|
History Of Gamma-ray Burst Research
The history of gamma-ray began with the serendipitous detection of a gamma-ray burst (GRB) on July 2, 1967, by the U.S. Vela satellites. After these satellites detected fifteen other GRBs, Ray Klebesadel of the Los Alamos National Laboratory published the first paper on the subject, ''Observations of Gamma-Ray Bursts of Cosmic Origin''. As more and more research was done on these mysterious events, hundreds of models were developed in an attempt to explain their origins. Discovery Gamma-ray bursts were discovered in the late 1960s by the U.S. Vela nuclear test detection satellites. The Velas were built to detect gamma radiation pulses emitted by nuclear weapon tests in space. The United States suspected that the USSR might attempt to conduct secret nuclear tests after signing the Nuclear Test Ban Treaty in 1963. While most satellites orbited at about 500 miles above Earth's surface, the Vela satellites orbited at an altitude of 65,000 miles. At this height, the satell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serendipitous
Serendipity is an unplanned fortunate discovery. Serendipity is a common occurrence throughout the history of product invention and scientific discovery. Etymology The first noted use of "serendipity" was by Horace Walpole on 28 January 1754. In a letter he wrote to his friend Horace Mann, Walpole explained an unexpected discovery he had made about a lost painting of Bianca Cappello by Giorgio Vasari by reference to a Persian fairy tale, ''The Three Princes of Serendip''. The princes, he told his correspondent, were "always making discoveries, by accidents and sagacity, of things which they were not in quest of." The name comes from ''Serendip'', an old Persian name for Sri Lanka (Ceylon), hence ''Sarandib'' by Arab traders. It is derived from the Sanskrit ''Siṃhaladvīpaḥ'' (Siṃhalaḥ, Sri Lanka + dvīpaḥ, island). The word has been exported into many other languages, with the general meaning of "unexpected discovery" or "fortunate chance". Applications Invention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit for the speed at which conventional matter or energy (and thus any signal carrying information) can travel through space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and very sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Starlight viewed on Earth left the stars many years ago, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When communicating with distant space probes, it can take minutes to hours for signals to travel from Earth to the spacecraft and vice versa. In computing, the speed of light fixes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 11
The Venera 11 (russian: Венера-11 meaning ''Venus 11'') was a Soviet uncrewed space mission which was part of the Venera program to explore the planet Venus. Venera 11 was launched on 9 September 1978 at 03:25:39 UTC. Separating from its flight platform on December 23, 1978 the lander entered the Venus atmosphere two days later on December 25 at 11.2 km/s. During the descent, it employed aerodynamic braking followed by parachute braking and ending with atmospheric braking. It made a soft landing on the surface at 06:24 Moscow Time (03:24 UT) on 25 December after a descent time of approximately 1 hour. The touchdown speed was 7 to 8 m/s. Information was transmitted to the flight platform for retransmittal to earth until it moved out of range 95 minutes after touchdown. Landing coordinates are . Flight platform After ejection of the lander probe, the flight platform continued on past Venus in a heliocentric orbit. Near encounter with Venus occurred on December 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
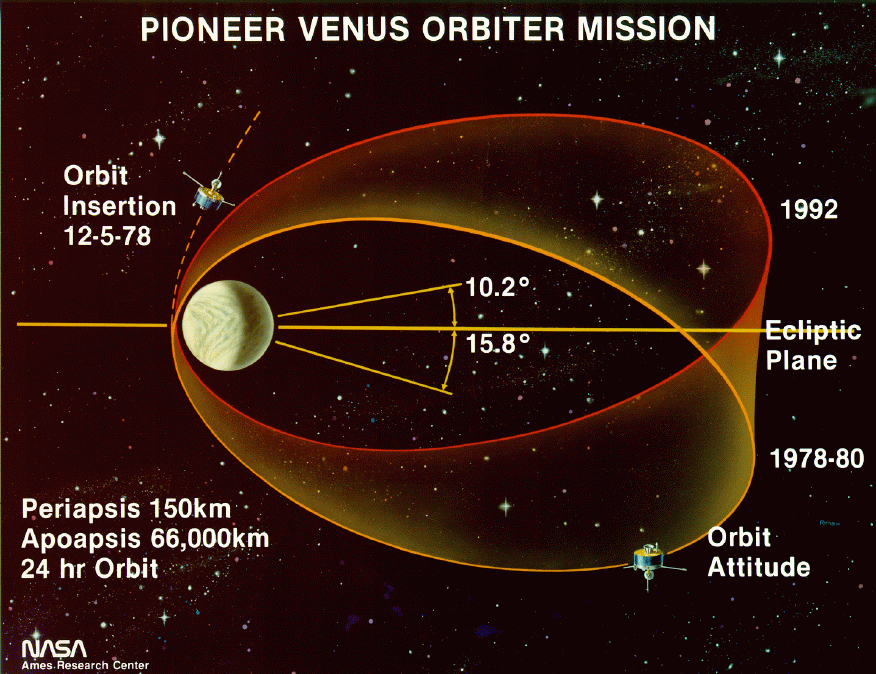
Pioneer Venus Orbiter
The Pioneer Venus Orbiter, also known as Pioneer Venus 1 or Pioneer 12, was a mission to Venus conducted by the United States as part of the Pioneer Venus project. Launched in May 1978 atop an Atlas-Centaur rocket, the spacecraft was inserted into an elliptical orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978. It returned data on Venus until October 1992. Launch and arrival at Venus The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was launched by an Atlas SLV-3D Centaur-D1AR rocket, which flew from Launch Complex 36A at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 13:13:00 on May 20, 1978, and deployed the Orbiter into heliocentric orbit for its coast to Venus. Venus orbit insertion occurred on December 4, 1978. Spacecraft Manufactured by Hughes Aircraft Company, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter was based on the HS-507 bus. The spacecraft was a flat cylinder, in diameter and long. All instruments and spacecraft subsystems were mounted on the forward end of the cylinder, except the magnetometer, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helios Probes
''Helios-A'' and ''Helios-B'' (after launch renamed ' and ') are a pair of probes that were launched into heliocentric orbit to study solar processes. As a joint venture between German Aerospace Center (DLR) and NASA, the probes were launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, on December10, 1974, and January15, 1976, respectively. The Helios project set a maximum speed record for spacecraft of . ''Helios-B'' performed the closest flyby of the Sun of any spacecraft until that time. The probes are no longer functional, but as of 2022 remain in elliptical orbits around the Sun. Construction The Helios project was a joint venture of West Germany's space agency DLR (70 percent share) and NASA (30 percent share). As built by the main contractor, Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, they were the first space probes built outside the United States and the Soviet Union to leave Earth orbit. Structure The two ''Helios'' probes look similar. ''Helios-A'' has a mass of , and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognoz SO-M
Prognoz, also known as SO (Solar Object, first three satellites), SO-M (SO-modified, next seven satellites) and SO-M2 (last two satellites, also known as Interball) was a Soviet Union, Soviet scientific research satellite programme. Twelve Prognoz satellites were launched between 14 April 1972 and 29 August 1996, by Molniya-M carrier rockets. The satellites were placed in High Earth orbits. First ten Prognoz spacescrafts were launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 31, Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome and last two from Plesetsk Cosmodrome Site 43, Site 43/3 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. The satellites were primarily used for Sun, Solar research, however the later satellites were used for other research, including research into the Big Bang theory, and Earth's magnetosphere.Encyclopedia Astronautica - Prognoz The ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterPlanetary Network
The InterPlanetary Network (IPN) is a group of spacecraft equipped with gamma ray burst (GRB) detectors. By timing the arrival of a burst at several spacecraft, its precise location can be found. The precision for determining the direction of a GRB in the sky is improved by increasing the spacing of the detectors, and also by more accurate timing of the reception. Typical spacecraft baselines of about one AU (astronomical unit) and time resolutions of tens of milliseconds can determine a burst location within several arcminutes, allowing follow-up observations with other telescopes. Rationale Gamma rays are too energetic to be focused with mirrors. The rays penetrate mirror materials instead of reflecting. Because gamma rays cannot be focused into an image in the traditional sense, a unique location for a gamma ray source cannot be determined as it is done with less energetic light. In addition, gamma ray bursts are brief flashes (often as little as 0.2 seconds) that occur random ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy. Radio astronomy is conducted using large radio antennas referred to as radio telescopes, that are either used singularly, or with multiple linked telescopes utilizing the techniques of radio interferometry and aperture synthesis. The use of interferometry allows radio astronomy to achieve high angular resolution, as the resolving power of an interferom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurley
Hurley may refer to: Places ;In the United Kingdom: * Hurley, Berkshire * Hurley, Warwickshire * Hurley Common, Warwickshire ;In the United States: * Hurley, Alabama * Hurley, Mississippi * Hurley, Missouri * Hurley, New Mexico * Hurley, New York, a town in Ulster County, New York, United States. ** Hurley (CDP), New York, a hamlet and census-designated place in the town of Hurley ** Hurley Historic District, a National Historic Landmark in the hamlet of Hurley * Hurley, South Dakota * Hurley, Wisconsin * Hurley, Virginia Sport * Hurley (stick), a wooden stick used in the Irish sport of hurling * Hurley Lock, freestyle kayaking capital of south-east England, on the River Thames People * Hurley (surname) * David Hurley (born 1953), Australian Governor-General * Hurley Goodall (1927-2021), American politician * Hurley Tarver (born 1975), American football player * O'Hurley * Abu Baker Asvat, a South African medical doctor and activist, nicknamed ''Hurley'' Fictional charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Enquirer
The ''National Enquirer'' is an American tabloid newspaper. Founded in 1926, the newspaper has undergone a number of changes over the years. The ''National Enquirer'' openly acknowledges that it pays Source (journalism), sources for tips, a common practice in tabloid journalism that results in conflicts of interest. It has also been embroiled in several controversies related to its catch and kill practices and allegations of blackmail. It has struggled with declining circulation figures because of competition from other glossy tabloid publications. In May 2014, American Media announced a decision to shift the headquarters of the ''National Enquirer'' from Florida, where it had been located since 1971, back to New York City, where it originally began as ''The New York Enquirer'' in 1926. On April 10, 2019, Chatham Asset Management, which had acquired control of 80 percent of AMI's stock, forced AMI to sell the ''National Enquirer''. This came after Chatham owner Anthony Melchio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |