|
Heaven's Great General
Tian Dajiangjun () is a Chinese constellation () in the region of ''Bond (Chinese constellation), Lóu'' (). It contains 11 or 12 stars, in the Western constellations Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda and Triangulum. Its name is translated as "Heaven's Great General" or "Celestial Grand General". In older Western sources its name was transliterated as ''Teen Ta Tseang Keun'' or ''Tëen ta tsëang keun''. Richard Hinckley Allen, R. H. Allen based identification of Chinese star names by the English astronomer John Williams (astronomer), John Williams (1797–1874) and the naturalist John Reeves (naturalist), John Reeves. But Allen lacked last word ''kuen'' as ''Tien Ta Tseang'' and also transliterated it as ''Tsien Ta Tseang''.Allen (1963): p.416. Identification of stars ; Notes * 54 And is designated as φ Per in recent times. Notes References * * 大崎正次 (1987): 「中国の星座・星名の同定一覧表」『中国の星座の歴史』 雄山閣出版, p. 326 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellation
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
She Shan Hill
Sheshan, known in Shanghainese as Zose, is a pair of hills in Songjiang District in western Shanghai, China. The two hills are distinguished as East and , although the more important western hill is also called Sheshan on its own. East Sheshan has an elevation of and West Sheshan has an elevation of , it is the highest point in Shanghai, there is a small valley between them. The area around the two hills is a forest park. Basilica It is surmounted by the ''Our Lady of China'' Catholic church, Sheshan Basilica, which was built there between 1922 and 1936 following the establishment of a chapel in 1867, soon replaced by a first church in 1871-1873 by French Jesuit missionaries. Services in the church are held in Chinese and Latin. The road to the top of Sheshan hill represents the stations of the cross Via Dolorosa (The Way of Suffering) that Christ took to his crucifixion. Every May pilgrims flock to the chapel and the holy road by the hundreds. Observatory The hill also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
58 Andromedae
58 Andromedae, abbreviated 58 And, is a single star in the northern constellation Andromeda. ''58 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78 The distance to this star, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is 186 light years. 58 And is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +8 km/s. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of per year. This star is 425 million years old with a stellar classification of A5 IV-V, indicating the spectrum displays mixed traits of an A-type main-sequence star and an older subgiant star. It is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 135 km/s, which is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is 6% larger than the polar radius. The star has double the mass of the Sun and about 1.9 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 36 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
56 Andromedae
56 Andromedae, abbreviated 56 And, is a probable binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''56 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.69, which is just bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions. The distance to this system can be ascertained from its annual parallax shift, measured at with the Gaia space observatory, which yields a separation of 330 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +62 km/s and is traversing the celestial sphere at a relatively high rate of per year. This pair is positioned near the line of sight to the open cluster NGC 752, located away. The brighter primary is an aging giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, having exhausted the hydrogen at its core and evolved off the main sequence. It is a red clump giant, having undergone helium flash and is presently ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Andromedae
Tau Andromedae is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. Its Bayer designation is Latinized from τ Andromedae, and abbreviated Tau And or τ And, respectively. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.94, which is bright enough to be viewed from dark suburban skies. From parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, the distance to this star can be estimated as roughly from Earth. The brightness of this star is diminished by 0.24 in magnitude due to extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −14 km/s. The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of B5 III, with the luminosity class of III indicating that this is a giant star. It is radiating about 851 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 12,670 K. The star is an estimated 217 million years old and is spinning with a high projected rotational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50 Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae (υ Andromedae, abbreviated Upsilon And, υ And) is a binary star located 44 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Andromeda. The system consists of an F-type main-sequence star (designated υ Andromedae A, officially named Titawin in the Amazigh language ) and a smaller red dwarf. , three extrasolar planets (designated Upsilon Andromedae b, c, d; named Saffar, Samh and Majriti, respectively) are believed to orbit υ Andromedae A. All three are likely to be jovian planets that are comparable in size to Jupiter. This was both the first multiple- planet system to be discovered around a main-sequence star, and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple-star system. Nomenclature ''υ Andromedae'' ( Latinised to ''Upsilon Andromedae'') is the system's Bayer designation. Under the rules for naming objects in binary star systems, the two components are designated A and B. Under the same rules, the first planet discovered orbiting υ And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Andromedae
Chi Andromedae ( Andromedae, And) is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.01, which is relatively faint for a naked-eye star. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, Chi Andromedae is located around from Earth. χ Andromedae is a member of (), meaning '' Heaven's Great General'', together with γ Andromedae, φ Persei, 51 Andromedae, 49 Andromedae, θ Andromedae, τ Andromedae, 56 Andromedae, β Trianguli, γ Trianguli and δ Trianguli. Consequently, the Chinese name for χ Andromedae itself is (, .) This is most likely a |
Omega Andromedae
Omega Andromedae (ω And, ω Andromedae) is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. Parallax measurements made during the ''Gaia'' mission make this system to be approximately from Earth. Its apparent visual magnitude is +4.83, which makes it bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. The primary component has a stellar classification of F5 IVe. The IV luminosity class indicates that it is probably a subgiant star that is in the process of evolving away from the main sequence as the supply of hydrogen at its core depletes. However, Abt (1985) gives a classification of F3 V, suggesting it is an F-type main-sequence star. The measured angular diameter of the primary star is . At the system's estimated distance this yields a size of about 2.2 times that of the Sun. It is emitting about seven times solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of . This heat gives it the yellow-white-hued glow of an F-type star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49 Andromedae
49 Andromedae is a star in the constellation Andromeda. ''49 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation (abbreviated 49 And), though it also bears the Bayer designation A Andromedae. It is visible to the naked eye under good viewing conditions with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.269. The distance to 49 Andromedae, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is around 333 light-years. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −11.5 km/s. With an estimated age of years, this is an aging red-clump giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, indicating it is generating energy by helium fusion at its core. The spectrum displays "slightly strong" absorption lines of cyanogen (CN). It has 2.07 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 11 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 71 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of . It is spinning with a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
51 Andromedae
51 Andromedae, abbreviated 51 And and formally named Nembus , is the 5th brightest star in the northern constellation of Andromeda, very slightly dimmer than the Andromeda Galaxy also being of 4th magnitude. It is an orange K-type giant star with an apparent magnitude of +3.57 and is about 169 light-years from the Earth/solar system. It is traditionally depicted as one of the two northern, far upper ends of the mythological, chained-to-the-rocks princess, the other being binary star system Gamma Andromedae. At an estimated age of 1.7 billion years, this is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of . The suffix notation indicates a mild enhancement of cyanogen absorption lines in its spectrum. This star has 1.8 times the mass of the Sun and it has expanded to 21.3 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 142 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,951 K. Nomenclature ''51 Andromedae'' is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
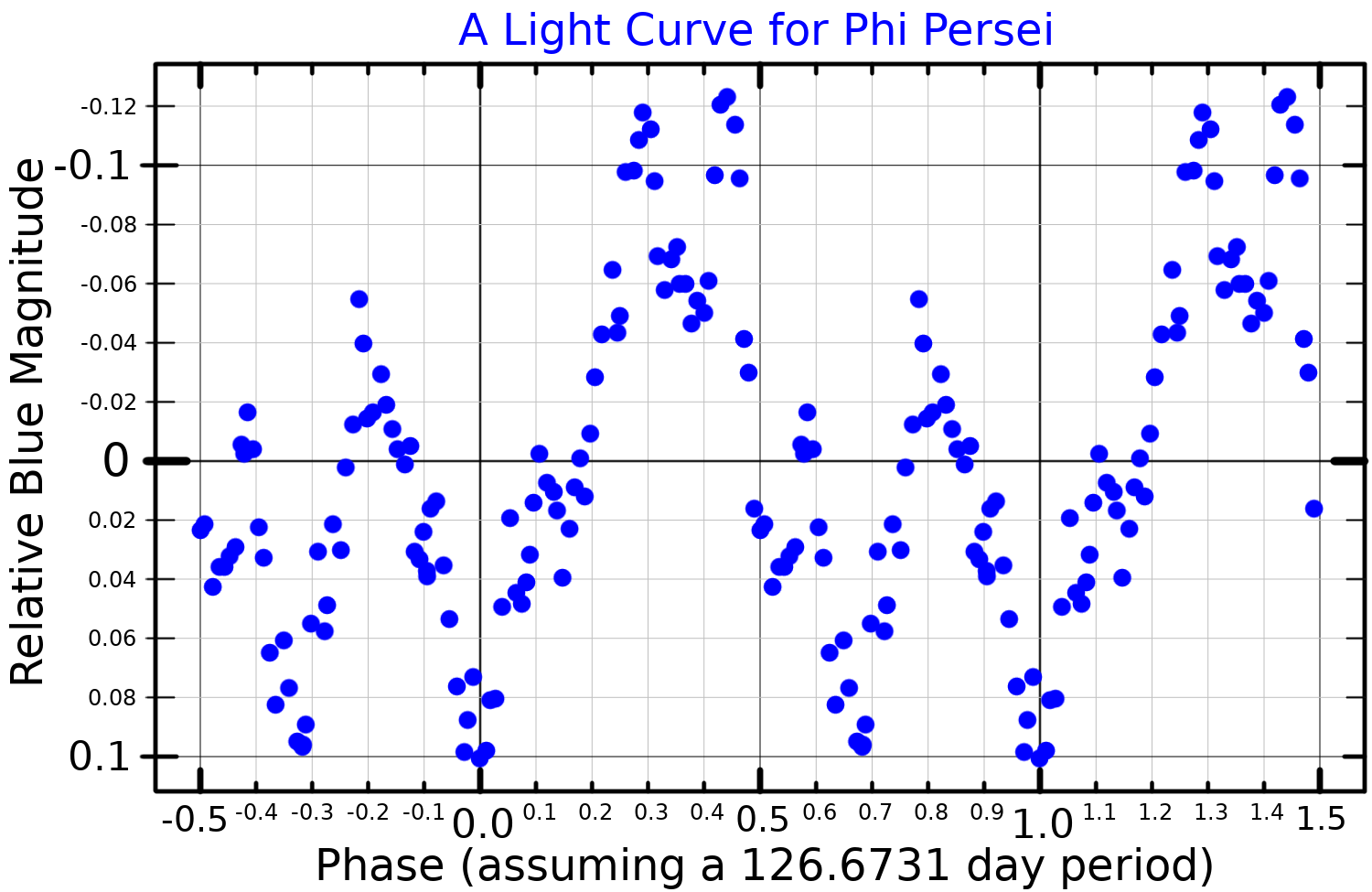
Phi Persei
Phi Persei (Phi Per, φ Persei, φ Per) is a Stellar classification, class B2Vep fourth-magnitude star in the constellation Perseus (constellation), Perseus, location about 720 light-years from Earth. System Phi Persei is spectroscopic binary consisting of a blue main sequence primary of class B2 and a Subdwarf B star, hot subdwarf secondary. The two stars have an orbit of 217 days and are separated by about . Phi Persei is a runaway star and extrapolating its space velocity (astronomy), space velocity backwards by the modelled age of the system (57 million years) places it within the Alpha Persei cluster. The primary star rotates rapidly with a projected equatorial velocity of . Due to its rapid rotation, the primary star has a polar radius about and an equatorial radius of about . With an effective temperature of nearly , it has a bolometric luminosity nearly 15,000 times higher than the Sun. The rapidly-spinning star is surrounded by a circumstel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |