|
Hangerliu
Constantine Hangerli (, ''Konstantinos Chatzeris''; c. 1760 – 18 February 1799), also written as Constantin Hangerliu, was a Prince of Wallachia between 1797 and the time of his death. He was the brother of Alexander Hangerli, who served as Prince of Moldavia in 1807. Biography Early life and investiture As a Phanariote, Hangerli claimed heritage from the Byzantine family of the Palaiologos.Mézière He was married to Doamna Roxana, who survived his death.Caragea, p. 85 According to one account, the surname ''Hangerli'' () had been assigned to one of his ancestors by Sultan Mehmed IV, after allegedly saving his life by curing him of a potentially fatal illness. The name was based on the word , which was indicative of closeness to the Sultan's person. The Hangerlis were related to other high-ranking Greek families, including the Ypsilantis and the Mourousis.Caragea, p. 84 After serving as Dragoman of the Fleet, Constantine surprised foreign diplomats through his appointment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtea Nouă
Curtea Nouă (, ''New Court'') was the residence of the List of rulers of Wallachia, Princes of Wallachia between 1776 and 1812. Located near the Mihai Vodă Monastery, on Dealul Spirii in Bucharest, it was built between 1775 and 1776 during the rule of Alexander Ypsilantis (1725–1805), Alexander Ypsilantis, and it meant to replace the old princely court at Curtea Veche. Location and general description Curtea Noua appears at the top of th Sulzer map (1781)It is isolated from the city of Bucharest, across the Dambovita river. Curtea Nouă was described as being in Byzantine architecture, Byzantine style, having three floors, four staircases and three towers. The Swiss chronicler Sulzer left a description of the building which suggests that he was not very impressed with it: "This palace is in all respects irregular and ill-proportioned, just like the boyars' residences, about which we mentioned that are built in octagonal and even twelve sides polygonal shapes, from well plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Hangerli
Alexander Hangerli or Handjeri (, , or ''Hangerliu'', Russian: Александр Ханжерли, ''Aleksandr Hanzherli'', Александр Хангерли, ''Aleksandr Hangerli'' or Александру Хангерли, ''Aleksandru Hangerli;'' 1768 – 12 June 1854) was a Dragoman of the Porte of the Ottoman Empire, and Prince of Moldavia between March 7 and July 24, 1807. He spent the latter part of his life as a refugee in the Russian Empire, where he became noted as a linguist. He was the brother of Constantine Hangerli, who reigned as Prince of Wallachia before being executed in 1799. Life Born in Constantinople, Hangerli received a thorough education, was trained to speak several European languages, as well as Ottoman Turkish and Arabic, and prepared for a high-ranking position in the Danubian Principalities.Mézière, Ernest. "Alexandre Handjeri", in ''Nouvelle biographie générale depuis les temps les plus reculés jusqu'à nos jours'', Tome 23, Firmin Didot, Pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Wallachia
This is a list of princes of Wallachia, from the first mention of a medieval polity situated between the Southern Carpathians and the Danube until the union with Moldavia in 1859, which unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, led to the creation of Romania. Notes Dynastic rule is hard to ascribe, given the loose traditional definition of the ruling family. On principle, princes were chosen from any family branch, including a previous ruler's bastard sons, being defined as ''os de domn'', "of Voivode marrow", or as having ''heregie'', "heredity" (from the Latin ''hereditas''); the institutions charged with the Elective monarchy, election, dominated by the boyars, had fluctuating degrees of influence. The system itself was challenged by usurpers, and became obsolete with the Phanariotes, Phanariote epoch, when rulers were appointed by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans; between 1821 and 1878 (the date of Romania's independence), various systems combining election and appointment were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypsilantis
The House of Ypsilantis or Ypsilanti (; ) was a Greek Phanariote family which grew into prominence and power in Constantinople during the last centuries of Ottoman Empire and gave several short-reign '' hospodars'' to the Danubian Principalities. History First mentioned in 1064, the family was originally from the Pontus region in the Black Sea. They became prominent during the Empire of Trebizond. In 1655, Antiochus Ypsilantis left Trabzon and settled in Constantinople. Since the end of the Ottoman Empire, members of the Ypsilanti family can be found all over the world. Notable members * Alexander Ypsilantis (1725–1805), Prince of Wallachia and Moldavia * Constantine Ypsilantis (), son of the above, Prince of Moldavia, fled to the Russian court * Elisavet Ypsilanti (1768–1866), wife of the above * Alexander Ypsilantis (1792–1828), eldest son of the above. A General in the Imperial Russian Army, he became the leader of the ''Filiki Eteria'', and began the Greek Revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Mavrocordatos
Constantine Mavrocordatos (Greek language, Greek: Κωνσταντίνος Μαυροκορδάτος, Romanian language, Romanian: ''Constantin Mavrocordat''; February 27, 1711November 23, 1769) was a Greeks, Greek noble who served as List of rulers of Wallachia, Prince of Wallachia and List of rulers of Moldavia, Prince of Moldavia at several intervals between 1730 and 1769. As a ruler he issued reforms in the laws of each of the two Danubian Principalities, ensuring a more adequate taxation and a series of measures amounting to the emancipation of Serfdom, serfs and a more humane treatment of slaves. Life First rules Born in Constantinople (now Istanbul) as a Phanariotes, Phanariote member of the Mavrocordatos family, Constantine succeeded his father, Nicholas Mavrocordatos, as Prince of Wallachia in 1730, after obtaining boyar support. He was deprived in the same year, but again ruled the principality five more times from 1731 to 1733, from 1735 to 1741, from 1744 to 1748, fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Romanian Taxes
This is a glossary of historical Romanian taxes used in the principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Taxes Romania history-related lists Romanian language Economic history of Romania History of Wallachia History of Moldavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( or ''Babıali''; ), was a synecdoche or metaphor used to refer collectively to the central government of the Ottoman Empire in Istanbul. It is particularly referred to the building which housed the office of the Grand Vizier, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of the Interior, and the Supreme Council of Judicial Ordinances. Today it houses the office of the Istanbul governerate. History The name has its origins in the old practice in which the ruler announced his official decisions and judgements at the gate of his palace. This was the practice in the Byzantine Empire and it was also adopted by Ottoman Turk sultans since Orhan I. The palace of the sultan, or the gate leading to it, therefore became known as the "High Gate". This name referred first to a palace in Bursa, Turkey. After the Ottomans had conquered Constantinople, now Istanbul, the gate now known as the Imperial Gate (), leading to the outermo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Văcăreşti Monastery
The Văcărești Monastery also known as the Prison of Văcărești was a religious architectural ensemble formerly located in București, Romania. It was built by Romanian Phanariot ruler Nicholas Mavrocordatos between 1716 and 1736 in the Brâncovenesc style and demolished between December 11, 1986, and early 1987 by the order of Romanian dictator Nicolae Ceaușescu. History First enclosure. Under Nicholas Mavrocordatos Nicholas Mavrocordatos was anointed as the ruler of Wallachia on January 5, 1716. Once on the throne, Mavrocordatos, an enlightened Phanariot ruler, lover of culture and initiator of reforms, proposed the construction of a grand place of prayer that would also have the function of a royal residence, and which, due to its dimensions, refinement and construction quality, to represent himself. The place chosen for the imposing ensemble was the crest of the ''"Dealul Văcărești" (Văcărești hill)'', as it was known to the people of București. The natural forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omen
An omen (also called ''portent'') is a phenomenon that is believed to foretell the future, often signifying the advent of change. It was commonly believed in ancient history, and still believed by some today, that omens bring divine messages from the gods. These omens include natural phenomena, for example an eclipse, abnormal births of animals (especially humans) and behaviour of the sacrificial lamb on its way to the slaughter. Specialists, known as diviners, variously existed to interpret these omens. They would also use an artificial method, for example, a clay model of a sheep liver, to communicate with their gods in times of crisis. They would expect a binary answer, either yes or no, favourable or unfavourable. They did these to predict what would happen in the future and to take action to avoid disaster. Though the word ''omen'' is usually devoid of reference to the change's nature, hence being possibly either "good" or "bad", the term is more often used in a foreb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calea Victoriei
Calea Victoriei (''Victory Avenue'') is a major avenue in central Bucharest. Situated in Sector 1, and having a length of , it leads from (which runs parallel to the Dâmbovița River) to the north and then northwest up to Piața Victoriei, where Șoseaua Kiseleff continues north. History Initially, the road was known as Ulița Mare (''Large Street''), also known as Drumul Brașovului (''Brașov Road''), being part of the trade route between Bucharest and the city of Brașov, in Transylvania. In 1692, ruler Constantin Brâncoveanu paved the road with wood and partly regularized it, making it pass through the domains of the Bălăceni, of the Saint John Monastery, Zlătari Monastery and of the Cantacuzenes up to the Sărindari Monastery. Since 1692 it was known as Podul Mogoșoaiei (''Mogoșoaia Wood-Paved Road'') because it also was connecting the Bucharest's center with Brâncoveanu's Mogoșoaia Palace some kilometres outside the city. Most roads in the Balkans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
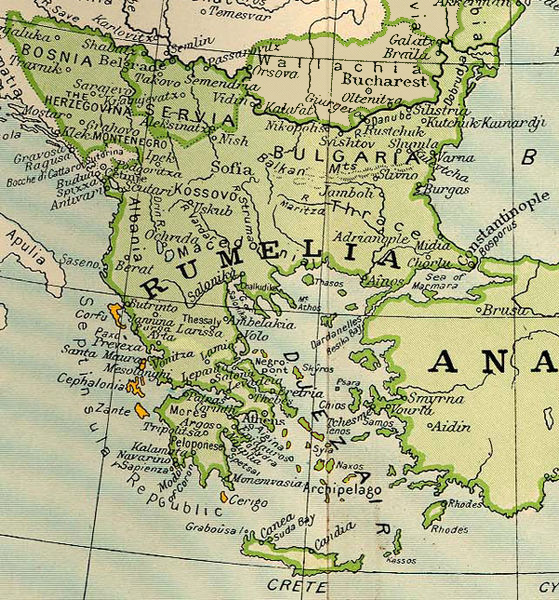
Rumelia
Rumelia (; ; ) was a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe. These would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans", although Hungary and Moldova are sometimes excluded. In contemporary English sources, Rumelia was known as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means 'Roman' and ''ėli'' means 'land', and thus ''Rumelia'' (, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means 'Land of the Romans' in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, most of which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the Eastern Roman Empire, Roman Empire. Although the term ''Byzantine Empire'' is used by modern historians, the empire's citizens and emperors called themselves Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman Pazvantoğlu
Osman Pazvantoğlu (; 1758 – January 27, 1807 in Vidin) was an Ottoman Bosnian soldier, governor of Vidin after 1794, and a rebel against Ottoman rule. He is also remembered as the friend of Rigas Feraios, a Greek revolutionary poet, whom he tried to rescue from the Ottoman authorities in Belgrade. His father was a janissary agha of the 31st janissary orta. Biography His grandfather was originally from the Eyalet of Bosnia, and part of the guards of the city of Sofia, hence Osman's name: ''pasban-oğlu'', "son of the guard".Ionescu, p.242 Initially a mercenary in service to the Wallachian prince Nicholas Mavrogenes, Osman Pazvantoğlu disobeyed the latter on one occasion, and was saved from reprisals through Feraios' intervention. Having gathered a large army of mercenaries, he rebelled against the Ottoman sultan Selim III, and, acting as an independent ruler, he minted his own coins and had diplomatic relations with foreign states (including the French Republic). In 179 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |