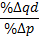|
Hicks–Marshall Laws Of Derived Demand
In economics, the Hicks–Marshall laws of derived demand assert that, other things equal, the own-wage elasticity of demand for a category of labor is high under the following conditions: * When the price elasticity of demand for the product being produced is high (scale effect). So when final product demand is elastic, an increase in wages will lead to a large change in the quantity of the final product demanded affecting employment greatly. * When other factors of production can be easily substituted for the category of labor (substitution effect). * When the supply of other factors of production is highly elastic (that is, usage of other factors of production can be increased without substantially increasing their prices) (substitution effect). That is, employers can easily replace labor as doing so will only moderately increase other factor prices. * When the cost of employing the category of labor is a large share of the total costs of production (scale effect) The "Hicks� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceteris Paribus
' (also spelled '; () is a Latin phrase, meaning "other things equal"; some other English translations of the phrase are "all other things being equal", "other things held constant", "all else unchanged", and "all else being equal". A statement about a causal, empirical, or logical relation between two states of affairs is ''ceteris paribus'' if it is acknowledged that the statement, although usually accurate in expected conditions, can fail because of, or the relation can be abolished by, intervening factors. chapter 2 A ''ceteris paribus'' assumption is often key to scientific inquiry, because scientists seek to eliminate factors that perturb a relation of interest. Thus epidemiologists, for example, may seek to control independent variables as factors that may influence dependent variables—the outcomes of interest. Likewise, in scientific modeling, simplifying assumptions permit illustration of concepts considered relevant to the inquiry. An example in economics is "If ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (economics)
In economics, elasticity measures the percentage change of one economic variable in response to a percentage change in another. If the price elasticity of the demand of something is -2, a 10% increase in price causes the demand quantity to fall by 20%. Introduction Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in the understanding of various economic concepts, such as the incidence of indirect taxation, marginal concepts relating to the theory of the firm, distribution of wealth, and different types of goods relating to the theory of consumer choice. An understanding of elasticity is also important when discussing welfare distribution, in particular consumer surplus, producer surplus, or government surplus. Elasticity is present throughout many economic theories, with the concept of elasticity appearing in several main indicators. These include price elasticity of demand, price elasticity of supply, income elasticity of demand, elastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item is a function of an item's perceived necessity, price, perceived quality, convenience, available alternatives, purchasers' disposable income and tastes, and many other options. Factors influencing demand Innumerable factors and circumstances affect a consumer's willingness or to buy a good. Some of the common factors are: The price of the commodity: The basic demand relationship is between potential prices of a good and the quantities that would be purchased at those prices. Generally, the relationship is negative, meaning that an increase in price will induce a decrease in the quantity demanded. This negative relationship is embodied in the downward slope of the consumer demand curve. The assumption of a negative relationship is reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Elasticity Of Demand
A good's price elasticity of demand (E_d, PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good, but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price, holding everything else constant. If the elasticity is −2, that means a one percent price rise leads to a two percent decline in quantity demanded. Other elasticities measure how the quantity demanded changes with other variables (e.g. the income elasticity of demand for consumer income changes). Price elasticities are negative except in special cases. If a good is said to have an elasticity of 2, it almost always means that the good has an elasticity of −2 according to the formal definition. The phrase "more elastic" means that a good's elasticity has greater magnitude, ignoring the sign. Veblen and Giffen goods are two classes of go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factors Of Production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output—that is, goods and services. The utilized amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the relationship called the production function. There are four ''basic'' resources or factors of production: land, labour, capital and entrepreneur (or enterprise). The factors are also frequently labeled "producer goods or services" to distinguish them from the goods or services purchased by consumers, which are frequently labeled "consumer goods". There are two types of factors: ''primary'' and ''secondary''. The previously mentioned primary factors are land, labour and capital. Materials and energy are considered secondary factors in classical economics because they are obtained from land, labour, and capital. The primary factors facilitate production but neither becomes part of the product (as with raw materials) nor becomes significantly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hicks
Sir John Richards Hicks (8 April 1904 – 20 May 1989) was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics were his statement of consumer demand theory in microeconomics, and the IS–LM model (1937), which summarised a Keynesian view of macroeconomics. His book ''Value and Capital'' (1939) significantly extended general-equilibrium and value theory. The compensated demand function is named the Hicksian demand function in memory of him. In 1972 he received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (jointly) for his pioneering contributions to general equilibrium theory and welfare theory. Early life Hicks was born in 1904 in Warwick, England, and was the son of Dorothy Catherine (Stephens) and Edward Hicks, a journalist at a local newspaper. He was educated at Clifton College (1917–1922) and at Balliol College, Oxford (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Theory Of Wages
''The Theory of Wages'' is a book by the British economist John R. Hicks published in 1932 (2nd ed., 1963). It has been described as a classic microeconomic statement of wage determination in competitive markets. It anticipates a number of developments in distribution and growth theory and remains a standard work in labour economics. Part I of the book takes as its starting point a reformulation of the marginal productivity theory of wages as determined by supply and demand in full competitive equilibrium of a free market economy. Part II considers regulated labour markets resulting from labour disputes, trade unions and government action. The 2nd edition (1963) includes a harsh critical review and, from Hicks, two subsequent related articles and an extensive commentary. The book presents: * labour demand as derived from the demand for output, such that for example a fall in the wage rate would lead to substitution away from other inputs and more labour use from increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist, and was one of the most influential economists of his time. His book '' Principles of Economics'' (1890) was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years. It brought the ideas of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production into a coherent whole. He is known as one of the founders of neoclassical economics. Life and career Marshall was born at Bermondsey in London, second son of William Marshall (1812–1901), clerk and cashier at the Bank of England, and Rebecca (1817–1878), daughter of butcher Thomas Oliver, from whom, on her mother's death, she inherited property. William Marshall was a devout strict Evangelical, "author of an Evangelical epic in a sort of Anglo-Saxon language of his own invention which found some favour in its appropriate circles" and of a tract titled ''Men's Rights and Women's Duties''. Marshall had two brothers and two sisters; a cousin was the econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles Of Economics (Marshall)
''Principles of Economics'' is a leading political economy or economics textbook of Alfred Marshall (1842–1924), first published in 1890. It was the standard text for generations of economics students. Called his ''magnum opus'', it ran to eight editions by 1920. A ninth ( variorum) edition was published in 1961, edited in 2 volumes by C. W. Guillebaud.Whittaker, J.K. (1987). "Marshall, Alfred," ''The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', p. 363. Writing Marshall began writing the ''Principles of Economics'' in 1881 and he spent much of the next decade at work on the treatise. His plan for the work gradually extended to a two-volume compilation on the whole of economic thought; the first volume was published in 1890 to worldwide acclaim that established him as one of the leading economists of his time. The second volume, which was to address foreign trade, money, trade fluctuations, taxation, and collectivism, was never published at all. Over the next two decades he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |