|
Heterogeneous Database System
A heterogeneous database system is an automated (or semi-automated) system for the integration of heterogeneous, disparate database management systems to present a user with a single, unified query interface. Heterogeneous database systems (HDBs) are computational models and software implementations that provide heterogeneous database integration. Problems of heterogeneous database integration This article does not contain details of distributed database management systems (sometimes known as federated database systems). Technical heterogeneity Different file formats, access protocols, query languages etc. Often called syntactic heterogeneity from the point of view of data. Data model heterogeneity Different ways of representing and storing the same data. Table decompositions may vary, column names (data labels) may be different (but have the same semantics), data encoding schemes may vary (i.e., should a measurement scale be explicitly included in a field or should it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Data Integration
Data integration refers to the process of combining, sharing, or synchronizing data from multiple sources to provide users with a unified view. There are a wide range of possible applications for data integration, from commercial (such as when a business merges multiple databases) to scientific (combining research data from different bioinformatics repositories). The decision to integrate data tends to arise when the volume, complexity (that is, big data) and need to share existing data explodes. It has become the focus of extensive theoretical work, and numerous open problems remain unsolved. Data integration encourages collaboration between internal as well as external users. The data being integrated must be received from a heterogeneous database system and transformed to a single coherent data store that provides synchronous data across a network of files for clients. A common use of data integration is in data mining when analyzing and extracting information from exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Database Management System
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Distributed Database Management System
A distributed database is a database in which data is stored across different physical locations. It may be stored in multiple computers located in the same physical location (e.g. a data centre); or maybe dispersed over a network of interconnected computers. Unlike parallel systems, in which the processors are tightly coupled and constitute a single database system, a distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical components. System administrators can distribute collections of data (e.g. in a database) across multiple physical locations. A distributed database can reside on organised network servers or decentralised independent computers on the Internet, on corporate intranets or extranets, or on other organisation networks. Because distributed databases store data across multiple computers, distributed databases may improve performance at end-user worksites by allowing transactions to be processed on many machines, instead of being limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Federated Database System
A federated database system (FDBS) is a type of Meta (prefix), meta-database management system (DBMS), which transparently maps multiple autonomous Database management system, database systems into a single federated database. The constituent databases are interconnected via a computer network and may be geographically decentralized. Since the constituent database systems remain autonomous, a federated database system is a contrastable alternative to the (sometimes daunting) task of merging several disparate databases. A federated database, or virtual database, is a composite of all constituent databases in a federated database system. There is no actual data integration in the constituent disparate databases as a result of data federation. Through data abstraction, federated database systems can provide a uniform user interface, enabling user (computing), users and Client (computing), clients to store and retrieve data from multiple noncontiguous databases with a single Informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
File Format
A file format is a Computer standard, standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary format, proprietary or open format, open. Some file formats are designed for very particular types of data: Portable Network Graphics, PNG files, for example, store Raster graphics, bitmapped Graphics file format, images using lossless data compression. Other file formats, however, are designed for storage of several different types of data: the Ogg format can act as a container format (digital), container for different types of multimedia including any combination of sound, audio and video, with or without text (such as subtitles), and metadata. A text file can contain any stream of characters, including possible control characters, and is encoded in one of various Character encoding, character encoding schemes. Some file formats, such as HTML, sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Protocol (computing)
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses predetermined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Encoding
In communications and Data processing, information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter (alphabet), letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes data compression, shortened or secrecy, secret, for communication through a communication channel or storage in a storage medium. An early example is an invention of language, which enabled a person, through speech, to communicate what they thought, saw, heard, or felt to others. But speech limits the range of communication to the distance a voice can carry and limits the audience to those present when the speech is uttered. The invention of writing, which converted spoken language into visual system, visual symbols, extended the range of communication across space and time. The process of encoding converts information from a communication source, source into symbols for communication or storage. Decoding is the reverse process, converting code symbols back into a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all Life, life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common Nutrient, nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a pentose, five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Ontology (information Science)
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as ''applied ontology''. Every academic discipline or field, in creating its terminology, thereby lays the groundwork for an ontology. Each uses ontological assumptions to frame explicit theories, research and applications. Improved ontologies may improve problem solving within that domain, interoperability of data systems, and discoverability of data. Translating research papers within every field is a problem made easier when experts from different countries mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
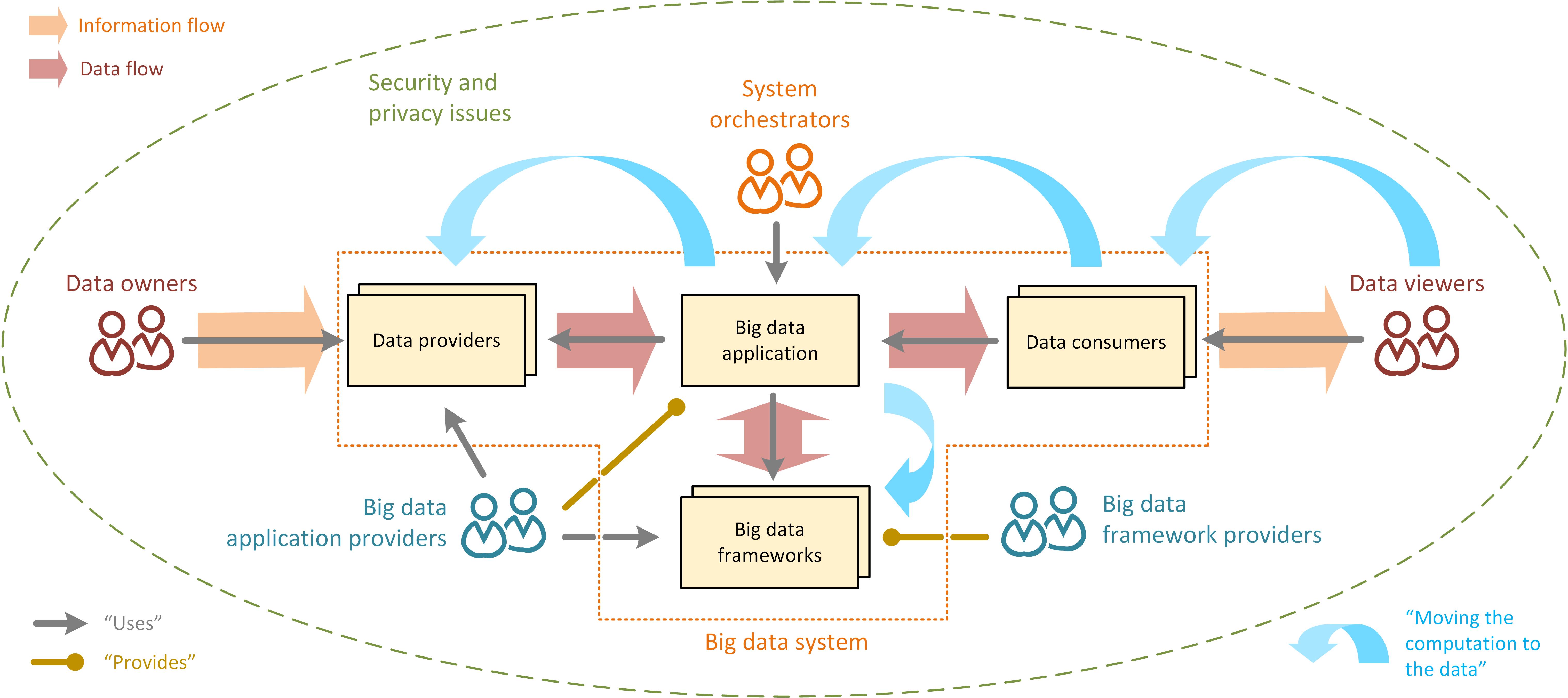 |
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Expert System
In artificial intelligence (AI), an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if–then rules rather than through conventional procedural programming code. Expert systems were among the first truly successful forms of AI software. They were created in the 1970s and then proliferated in the 1980s, being then widely regarded as the future of AI — before the advent of successful artificial neural networks. An expert system is divided into two subsystems: 1) a ''knowledge base'', which represents facts and rules; and 2) an '' inference engine'', which applies the rules to the known facts to deduce new facts, and can include explaining and debugging abilities. History Early development Soon after the dawn of modern computers in the late 1940s and early 1950s, researchers started realizing the immense potential th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |