|
Hart's Line
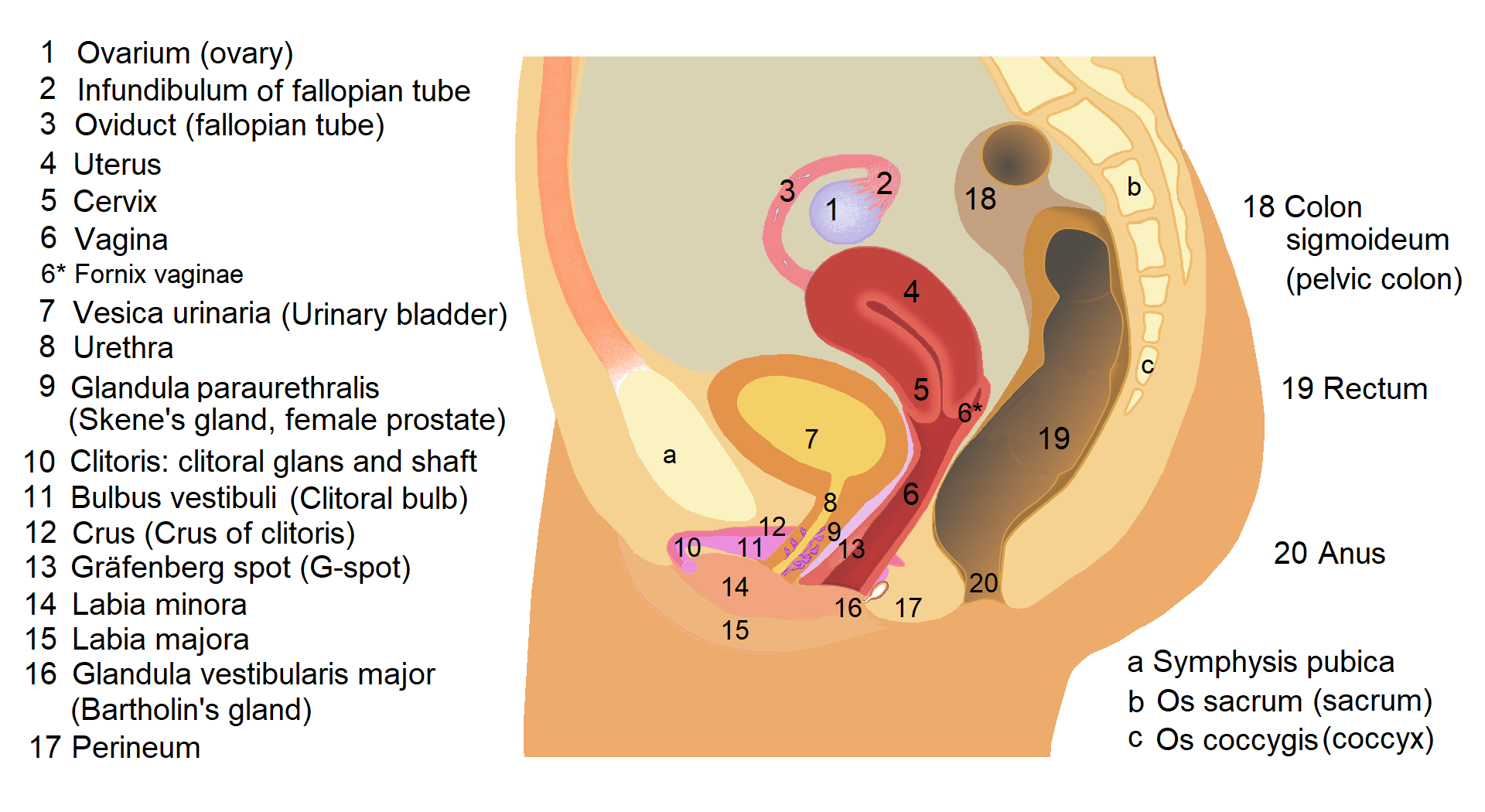
The vulval vestibule (also known as the vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is the part of the vulva between the labia minora. At the innermost part are the vaginal introitus and urinary meatus. The Bartholin's and Skene's glands each have two openings to the vestibule on the inside. The outer edge, marked by a coloration difference in the tissues, is called Hart's line, named after David Berry Hart. The vestibule represents the distal end of the urogenital sinus of the embryo.''Manual of Obstetrics''. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1–16. . Structure Structures opening in the vulval vestibule are the urethra (urinary meatus), vagina, Bartholin's glands, and Skene's glands. The external urethral orifice is placed about 25–30 millimetres (1–1.2 in) behind the clitoris and immediately in front of that of the vagina; it usually assumes the form of a short, sagittal cleft with slightly raised margins. Nearby are the openings of the Skene's ducts. The vaginal orifice is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Sinus
The urogenital sinus is a body part of a human or other Placentalia, placental only present in the development of the urinary system, development of the urinary and development of the reproductive organs, reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca (embryology), cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh weeks of development. In males, the UG sinus is divided into three regions: upper, pelvic, and phallic. The upper part gives rise to the urinary bladder and the pelvic part gives rise to the prostatic and membranous parts of the urethra, the prostate and the bulbourethral glands (Cowper's). The phallic portion gives rise to the spongy (bulbar) part of the urethra and the urethral glands (Littré's). In females, the pelvic part of the UG sinus gives rise to the sinovaginal bulbs, structures that will eventually form the inferior two thirds of the vagina. This process begins when the lower tip of the paramesonephric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placentalia
Placental mammals ( infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished from monotremes and marsupials in that the fetus is carried in the uterus of its mother to a relatively late stage of development. The name is something of a misnomer, considering that marsupials also nourish their fetuses via a placenta, though for a relatively briefer period, giving birth to less-developed young, which are then nurtured for a period inside the mother's pouch. Placentalia represents the only living group within Eutheria, which contains all mammals that are more closely related to placentals than they are to marsupials. Anatomical features Placental mammals are anatomically distinguished from other mammals by: * a sufficiently wide opening at the bottom of the pelvis to allow the birth of a large baby relative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Ape
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the eastern and western gorilla); '' Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') remain. Numerous revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''hominid'' to change over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans and other apes were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''hominin'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (''Pan''). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenulum Of Labia Minora
The frenulum of labia minora (fourchette or posterior commissure of the labia minora) is a frenulum where the labia minora meet posterior (anatomy), posteriorly. Pathology The fourchette may be torn during Childbirth, delivery due to the sudden stretching of the vulval orifice, or during copulation. To prevent this tearing in a haphazard manner, obstetricians and, less frequently, midwife, midwives may perform an episiotomy, which is a deliberate cut made in the perineum starting from the fourchette and continuing back along the perineum toward the anus. Sometimes this surgical cut may extend to involve the perineal body and thus reduce anal sphincter function. Thus some obstetricians have opted to perform a posterior-lateral cut in the perineum to prevent this potential complication from occurring. The fourchette may also be torn in acts of violence wherein forced entry occurs such as rape. When the fourchette is torn, the bleeding which ensues sometimes requires surgical surgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 Nerve, nerve endings. * * Peters, B; Uloko, M; Isabey, PHow many Nerve Fibers Innervate the Human Clitoris? A Histomorphometric Evaluation of the Dorsal Nerve of the Clitoris 2 p.m. ET 27 October 2022, 23rd annual joint scientific meeting of Sexual Medicine Society of North America and International Society for Sexual Medicine Sexology, Sexological, medical, and psychological debate has focused on the clitoris, and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies. Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoral Hood
In female humans and other mammals, the clitoral hood (also called preputium clitoridis, clitoral prepuce, and clitoral foreskin) is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external clitoral shaft, develops as part of the labia minora and is homologous with the foreskin (also called the ''prepuce'') in the male reproductive system. The clitoral hood is composed of mucocutaneous tissues; these tissues are between the mucous membrane and the skin, and they may have immunological importance because they may be a point of entry of mucosal vaccines. Development and variation The clitoral hood is formed during the fetal stage by the cellular lamella. The cellular lamella grows down on the dorsal side of the clitoris and is eventually fused with the clitoris. The clitoral hood varies in the size, shape, thickness, and other aesthetic aspects. Some women have large clitoral hoods that completely cover the clitoral glans. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymen
The hymen is a thin piece of mucosal tissue that surrounds or partially covers the vaginal opening. A small percentage of females are born with hymens that are imperforate and completely obstruct the vaginal canal. It forms part of the vulva and is similar in structure to the vagina. The word is from the Greek ''ὑμήν'' meaning a thin skin or membrane. In children, a common appearance of the hymen is crescent-shaped, although many shapes are possible. Each shape in the natural range has a Latinate name. During puberty, estrogen causes the hymen to change in appearance and become very elastic. Normal variations of the post-pubertal hymen range from thin and stretchy to thick and somewhat rigid. Very rarely, it may be completely absent. The hymen can rip or tear during first penetrative intercourse, which usually results in pain and, sometimes, mild temporary bleeding or spotting. Minor injuries to the hymen may heal on their own, and not require surgical intervention. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse plane, transverse and coronal plane, coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts (mid-sagittal plane, mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). The term ''sagittal'' was coined by Gerard of Cremona. Variations in terminology Examples of sagittal planes include: * The terms ''median plane'' or ''mid-sagittal plane'' are sometimes used to describe the wikt:sagittal plane, sagittal plane running through the midline. This plane cuts the body into halves (assuming bilateral symmetry), passing through midline structures such as the navel and Vertebral column, spine. It is one of the planes which, combined with the umbilical plane, defines the Quadrant (abdomen), four quadrants of the human abdomen. * The term ''parasagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 Nerve, nerve endings. * * Peters, B; Uloko, M; Isabey, PHow many Nerve Fibers Innervate the Human Clitoris? A Histomorphometric Evaluation of the Dorsal Nerve of the Clitoris 2 p.m. ET 27 October 2022, 23rd annual joint scientific meeting of Sexual Medicine Society of North America and International Society for Sexual Medicine Sexology, Sexological, medical, and psychological debate has focused on the clitoris, and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies. Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Urethral Orifice
The urinary meatus (, ; : meati or meatuses), also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the penis or vulva where urine exits the urethra during urination. It is also where semen exits during male ejaculation, and other fluids during female ejaculation. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. In human males The male external urethral orifice is the external opening of the urethra, normally located at the tip of the glans penis, at its junction with the frenular delta. It presents as a vertical slit, and continues longitudinally along the front aspect of the glans, which facilitates micturition. In some cases, the opening may be more rounded. This can occur naturally or may also occur as a side effect of excessive skin removal during circumcision. The meatus is a sensitive part of the male reproductive system. In human females The female external urethral orifice is where urine exits the urethra during urination. It is located about behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |