|
History Of Diabetes
The condition known today as diabetes (usually referring to ''diabetes mellitus'') is thought to have been described in the Ebers Papyrus (). Ayurvedic physicians (5th/6th century BC) first noted the sweet taste of diabetic urine, and called the condition ''madhumeha'' ("honey urine"). The term ''diabetes'' traces back to Demetrius of Apamea (1st century BC). For a long time, the condition was described and treated in traditional Chinese medicine ''as'' (; "wasting-thirst"). Physicians of the medieval Islamic world, including Avicenna, have also written on diabetes. Early accounts often referred to diabetes as a disease of the kidneys. In 1674, Thomas Willis suggested that diabetes may be a disease of the blood. Johann Peter Frank is credited with distinguishing diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus in 1794. In regard to ''diabetes mellitus'', Joseph von Mering and Oskar Minkowski are commonly credited with the formal discovery (1889) of a role for the pancreas in causing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frederick Banting
Sir Frederick Grant Banting (November 14, 1891 – February 21, 1941) was a Canadian pharmacologist, orthopedist, and field surgeon. For his co-discovery of insulin and its therapeutic potential, Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with John Macleod (physiologist), John Macleod. Banting and his student, Charles Best (medical scientist), Charles Best, isolated insulin at the University of Toronto in the lab of Scottish physiologist John Macleod. When he and Macleod received the 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Banting shared the honours and award money with Best. That same year, the government of Canada granted Banting a lifetime annuity to continue his work. Frederick Banting, who received the Nobel Prize at age 32, is the youngest Nobel laureate for Physiology/Medicine. Early life Banting was born on November 14, 1891, in his family's farmhouse in Essa, Ontario, two miles from nearby Alliston. He was the youngest of five children of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Georg Ebers
Georg Moritz Ebers (1 March 1837 – 7 August 1898) was a German Egyptologist and novelist. He is best known for his purchase of the Ebers Papyrus, one of the oldest Egyptian medical documents in the world. Life Georg Ebers was born in Berlin and was the youngest of the five children of an affluent family of bankers and porcelain manufacturers. The Ebers children were raised by their mother on her own, after their father committed suicide shortly after Ebers was born. His mother ran a salon popular among members of the intelligentsia, which included Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, the Grimm Brothers, and Alexander von Humboldt. At Göttingen, Ebers studied jurisprudence, and at Berlin Oriental languages and archaeology. Having made a special study of Egyptology, he became in 1865 '' Dozent'' in Egyptian language and antiquities at Jena, becoming professor in 1868. In 1870 he was appointed professor in these subjects at Leipzig. He had made two scientific journeys to Egypt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
First Dynasty Of Egypt
The First Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty I) covers the first series of Egyptian kings to rule over a unified Egypt. It immediately follows the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, by Menes, or Narmer, and marks the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, when power was centered at Thinis. The date of this period is subject to scholarly debate about the Egyptian chronology. It falls within the early Bronze Age and is variously estimated to have begun anywhere between the 34th and the 30th centuriesBC. In a 2013 study based on radiocarbon dates, the accession of Hor-Aha, the second king of the First Dynasty, was placed between 3111 and 3045 BC with 68% confidence, and between 3218 and 3035 with 95% confidence. The same study placed the accession of Den, the sixth king of the dynasty, between 2928 and 2911 BC with 68% confidence, although a 2023 radiocarbon analysis placed Den's accession potentially earlier, between 3011 and 2921, within a broader window of 3104 to 2913. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can also refer to a document written on sheets of such material, joined side by side and rolled up into a scroll, an early form of a book. Papyrus was first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used History of the Mediterranean, throughout the Mediterranean region. Apart from writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets. History Papyrus was first manufactured in Egypt as far back as the third millennium BCE.H. Idris Bell and T.C. Skeat, 1935"Papyrus and its uses"(British Museum pam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Berta Scharrer
Berta Vogel Scharrer (December 1, 1906 – July 23, 1995) was an American scientist who helped to found the scientific discipline now known as neuroendocrinology. Career She received her Ph.D. from the University of Munich, Germany in 1930. She worked at the university with Professor Karl von Frisch, who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1973 for his work with bees. After completing her education, Berta and her husband, Ernst Scharrer embarked on a remarkable scientific career together. Their journey began at the Research Institute of Psychiatry in Munich, where Berta focused on the study of spirochaete infections in the brains of birds and amphibians. Berta Scharrer was forced to emigrate at the onset of the Holocaust in 1937. She arrived with Ernst in the United States with a total of eight dollars. Ernst had secured a Rockefeller Fellowship at the University of Chicago and Berta continued her research, initially working with Drosophila and later with cockroac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
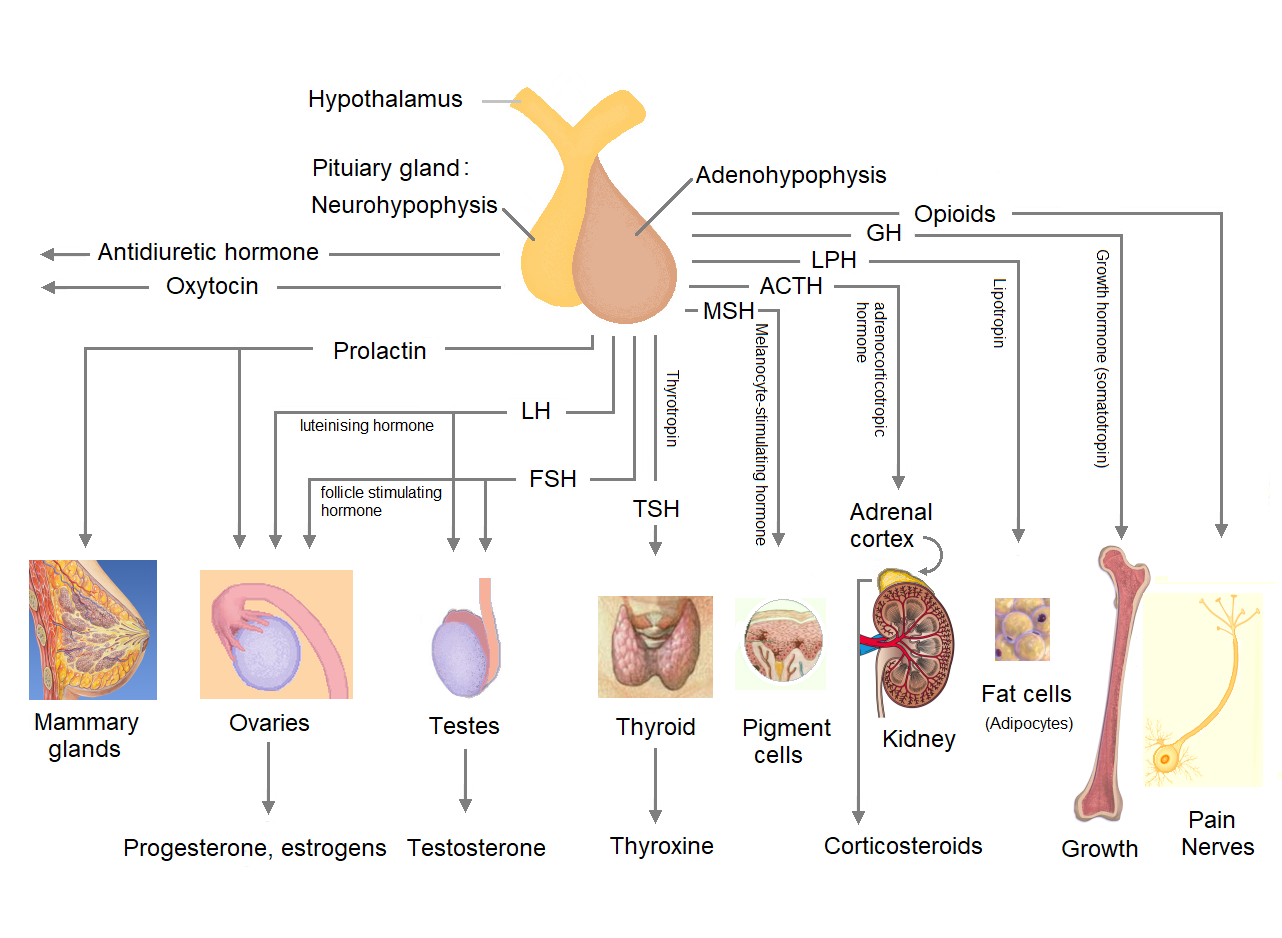
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antidiuretic
An antidiuretic is a chemical substance, substance that helps to control fluid balance in an animal's body by reducing urination, opposing diuresis. Its effects are opposite that of a diuretic. The major endogeny (biology), endogenous antidiuretics are Vasopressin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH; also called vasopressin) and oxytocin. Both of those are also used exogeny, exogenously as pharmaceutical drug, medications in people whose bodies need extra help with fluid balance via suppression of diuresis. In addition, there are various other antidiuretic drugs, some molecule, molecularly close to ADH or oxytocin and others not. Antidiuretics reduce urine volume, particularly in diabetes insipidus (DI), which is one of their main indication (medicine), indications. The antidiuretic hormone class includes vasopressin (ADH), argipressin, desmopressin, lypressin, ornipressin, oxytocin, and terlipressin. Miscellaneous others include chlorpropamide and carbamazepine. See also *Diuretic *Electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university whose main campus is located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada. Originally controlled by the Church of England, the university assumed its present name in 1850 upon becoming a secular institution. It has three campuses: University of Toronto Mississauga, Mississauga, #St. George campus, St. George, and University of Toronto Scarborough, Scarborough. Its main campus, St. George, is the oldest of the three and located in Downtown Toronto. U of T operates as a collegiate university, comprising 11 #Colleges, colleges, each with substantial autonomy on financial and institutional affairs and significant differences in character and history. The University of Toronto is the largest university in Canada with a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |