%). Timeline of key developments 2013 In 2013, with the promulgation of the law 20,698, the target was increased to 20% by the year 2025, and a new progression for the following years was defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tocopilla Nitrate Railway
The Tocopilla railway was a mountain railway built to serve the sodium nitrate mines in the Toco area of Antofagasta Region, Chile. With a 3 ft 6 in gauge railways, gauge of 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm), it ran from the port of Tocopilla on the Pacific coast up to a height of with Grade (slope)#Railways, gradients up to 1 in 24. The line was electrified in the mid-1920s, and expanded in 1930 with the addition of lines serving new areas of mining. Running from María-Elena to Tocopilla, it was the last operating nitrate railway in Chile, and the last operating section of a railway system that moved caliche#Chilean caliche, caliche ore to processing plants and nitrate to the port of Tocopilla. It was a magnet for rail fans before closing in August 2015 after severe rainfall damaged the tracks to the extent that the owner decided it was beyond economic repair. Its history was influenced primarily by two factors: the rise and fall of the Chilean nitrate industry in particular Sociedad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferronor
file:Ferronor chile logo.png, 200px Ferronor (Empresa de Transporte Ferroviario S.A.) is a Chilean railway company operating on the old Red Norte (northern network) of Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado, which was privatised in 1997. Since 2004 the primary shareholder is APCO. Currently Ferronor owns a railway network of about , consisting of a main line between La Calera, Chile, La Calera and Iquique and various spur lines. However, about 60% of the railway network are currently unused due to damage like landslides, washouts and rail theft. Ferronor mostly transports mining supplies and products. Ferronor transports 7,000,000 tonnes of iron ore concentrate, 900,000 tonnes of salt, 290,000 tonnes of copper concentrate, 530,000 tonnes of sulfuric acid, 230,000 tonnes of Copper extraction techniques#Electrorefining, copper cathodes and 35,000 tonnes of fuel annually. Other railway operators transport 2,200,000 tonnes of freight on Ferronor lines annually. Diego de Almagro div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Railway
The Andean Railway (native name: Ferrocarril Andino) was a state-owned railway company in Argentina which, towards the end of the 19th century, built and operated a line connecting Villa María in Córdoba Province with the cities of Mendoza, San Luis and San Juan. The network was later sold to a number of British-owned railway companies. History The first plan to reach the Andes through railway had been carried out with a concession granted to Central Argentine Railway (CAR) and later with the project to make Buenos Aires Western Railway a trans-andean line. The aim of the railway was linking the three provinces of the Cuyo region, San Juan, San Luis and Mendoza with the city of Rosario, via the CAR. The AR was the first state-owned railway in Argentina and was founded on 15 November 1867 by decree promulgated in November 1867, from Villa María to Villa Nueva, then extending to Río Cuarto. At the beginning of 1870 the Government signed an agreement to British entrepre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, warm valleys, high-altitude Andean plateaus, and snow-capped peaks, encompassing a wide range of climates and biomes across its regions and cities. It includes part of the Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, along its eastern border. It is bordered by Brazil to the Bolivia-Brazil border, north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the Argentina-Bolivia border, south, Chile to the Bolivia–Chile border, southwest, and Peru to the west. The seat of government is La Paz, which contains the executive, legislative, and electoral branches of government, while the constitutional capital is Sucre, the seat of the judiciary. The largest city and principal industrial center is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
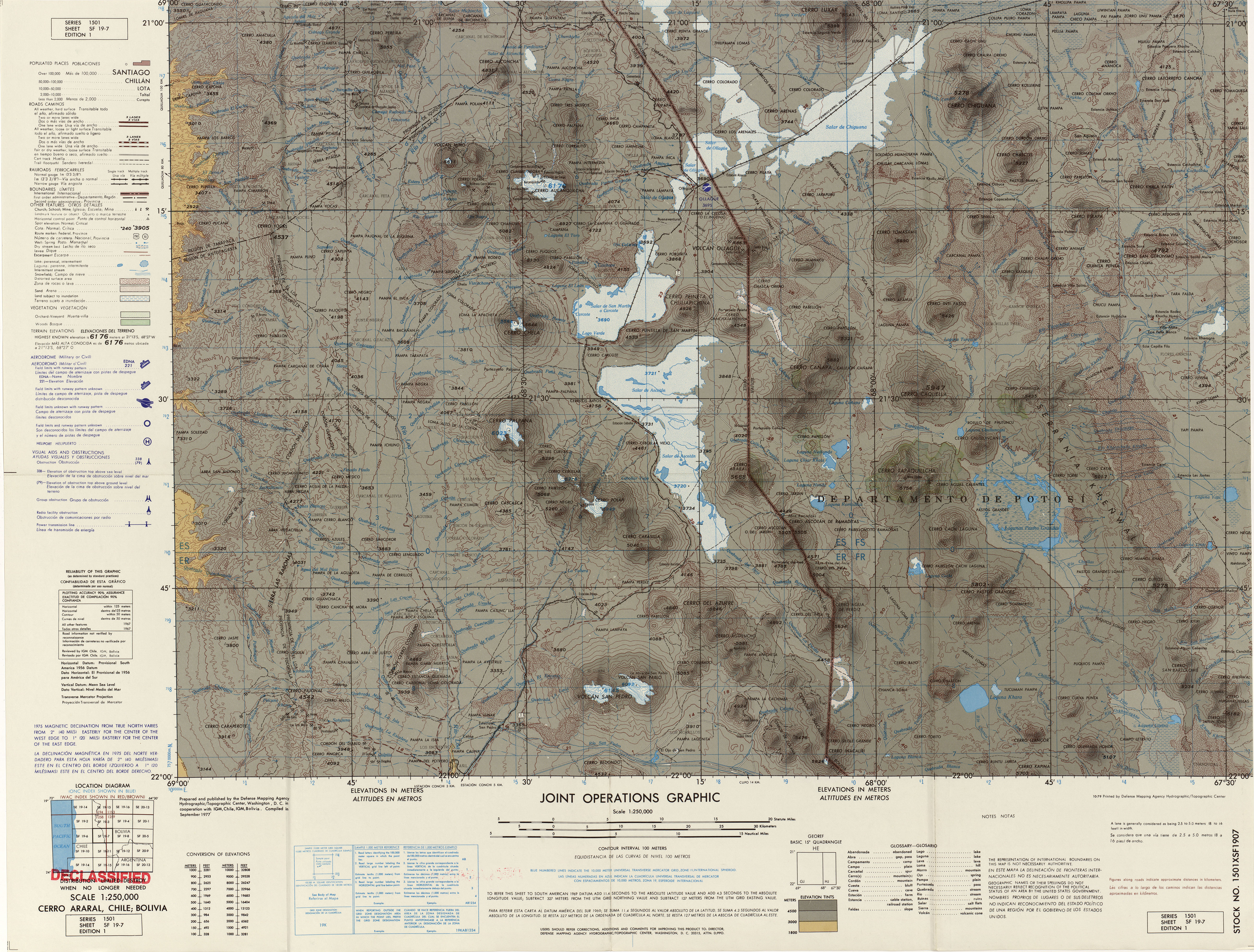
Ollagüe
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of Andesite, andesitic lava flows. A fault (geology), fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of Dacite, dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu (Nor Lípez), Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconcagua River
The Aconcagua River is a river in Chile that rises from the conflux of two minor tributary rivers at above sea level in the Andes, Juncal River from the east (which rise in the Nevado Juncal) and Blanco River from the south east. The Aconcagua river flows westward through the broad Aconcagua valley and enters the Pacific Ocean near the city of Concon, north of Valparaíso. The river has a course of about , and its waters irrigate the most populous sections of the Chilean provinces of San Felipe de Aconcagua and Los Andes, being the most important economic resource of those regions. During the course of the Aconcagua river, it receives contributions from many others rivers and swamps, reaching a mean flow of . The Aconcagua River valley was used as the route of the Transandine Railway on the Chilean side. The river flows alongside Chile Route 5 from Llaillay to La Calera. For much of their lengths, the two separate stretches of Chile Route 60 follow the course of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoza, Argentina
Mendoza (), officially the City of Mendoza (), is the capital of the Provinces of Argentina, province of Mendoza Province, Mendoza in Argentina. It is located in the northern-central part of the province, in a region of foothills and high plains, on the eastern side of the Andes. As of the , Mendoza had a population of 115,041 with a metropolitan population of 1,055,679, making Greater Mendoza the fourth largest census metropolitan area in the country. National Route 7 (Argentina), Ruta Nacional 7, the major road running between Buenos Aires and Santiago, Chile, Santiago, runs through Mendoza. The city is a frequent stopover for climbers on their way to Aconcagua (the highest mountain in the Western and Southern Hemispheres) and for adventure travelers interested in mountaineering, hiking, horse riding, rafting, and other sports. In the winter, skiers come to the city for easy access to the Andes. Two of the main industries of the Mendoza area are olive oil production and Argen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Andes, Chile
Los Andes, founded on July 31, 1791 as Santa Rosa de Los Andes, is a Chilean List of cities in Chile, city and Communes of Chile, commune located in the Province of Los Andes, Chile, province of the same name, in Valparaíso Region ("Fifth Region" of Chile). It lies on the route between Santiago, Chile, Santiago and Chile's primary border crossing with Argentina by way of the summit of the Uspallata Pass in the Andes mountain range. Demographics According to the 2002 census of the National Statistics Institute (Chile), National Statistics Institute, Los Andes spans an area of and has 60,198 inhabitants (30,247 men and 29,951 women). Of these, 55,388 (92%) lived in urban areas and 4,810 (8%) in rural areas. The population grew by 21% (10,451 persons) between the 1992 and 2002 censuses. Administration As a municipality, Los Andes is a third-level administrative division of Chile governed by a municipal council, headed by an alcalde who is directly elected every four years. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Northeastern United States, originally connecting Pavonia Terminal in Jersey City, New Jersey, with Lake Erie at Dunkirk, New York. The railroad expanded west to Chicago following its 1865 merger with the former Atlantic and Great Western Railroad, also known as the New York, Pennsylvania and Ohio Railroad (NYPANO RR). The mainline route of the Erie Railroad proved influential in the development and economic growth of the Southern Tier of New York state, including the cities of Binghamton, Elmira, and Hornell. The Erie Railroad repair shops were located in Hornell and was Hornell's largest employer. Hornell was also where Erie's mainline split into two routes with one proceeding northwest to Buffalo and the other west to Chicago. On October 17, 1960, Erie Railroad merged with its former rival, Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad, to form the Erie Lackawanna Railway. The Hornell repair shops were closed in 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer. Biography Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland, and immigrated to the United States with his parents, Louis and Cecile (Braun) Agassiz, in 1846. He graduated from Harvard University in 1855, subsequently studying engineering and chemistry, and taking the degree of Bachelor of Science at the Lawrence Scientific School of the same institution in 1857; in 1859 became an assistant in the United States Coast Survey. Thenceforward he became a specialist in marine ichthyology. Agassiz was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1862. Up until the summer of 1866, Agassiz worked as assistant curator in the museum of natural history that his father founded at Harvard. E. J. Hulbert, a friend of Agassiz's brother-in-law, Quincy Adams Shaw, had discovered a rich copper lode known as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |