|
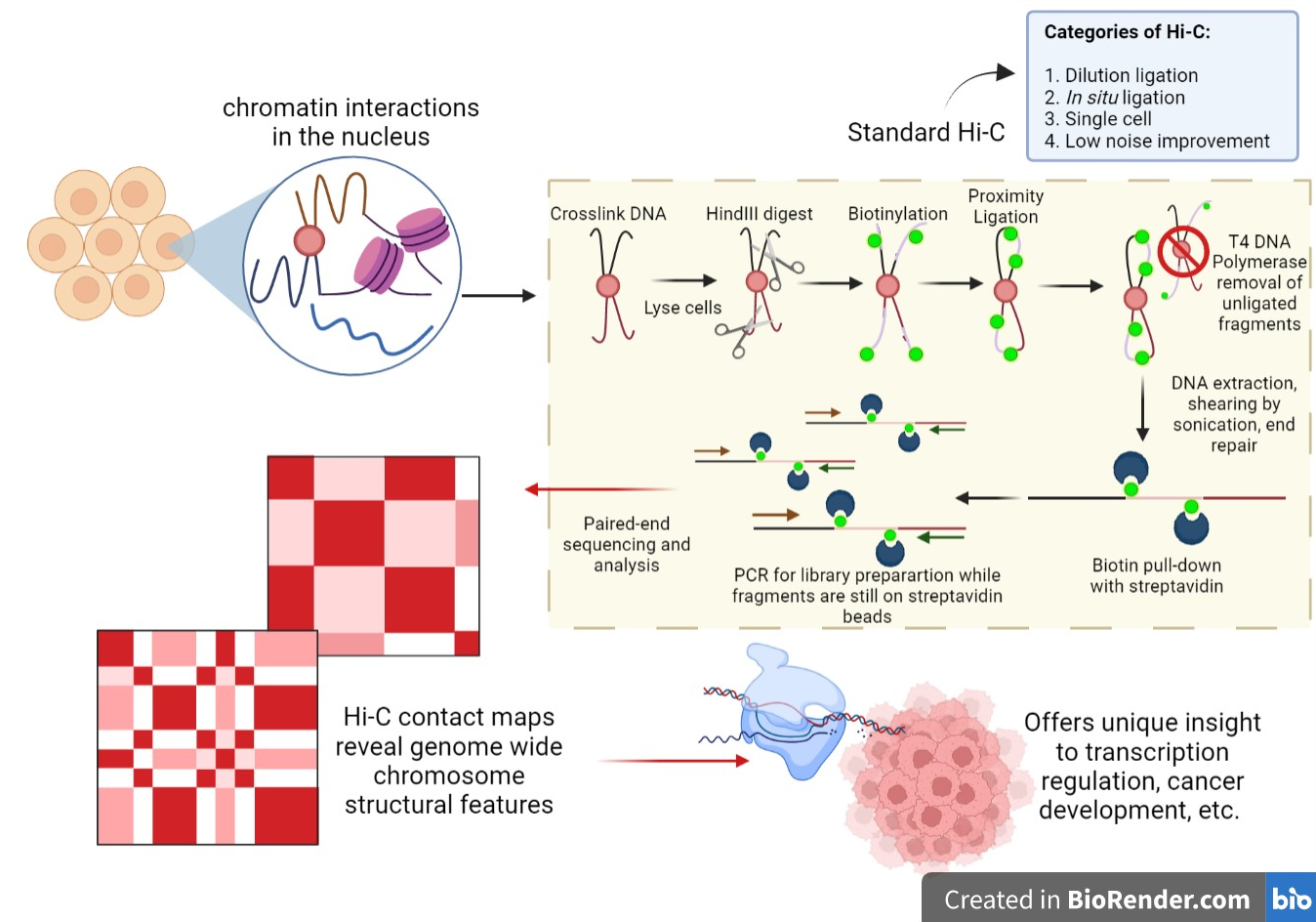
Hi-C (genomic Analysis Technique)
] Hi-C is a high-throughput Genomics, genomic and Epigenomics, epigenomic technique to Chromosome conformation capture, capture chromatin conformation (3C). In general, Hi-C is considered as a derivative of a series of chromosome conformation capture technologies, including but not limited to 3C (chromosome conformation capture), 4C (chromosome conformation capture-on-chip/circular chromosome conformation capture), and 5C (chromosome conformation capture carbon copy). Hi-C comprehensively detects genome-wide chromatin interactions in the cell nucleus by combining 3C and massive parallel sequencing, next-generation sequencing (NGS) approaches and has been considered as a qualitative leap in C-technology (chromosome conformation capture-based technologies) development and the beginning of 3D genomics. Similar to the classic 3C technique, Hi-C measures the frequency (as an average over a cell population) at which two DNA fragments physically associate in 3D space, linking chromosomal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (Dragon Ball), Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * Cell (novel), ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling *The Cell (play), ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * Cell (album), ''Cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticky And Blunt Ends
DNA ends refer to the properties of the ends of linear DNA molecules, which in molecular biology are described as "sticky" or "blunt" based on the shape of the complementary strands at the terminus. In sticky ends, one strand is longer than the other (typically by at least a few nucleotides), such that the longer strand has bases which are left unpaired. In blunt ends, both strands are of equal length – i.e. they end at the same base position, leaving no unpaired bases on either strand. The concept is used in molecular biology, in cloning, or when subcloning insert DNA into vector DNA. Such ends may be generated by restriction enzymes that break the molecule's phosphodiester backbone at specific locations, which themselves belong to a larger class of enzymes called exonucleases and endonucleases. A restriction enzyme that cuts the backbones of both strands at non-adjacent locations leaves a staggered cut, generating two overlapping sticky ends, while an enzyme that makes a str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topologically Associating Domain
A topologically associating domain (TAD) is a self-interacting genomic region, meaning that DNA sequences within a TAD physically interact with each other more frequently than with sequences outside the TAD. The average size of a topologically associating domain (TAD) is 1000 kb in humans, 880 kb in mouse cells, and 140 kb in fruit flies. Boundaries at both side of these domains are conserved between different mammalian cell types and even across species and are highly enriched with CTCF, CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and cohesin. In addition, some types of genes (such as transfer RNA genes and housekeeping genes) appear near TAD boundaries more often than would be expected by chance. The functions of TADs are not fully understood and are still a matter of debate. Most of the studies indicate TADs regulate gene expression by limiting the Enhancer (genetics), enhancer-Promoter (genetics), promoter interaction to each TAD; however, a recent study uncouples TAD organization and gene exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Distinction is sometimes made between aldimines and ketimines, derived from aldehydes and ketones, respectively. Structure In imines the five core atoms (C2C=NX, ketimine; and C(H)C=NX, aldimine; X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29–1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C−N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E–Z notation, ''E'' and ''Z'' isomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sometimes written sodium laurilsulfate, is an organic compound with the formula and structure . It is an anionic surfactant used in many cleaning and hygiene products. This compound is the sodium salt of the 12-carbon organosulfate. Its hydrocarbon tail combined with a polar " headgroup" give the compound amphiphilic properties that make it useful as a detergent. SDS is also component of mixtures produced from inexpensive coconut and palm oils. SDS is a common component of many domestic cleaning, personal hygiene and cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food products, as well as of industrial and commercial cleaning and product formulations. Physicochemical properties The critical micelle concentration (CMC) in water at 25 °C is 8.2 mM, and the aggregation number at this concentration is usually considered to be about 62. The micelle ionization fraction (α) is around 0.3 (or 30%). Applications Cleaning and hygie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrococcal Nuclease
Micrococcal nuclease (, ''S7 Nuclease'', ''MNase'', ''spleen endonuclease'', ''thermonuclease'', ''nuclease T'', ''micrococcal endonuclease'', ''nuclease T, ''staphylococcal nuclease'', ''spleen phosphodiesterase'', ''Staphylococcus aureus nuclease'', ''Staphylococcus aureus nuclease B'', ''ribonucleate (deoxynucleate) 3'-nucleotidohydrolase'') is an endo-exonuclease that preferentially digests single-stranded nucleic acids. The rate of cleavage is 30 times greater at the 5' side of A or T than at G or C and results in the production of mononucleotides and oligonucleotides with terminal 3'-phosphates. The enzyme is also active against double-stranded DNA and RNA and all sequences will be ultimately cleaved. Characteristics The enzyme has a molecular weight of 16.9kDa. The pH optimum is reported as 9.2. The enzyme activity is strictly dependent on Ca2+ and the pH optimum varies according to Ca2+ concentration. The enzyme is therefore easily inactivated by EGTA. Source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DnaseI
Deoxyribonuclease I (usually called DNase I), is an endonuclease of the DNase family coded by the human gene DNASE1. DNase I is a nuclease that cleaves DNA preferentially at phosphodiester linkages adjacent to a pyrimidine nucleotide, yielding 5'-phosphate-terminated polynucleotides with a free hydroxyl group on position 3', on average producing tetranucleotides. It acts on single-stranded DNA, double-stranded DNA, and chromatin. In addition to its role as a waste-management endonuclease, it has been suggested to be one of the deoxyribonucleases responsible for DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. DNase I binds to the cytoskeletal protein actin. It binds actin monomers with very high (sub-nanomolar) affinity and actin polymers with lower affinity. The function of this interaction is unclear. However, since actin-bound DNase I is enzymatically inactive, the DNase-actin complex might be a storage form of DNase I that prevents damage of the genetic information. This protein is stored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Enzyme
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA enzyme substrate (biology), substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each backbone chain, sugar-phosphate backbone (i.e. each strand) of the DNA double helix. These enzymes are found in bacteria and archaea and provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses. Inside a prokaryote, the restriction enzymes selectively cut up ''foreign'' DNA in a process called ''restriction digestion''; meanwhile, host DNA is protected by a modification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a Redundancy (information theory), redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Evolution
Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large. History Since the first sequenced genomes became available in the late 1970s, scientists have been using comparative genomics to study the differences and similarities between various genomes. Genome sequencing has progressed over time to include more and more complex genomes including the eventual sequencing of the entire human genome in 2001. By comparing genomes of both close relatives and distant ancestors the stark differences and similarities between species began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |