|
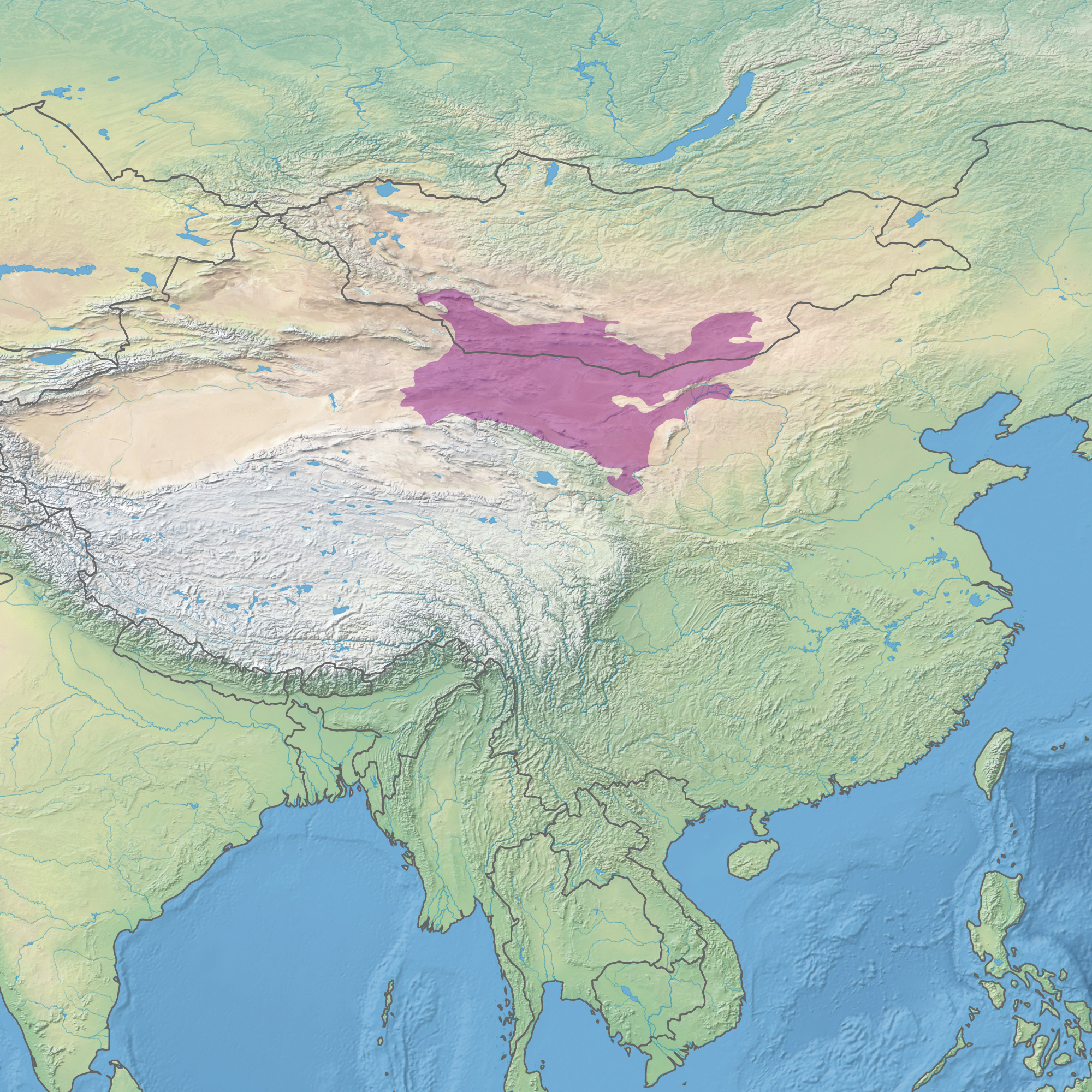
Helanshan Montane Conifer Forests
The Helanshan montane conifer forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0508) covers an isolated, forested mountain range surrounded by desert and semi-arid basins. As such, it has been called a "mountain island in the sky", and supports endemic species of plants and animals. The region supports the endangered Helan Shan pika. Location and description The Helan Mountains ecoregions lies to the east of the Alashan Plateau semi-desert ecoregion, and to the west of the Ordos plateau steppe ecoregion. It is thus surrounded by arid basins. The mountain range is 180 km long, and reaches a peak altitude of 3,556 meters. The lower valleys between ridges are less forested. Climate The climate of the ecoregion is '' cold semi-arid'' (Köppen climate classification (BSk)). This climate is generally characterized as a 'steppe' climate, with precipitation greater than a true desert, and also a colder temperature. Flora and fauna Within the ecoregion, tree cover depends on the altitude zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helan Mountains
The Helan Mountains, frequently called Alashan Mountains in older sources, are an isolated desert mountain range forming the border of Inner Mongolia's Alxa League and Ningxia. They run north-south parallel to the north-flowing Yellow River in the Ordos Loop section. The river is mostly east of the mountains, but in the north it crosses without making a significant gorge and flows on the west side. To the west lies the extremely arid Tengger Desert, while to the east is an irrigated area beside the Yellow River, in which lie the cities of Yinchuan and Shizuishan - a little further east of which lies the Mu Us portion of the Ordos Desert. To the north lies the Inner Mongolian city of Wuhai. They are about from north to south, from wide and average about in altitude (the Yellow River here is about above sea level). Their highest peak is . Emerging wine industry With the increasing popularity of Ningxia wines, the Chinese authorities have given approval to the developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulmus Pumila
''Ulmus pumila'', the Siberian elm, is a tree native to Asia. It is also known as the Asiatic elm and dwarf elm, but sometimes mistakenly called the "Chinese" elm (''Ulmus parvifolia''). ''U. pumila'' has been widely cultivated throughout Asia, North America, Argentina, and southern Europe, becoming naturalized in many places, notably across much of the United States. Description The Siberian elm is usually a small to medium-sized, often bushy, deciduous tree growing to tall, the diameter at breast height to . The bark is dark gray and irregularly longitudinally fissured. The branchlets are yellowish gray, glabrous or pubescent, unwinged, and without a corky layer, with scattered lenticels. The winter buds are dark brown to red-brown, globose to ovoid. The petiole is and pubescent; the leaf blade is elliptic-ovate to elliptic-lanceolate, , the colour changing from dark green to yellow in autumn.Fu, L., Xin, Y. & Whittemore, A. (2002). Ulmaceae, in Wu, Z. & Raven, P. ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregions Of China
{{Short description, none The following is a list of terrestrial ecoregions of the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, according to the World Wide Fund for Nature. The transition between two of the planet's eight terrestrial biogeographic realms – the Palearctic, which includes temperate and boreal Eurasia, and Indomalaya, which includes tropical South and Southeast Asia – extends through southern China. Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests * Guizhou Plateau broadleaf and mixed forests * Hainan Island monsoon rain forests * Jiang Nan subtropical evergreen forests * Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests * Northern Indochina subtropical forests * South China Sea Islands * South China-Vietnam subtropical evergreen forests * South Taiwan monsoon rain forests (Taiwan) * Taiwan subtropical evergreen forests (Taiwan) * Yunnan Plateau subtropical evergreen forests Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests * Central China loess plateau mixed forests * Chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic Ecoregions
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across Europe and Asia, north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Mediterranean Basin; North Africa; North Arabia; Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. Both the eastern and westernmost extremes of the Paleartic span into the Western Hemisphere, including Cape Dezhnyov in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the east and Iceland to the west. The term was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/Afrotropic, Indian/Indomalayan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picea Asperata
''Picea asperata'' (dragon spruce; ) is a spruce native to western China, from eastern Qinghai, southern Gansu and southwestern Shaanxi south to western Sichuan. Description It is a medium-sized evergreen tree growing to 25–40 m tall, and with a trunk diameter of up to 1.5 m. The shoots are orange-brown, with scattered pubescence. The leaves are needle-like, 1–2.5 cm long, rhombic in cross-section, greyish-green to bluish-green with conspicuous stomatal lines. The cones are cylindric-conic, 6–15 cm long and 2–3 cm broad, maturing pale brown 5–7 months after pollination, and have stiff, rounded to bluntly pointed scales. Varieties It is a variable species with several varieties listed. These were first described as distinct species (and are still so treated by some authors), although they differ only in minor details, and some may not prove to be distinct at all if a larger population is examined: *''Picea asperata'' var. ''asperata''. Cones 6–12 cm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostryopsis
''Ostryopsis'' is a small genus of deciduous shrubs belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. The species have no common English name, though hazel-hornbeam has been suggested, reflecting their similarities to the closely related hazels and hop-hornbeams. The genus is native to China. They are shrubs reaching 3–5 m tall, with alternate, double-toothed hazel-like leaves 2–7 cm long. The flowers are produced in spring, with separate male and female catkins. The fruit form in clusters 3–5 cm long with 6-10 seeds; each seed is a small nut 4–6 mm long, fully enclosed in a sheath-like involucre. The local people in Northeast China has found hazelnut The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to ...s of '' Ostryopsis davidiana'' and '' Corylus mandshurica'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caragana
''Caragana'' is a genus of about 80–100 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, native to Asia and eastern Europe. They are shrubs or small trees growing tall. They have even-pinnate leaves with small leaflets, and solitary or clustered mostly yellow (rarely white or pink) flowers and bearing seeds in a linear pod. ''Caragana'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including dark dagger. Sections and species Section ''Bracteolatae'' *'' Caragana ambigua'' Stocks *'' Caragana bicolor'' Kom. *''Caragana brevispina'' Royle ex Benth. *'' Caragana conferta'' Benth. ex Baker *'' Caragana franchetiana'' Kom. *'' Caragana gerardiana'' Royle ex Benth. *'' Caragana jubata'' (Pall.) Poir. *'' Caragana sukiensis'' C.K.Schneid. *'' Caragana tibetica'' (Maxim. ex C.K. Schneid.) Kom. Section ''Caragana'' *'' Caragana arborescens'' Lam. *'' Caragana boisii'' C.K.Schneid. *'' Caragana bungei'' Ledeb. *''Caragana korshinskii'' Kom. *''Cara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Tabuliformis
''Pinus tabuliformis'', also called Chinese red pine, Manchurian red pine, or Southern Chinese pine is a pine native to northern China and northern Korea. Description ''Pinus tabuliformis'' is a medium-sized evergreen tree growing to tall, with a flat-topped crown when mature. The growth rate is fast when young, but slows with age. The grey-brown bark fissures at an early age compared to other trees. The broadly spreading shape is very pronounced, in part due to the long horizontal branching pattern. The needle-like leaves are shiny grey-green, long and broad, usually in pairs but occasionally in threes at the tips of strong shoots on young trees. The cones are green, ripening brown about 20 months after pollination, broad ovoid, long, with broad scales, each scale with a small prickle. The seeds are long with a wing, and are wind- dispersed. Varieties There are two varieties: *''Pinus tabuliformis'' var. ''tabuliformis''. China, except for Liaoning. Broadest cone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across Europe and Asia, north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Mediterranean Basin; North Africa; North Arabia; Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. Both the eastern and westernmost extremes of the Paleartic span into the Western Hemisphere, including Cape Dezhnyov in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the east and Iceland to the west. The term was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/ Afrotropic, Indian/ I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordos Desert
The Ordos Desert () is a desert/ steppe region in Northwest China, administered under the prefecture of Ordos City in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region (centered ca. ). It extends over an area of approximately , and comprises two sub-deserts: China's 7th-largest desert, the Kubuqi Desert, in the north; and China's 8th-largest desert, the Mu Us Desert, in the south. Wedged between the arable Hetao region to the north and the Loess Plateau to the south, the soil of the Ordos Desert is mostly a mixture of dry clay and sand, and as a result is poorly suited for agriculture. Location The Ordos Desert is almost completely encircled in the west, north and east by a great rectangular bend of the middle Yellow River known as the Ordos Loop. Mountain ranges separate the Ordos from the Gobi Desert north and east of the Yellow River. The northern border serves as the southern border of the Mu Us Desert. The mountain chains separating the Ordos from the central Gobi in the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |