|
History Of Detroit
Detroit, the largest city in the state of History of Michigan, Michigan, was settled in 1701 by French colonists. It is the first European settlement above tidewater in North America., p. 56. Founded as a New France Beaver, fur fur trade, trading post, it began to expand during the 19th century with American pioneer, U.S. settlement around the Great Lakes. By 1920, based on the booming auto industry and immigration, it became a world-class industrial powerhouse and the fourth-largest city in the United States. It held that standing through the mid-20th century. The first Europeans to settle in Detroit were French country traders and colonists from Montreal and Quebec; they had to contend with the powerful Five Nations of the League of the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee), who took control of the southern shores of lake Erie, Lakes Erie and Lake Huron, Huron through the Beaver Wars of the 17th century. Also present and powerful, but further to the north, were the Council of Three Fires ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Detroit
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
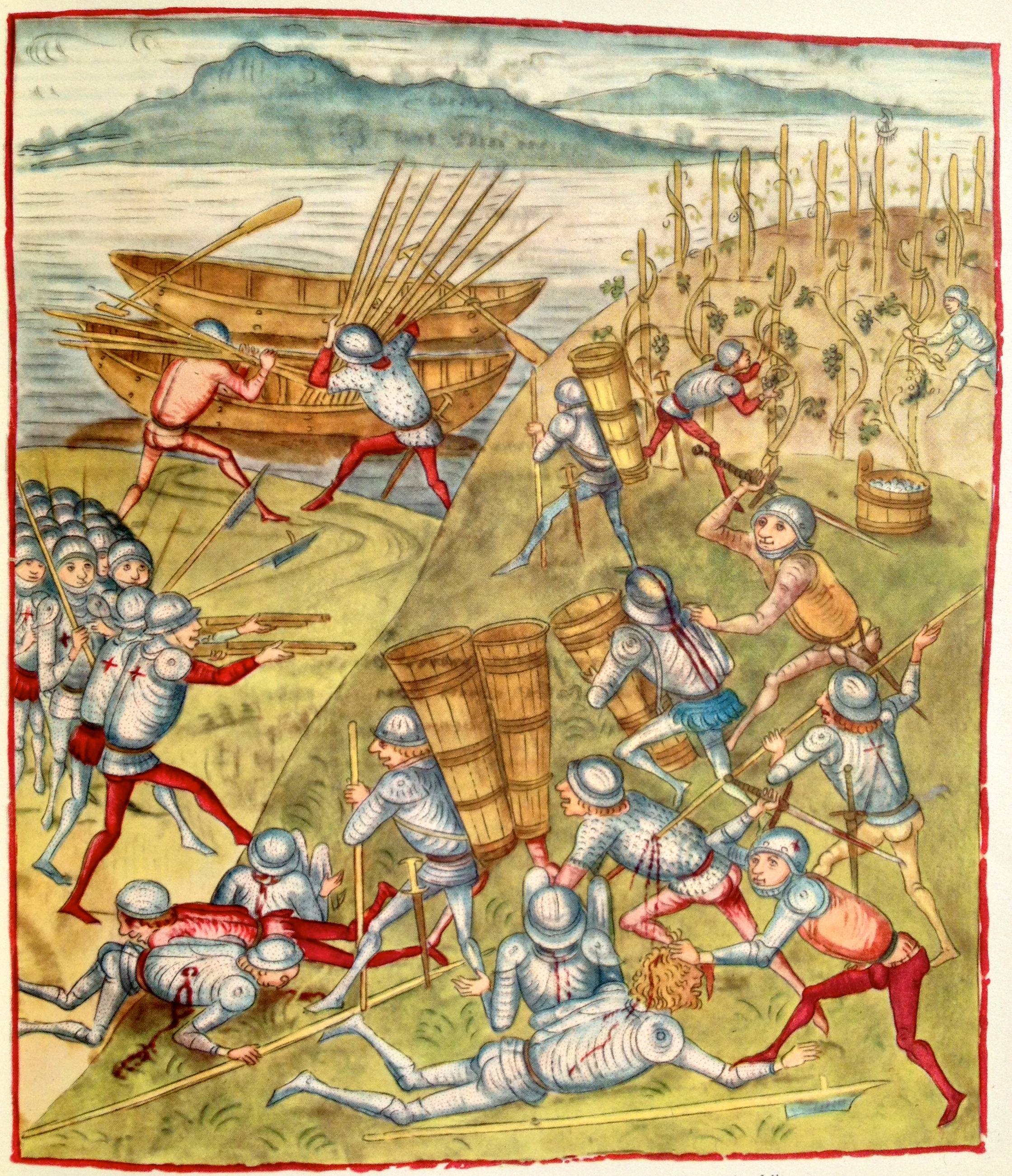
Arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier. The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms from the 15th to 17th centuries, but it originally referred to "a hand cannon, hand-gun with a hook-like projection or lug on its under surface, useful for steadying it against battlements or other objects when firing". These "hook guns" were in their earliest forms defensive weapons mounted on German city walls in the early 15th century. The addition of a shoulder stock, priming pan, and matchlock mechanism in the late 15th century turned the arquebus into a handheld firearm and also the first firearm equipped with a trigger. The exact dating of the matchlock's appearance is disputed. It could have appeared in the Ottoman Empire as early as 1465 and in Europe a little before 1475. The heavy arquebus, which was then called a musket, was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi River in Cairo, Illinois, Cairo, Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the Mississippi River. It is also the sixth oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six U.S. state, states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern United States. It is the source of drinking water for five million people. The river became a primary transportation route for pioneers during the westward expansion of the early U.S. The lower Ohio River just below Louisville was obstructed by rapids known as the Falls of the Oh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monongahela River
The Monongahela River ( , ), sometimes referred to locally as the Mon (), is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 river on the Allegheny Plateau in north-central West Virginia and Southwestern Pennsylvania. The river flows from the confluence of its west and east forks in north-central West Virginia northeasterly into southwestern Pennsylvania, then northerly to Pittsburgh and its confluence with the Allegheny River to form the Ohio River. The river includes a series of locks and dams that makes it navigable. Etymology The Unami word ''Monongahela'' means "falling banks", in reference to the geological instability of the river's banks. Moravian missionary David Zeisberger (1721–1808) gave this account of the naming: "In the Indian tongue the name of this river was ''Mechmenawungihilla'' (alternatively spelled ''Menawngihella''), which signifies a high bank, which is ever washed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegheny River
The Allegheny River ( ; ; ) is a tributary of the Ohio River that is located in western Pennsylvania and New York (state), New York in the United States. It runs from its headwaters just below the middle of Pennsylvania's northern border, northwesterly into New York, then in a zigzag southwesterly across the border and through Western Pennsylvania to join the Monongahela River at the Forks of the Ohio at Point State Park in Downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The Allegheny River is, by volume, the main headstream of both the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers. Historically, the Allegheny was considered to be the upper Ohio River by both Native Americans and European settlers. This shallow river has been made navigable upstream from Pittsburgh to East Brady, Pennsylvania, East Brady by a series of locks and dams that were constructed during the early 20th century. A 24-mile-long portion of the upper river in Warren County, Pennsylvania, Warren and McKean County, Pennsylvania, McKean c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
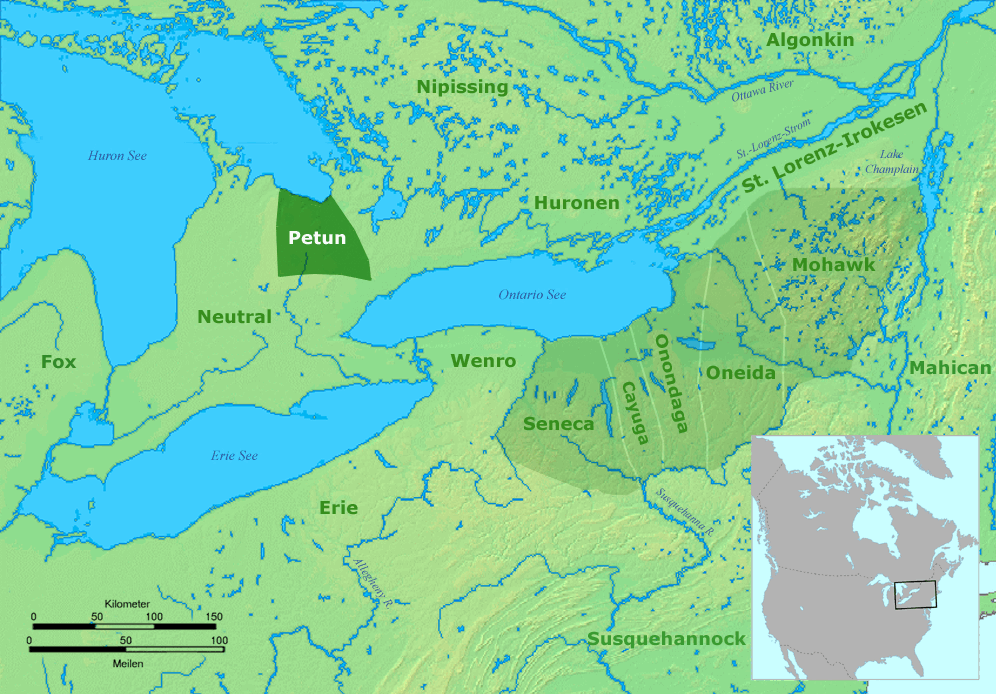
Erie People
The Erie people were an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian-speaking tribe, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvania, and northern Ohio before 1658. Their nation was almost exterminated in the mid- 17th century by five years of prolonged warfare with the powerful neighboring Iroquois for helping the Huron in the Beaver Wars for control of the fur trade. Captured survivors were adopted or enslaved by the Iroquois. Their villages were burned by Haudenosaunee warriors. This destroyed their stored maize and other foods, added to their loss of life, and threatened their future, as they had no way to survive the winter. The attacks likely forced their emigration. The Haudenosaunee Confederacy was known for adopting captives and refugees into their tribes. The surviving Erie are believed to have been largely absorbed by other Iroquoian tribes, particularly families of the Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( ) is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest average water lake retention time, residence time. At its deepest point, Lake Erie is deep, making it the only Great Lake whose deepest point is above sea level. Located on the Canada–United States border, International Boundary between Canada and the United States, Lake Erie's northern shore is the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario, specifically the Ontario Peninsula, with the U.S. states of Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York (state), New York on its western, southern, and eastern shores. These jurisdictions divide the surface area of the lake with water boundaries. The largest city on the lake is Cleveland, anchoring the third largest U.S. metro area in the Great Lakes region, after Chicago metropoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenro People
The Wenrohronon or Wenro people were an Iroquoian indigenous nation of North America, originally residing in present-day western New York (and possibly fringe portions of northern & northwestern Pennsylvania), who were conquered by the Confederation of the Five Nations of the Iroquois in two decisive wars between 1638–1639 and 1643. This was likely part of the Iroquois Confederacy campaign against the Neutral people, another Iroquoian-speaking tribe, which lived across the Niagara River. This warfare was part of what was known as the Beaver Wars, as the Iroquois worked to dominate the lucrative fur trade. They used winter attacks, which were not usual among Native Americans, and their campaigns resulted in attrition of both the larger Iroquoian confederacies, as they had against the numerous Huron. After defeating the Huron in 1649, the Iroquois conducted a December 1649 attack against the Tabacco people, who fell in 1650–1651. The Iroquois continued to campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The Canada–United States border spans the centre of the lake. On the Canadian side, the major cities are Kingston, Ontario, Kingston, Mississauga, Toronto, Hamilton, Ontario, Hamilton, and St. Catharines. On the American side, the major cities are Rochester, New York, Rochester and Watertown, New York, Watertown. The last in the Great Lakes chain, Lake Ontario serves as the outlet to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River, comprising the western end of the Saint Lawrence Seaway. Its primary inlet is the Niagara River from Lake Erie. The Long Sault Dam, Long Sault control dam, primarily along with the Moses-Saunders Power Dam regulates the water level of the lake. The name ''Ontarí'io'' is most often translated from Wyandot language, Huron as "beauti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral People
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ) was a tribal confederation of Iroquoian peoples. Its heartland was in the floodplain of the Grand River (Ontario), Grand River in what is now Ontario, Canada. At its height, its wider territory extended toward the shores of lakes Lake Erie, Erie, Lake Huron, Huron, and Lake Ontario, Ontario, as well as the Niagara River in the east. To the northeast were the neighbouring territories of Huronia (region), Huronia and the Petun Country, which were inhabited by other Iroquoian confederacies from which the term Neutrals was derived. The five-nation Iroquois Confederacy was across Lake Ontario to the southeast. Like others of Iroquoian language and culture, the tribes would raid and feud with fellow Iroquoian tribes. They were generally wary of rival Algonquian languages, Algonquian-speaking peoples, such as those who inhabited Canada to the East, along the St. Lawrence River, St. Lawrence Valley Drainage basin, basin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabacco People
The Petun (from ), also known as the Tobacco people or Tionontati (Dionnontate, Etionontate, Etionnontateronnon, Tuinontatek, Dionondadie, or Khionotaterrhonon) ("People among the hills/mountains"), were an indigenous Iroquoian people of the woodlands of eastern North America. Their last known traditional homeland was south of Lake Huron's Georgian Bay, in what is today's Canadian province of Ontario. The Petun were closely related to the Huron, or Wendat. Similarly to other Iroquoian peoples, they were structured as a confederacy. One of the less numerous Iroquoian peoples when they became known to Europeans, they had eight or nine villages in the early 17th century, and are estimated to have numbered around 8000 prior to European contact. A number of disease epidemics were documented in Huron–Petun societies between 1634 and 1640, which have been linked to the arrival of settlers from urban Europe; this decimated their population. Although they each spoke Iroquoian langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |